Historical Context of Ancient Egyptian Architecture
Ancient Egyptian architecture stands as a testament to the civilization’s ingenuity and spiritual depth, reflecting their beliefs, social hierarchy, and connection to the divine. Developed over thousands of years, this architectural tradition introduced monumental structures such as pyramids, temples, and tombs that have endured as symbols of eternal life and power. The innovations and craftsmanship of Egyptian architects played a crucial role in shaping the distinctive and iconic style that continues to fascinate historians and visitors alike.
Overview of Egyptian Civilization
Ancient Egyptian architecture is a remarkable reflection of the civilization’s religious beliefs, social organization, and technological advancements. It developed over thousands of years, beginning around 3100 BCE with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, and continued until the end of the Pharaonic period. The architecture of this era was characterized by monumental structures such as temples, tombs, and pyramids that showcased the Egyptians’ dedication to the afterlife and their divine kingship.
Egyptian civilization thrived along the Nile River, where the annual flooding provided fertile land and supported a prosperous society. The society was highly organized, with a centralized government led by the Pharaoh, who was regarded as a divine ruler. This theocratic authority heavily influenced architectural projects, as grand monuments served both religious and political purposes. The construction of these structures required advanced engineering skills and precise planning, led by skilled architects and artisans who preserved detailed knowledge of building techniques and symbolic design elements.
Architects in ancient Egypt were highly esteemed and played a crucial role in translating the religious and cultural ideals of their society into enduring structures. They utilized local materials such as limestone and sandstone, and employed innovative techniques like corbeling and the use of precise measurements. Their work not only demonstrated technical mastery but also reflected a deep spiritual significance, aiming to ensure the eternal life of the deceased and the honor of their gods. The legacy of Egyptian architecture continues to influence the study of ancient engineering and sacred design to this day.
Influences and Cultural Significance
Ancient Egyptian architecture is renowned for its durability, grandeur, and symbolic significance, reflecting the civilization’s religious beliefs and societal organization. It emerged around 3000 BCE, with early structures evolving from simple tombs to monumental temples and pyramids that showcased the technological and artistic advancements of the time. The architecture was deeply intertwined with the Egyptians’ focus on the afterlife, with structures designed to honor gods and pharaohs, embodying their divine authority.
Influences on Egyptian architecture stem from their environment, religious concepts, and interactions with neighboring cultures. The abundance of readily available limestone, sandstone, and granite influenced the choice of durable materials used in construction. Religious and mythological themes dictated architectural forms, such as the use of hypostyle halls, columned courtyards, and massive gateways. Contact with the Nubians, Persians, and Greeks also introduced new styles and techniques, yet the core principles remained rooted in tradition.
Culturally, these architectural achievements served to reinforce the divine status of rulers and the societal importance of religion. Temple complexes, with their imposing pylons and intricate carvings, functioned as centers of worship and community gathering. Pyramids not only served as tombs but also symbolized the journey of the soul and cosmic order, reflecting the Egyptians’ profound spiritual outlook. Overall, ancient Egyptian architecture stands as a testament to their sophisticated engineering and the central role of spirituality in their civilization.
Role of Architects in Society
Ancient Egyptian architecture reflects the civilization’s religious beliefs, societal organization, and technological advancements. It was characterized by monumental structures such as pyramids, temples, and statues that served religious and political functions. These structures often featured precise mathematical planning and extensive use of durable materials like limestone and sandstone, showcasing the Egyptians’ craftsmanship and engineering skills. The construction of such grand edifices demonstrated the society’s emphasis on the afterlife, divine kingship, and the importance placed on order and stability.
Architects in ancient Egypt held a prestigious position in society, often regarded as both master builders and scribes. They were essential figures responsible for translating religious and royal visions into tangible forms, ensuring that each monument adhered to strict aesthetic and symbolic standards. Their role extended beyond mere construction; they were involved in the planning of complex layouts, sourcing and managing resources, and maintaining the cultural and religious integrity of the structures. As custodians of sacred knowledge, architects contributed significantly to the preservation of Egyptian cultural identity and social hierarchy, embodying wisdom, skill, and loyalty to the divine authority of the pharaohs.
Types of Architectural Structures
Architectural structures in ancient Egypt showcase the remarkable ingenuity and cultural significance of their civilization. From towering pyramids and magnificent temples to elaborate tombs, these structures reflect the religious beliefs, social hierarchy, and technological advancements of the time. Understanding the different types of architectural structures helps to appreciate the sophistication and artistry that defined ancient Egyptian architecture.
Pyramids and Tombs
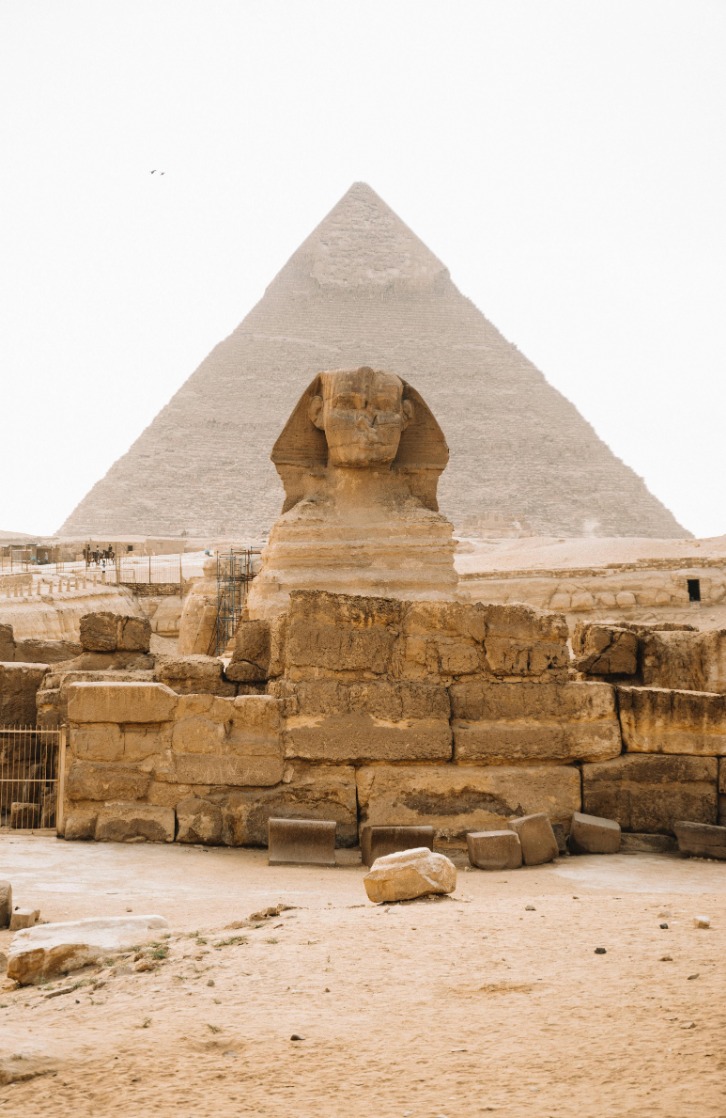
Ancient Egyptian architects played a crucial role in designing and constructing some of the most iconic architectural structures in history, including elaborate tombs and monumental pyramids. These structures served both as everlasting resting places for pharaohs and as symbols of divine power and religious beliefs. Pyramids, such as the Great Pyramid of Giza, are characterized by their massive scale, precise geometric form, and complex internal passages. They exemplify the Egyptians’ advanced understanding of mathematics and engineering. In addition to pyramids, tombs like mastabas and rock-cut tombs were constructed for nobility and officials, often decorated with intricate carvings and paintings that depicted the deceased’s life and journey to the afterlife. Overall, these architectural structures reflect the Egyptians’ religious dedication, mastery of engineering, and cultural values, showcasing their remarkable achievements in construction and design.
Temples and Shrines
Ancient Egyptian architecture is renowned for its impressive temples and shrines, which served religious and ceremonial purposes. These structures were designed with precise symbolism and grandeur, reflecting the civilization’s spiritual beliefs. Temples often featured massive pylons, courtyards, hypostyle halls, and sanctuaries dedicated to gods and pharaohs. Shrines, smaller in scale, housed statues and offerings, and were integral to personal worship. The construction of these architectural structures demonstrated advanced engineering skills and reverence for the divine, leaving a lasting legacy in the history of architecture.
Pylons and Palaces
Ancient Egyptian architecture is renowned for its grandeur and durability, featuring a variety of structures such as pylons and palaces that exemplify their engineering expertise and artistic expression. Pylons are massive gateway towers with sloping sides, often serving as the monumental entrances to temples, symbolizing the horizon and the gateway to divine realms. These structures are characterized by their imposing size, decorated with reliefs and inscriptions depicting gods and pharaohs.
Palaces in ancient Egypt were elaborate residences for pharaohs and high-ranking officials, reflecting their power and divine status. They typically included courtyards, reception halls, private chambers, and service areas, constructed using sun-dried bricks and stone. The design emphasized symmetry and grandeur, with intricate carvings and decorations that conveyed religious and political themes. Such architectural elements highlight the Egyptians’ skill in creating durable, functional, and aesthetically impressive structures that have inspired generations.
Notable Ancient Egyptian Architects
Ancient Egypt was renowned for its extraordinary architecture, characterized by grand temples, tombs, and monuments that have stood the test of time. Behind these impressive structures were visionary architects whose skills and ingenuity shaped the landscape of ancient Egyptian civilization. Their work not only demonstrated technical mastery but also reflected profound religious and cultural beliefs, leaving a lasting legacy in the history of architecture.
Imhotep: The Pioneering Architect
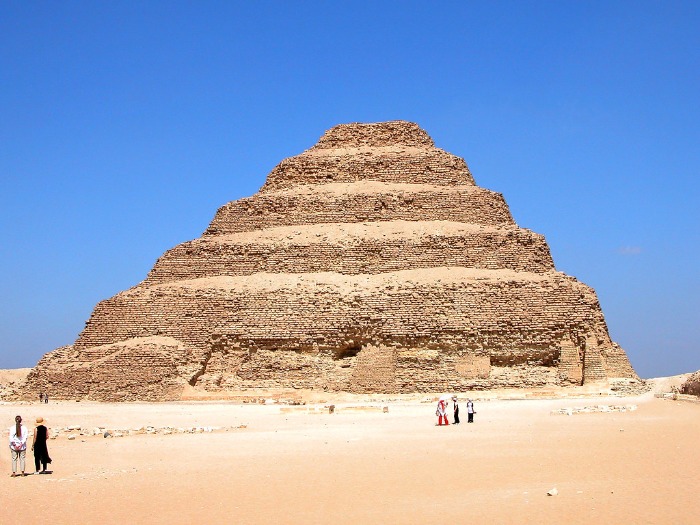
Imhotep is recognized as one of the most notable architects in ancient Egypt and is often regarded as the world’s first known architect. Serving during the 27th century BCE, he was a polymath who excelled not only in architecture but also in medicine, astronomy, and writing. Imhotep’s most famous achievement is the design of the Step Pyramid at Saqqara, which marked a significant innovation in monumental architecture, transitioning from traditional mastaba tombs to the revolutionary pyramid shape. His pioneering work laid the foundation for future pyramid construction and cemented his legacy as a visionary architect whose influence extended well beyond his era.
Other Recognized Architects and Their Contributions
Ancient Egypt is renowned for its exceptional architectural achievements, many of which were designed by notable architects whose contributions have left a lasting legacy. These architects played crucial roles in the construction of iconic monuments, temples, and tombs that continue to amaze modern observers.
Among the notable ancient Egyptian architects, the most famous is Imhotep. He served as the vizier to Pharaoh Djoser and is credited with designing the Step Pyramid at Saqqara, marking the transition from mastaba-style tombs to true pyramids. Imhotep’s innovative architectural ideas laid the groundwork for later pyramid construction and earned him lasting recognition.
Other recognized architects and their contributions include:
- Imhotep – Known for the design of the Step Pyramid of Djoser, considered the earliest colossal stone building in Egypt and a pioneering example of monumental architecture.
- Sensheru – An architect responsible for the construction of various mortuary temples and tomb complexes, integrating intricate carvings and spatial planning.
- Mereruka – An overseer and architect who contributed to the designing and construction of tombs during the Middle Kingdom, showcasing detailed interior layouts.
- Senemut – An architect and vizier known for designing the tomb of Queen Hatshepsut and contributing to the architectural style of her mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahri.
These architects combined artistic innovation with technical skill, creating timeless structures that exemplify ancient Egyptian engineering and aesthetics. Their work has influenced architectural design throughout history and continues to inspire contemporary architecture.
Design Principles and Construction Techniques
Architects in ancient Egypt demonstrated remarkable mastery of design principles and construction techniques that have stood the test of time. Their innovative approaches to spatial organization, material selection, and structural integrity laid the foundation for some of the most iconic monuments in history. Understanding these principles offers insight into the sophistication and ingenuity of ancient Egyptian architecture, reflecting both cultural significance and technological advancement.
Use of Materials and Tools

Architects in ancient Egypt demonstrated remarkable expertise in design principles and construction techniques, which contributed to the enduring grandeur of their monuments. They employed a combination of precise planning, geometric accuracy, and an understanding of structural stability to create monuments such as pyramids, temples, and tombs that have withstood thousands of years. Their construction methods often involved the use of large limestone and sandstone blocks, meticulously cut and assembled using copper tools and sledges to transport heavy materials across vast distances.
The use of durable materials was central to their architectural achievements. Limestone was commonly used for inner chambers and casing stones, while granite was reserved for more important elements like obelisks and columns due to its strength. The ancient Egyptians also incorporated mud bricks in less prominent structures. Their tools, primarily made of copper, stone, and later bronze, were used to carve, shape, and inscribe the materials, demonstrating clever adaptation of available resources. Techniques such as levering, stacking, and precise alignment with astronomical points ensured their structures remained stable and aligned with the spiritual beliefs of the time.
Structural Innovations
Architects in ancient Egypt demonstrated remarkable mastery of design principles and construction techniques that have profoundly influenced architectural history. They emphasized symmetry, proportion, and harmony, often reflecting religious and cultural values in their structures. The use of massive stone blocks and carefully aligned joint systems ensured stability and durability, allowing edifices like temples and tombs to withstand the test of time. Structural innovations such as the development of columned halls, the integration of hypostyle rooms, and the precise carving of obelisks showcase their advanced understanding of engineering and aesthetics. These techniques combined form and function seamlessly, illustrating the ancient Egyptians’ sophisticated approach to architecture that balanced spiritual symbolism with practical construction methods.
Symbolism in Architectural Design
Architects in ancient Egypt were masters of design principles and construction techniques that reflected their deep understanding of symbolism and cultural values. Their approach to architecture was rooted in harmony, proportion, and a meticulous attention to detail, which is evident in iconic structures such as temples, tombs, and pyramids. Techniques such as precise stone cutting, the use of large stone blocks, and innovative construction methods enabled the creation of enduring monuments that conveyed spiritual and societal significance.
Symbolism played a central role in ancient Egyptian architectural design. Structures were often imbued with religious and mythological meaning, with every element serving a symbolic purpose. For instance, the pyramids represented the primordial mound and the ascension to the heavens, aligning with the Egyptians’ beliefs about the afterlife. Architectural features like pylons, columns, and wall reliefs were decorated with hieroglyphs and motifs that depicted gods, royal power, and cosmic order, reinforcing the connection between the earthly realm and divine forces.
Overall, the architects of ancient Egypt seamlessly integrated advanced construction techniques with rich symbolic language, creating structures that were not only architectural achievements but also profound expressions of spiritual and cultural identity.
Architectural Features and Iconography
Architectural features and iconography in ancient Egyptian architecture reveal a rich tapestry of cultural symbolism and innovative design. These structures reflect the civilization’s religious beliefs, social hierarchy, and artistic achievements. From towering temples to intricately carved tombs, the use of symbolic motifs and distinctive construction techniques underscores the significance of architecture in expressing the divine and eternal nature of the ancient Egyptian world.
Hieroglyphic Decorations
Ancient Egyptian architects were masterful at integrating architectural features with rich iconography and hieroglyphic decorations, creating structures that were both functional and spiritually significant. Their designs often incorporated massive stone blocks, iconic columns, and intricately carved facades that conveyed religious and cultural messages. Hieroglyphic inscriptions adorned temples, tombs, and monuments, serving to honor gods, record royal achievements, and provide guidance for the afterlife. These decorations frequently included symbolic motifs such as the ankh, scarabs, and papyrus plants, which conveyed themes of life, rebirth, and divine power. The harmonious blend of structural engineering and detailed ornamentation reflected Egypt’s deep religious beliefs and reverence for the divine, making their architectural works enduring symbols of their civilization’s artistry and spiritual worldview.
Statues and Reliefs
Architects in ancient Egypt played a crucial role in shaping the country’s monumental structures, and their work is characterized by distinctive architectural features and intricate iconography. They designed grand temples, tombs, and other structures that reflected religious beliefs and social hierarchy. These buildings often featured massive stone columns, courtyards, and hypostyle halls adorned with detailed hieroglyphic inscriptions and religious symbolism. The use of axial symmetry and precise alignment with celestial bodies were key elements in their architectural approach, emphasizing harmony and order.
Statues and reliefs were integral to ancient Egyptian architecture, serving both decorative and symbolic purposes. Statues of gods, pharaohs, and important officials were typically placed within temples and tombs to worship and commemorate these figures. They were crafted with meticulous attention to detail, often depicting their divine attributes, regalia, and gestures of reverence. Reliefs, carved into walls and pillars, conveyed narratives of divine mythology, royal achievements, and religious rituals, reinforcing the connection between the physical space and spiritual beliefs. The iconography used in these artworks was highly symbolic, employing standardized poses, symbols, and motifs to communicate specific meanings and ensure their role in religious and political contexts was clearly understood.
Alignment and Orientation
Architects in ancient Egypt demonstrated remarkable expertise through their development of distinct architectural features and iconography that reflected religious and cultural significance. They utilized massive stone blocks, precise alignment with celestial bodies, and monumental scales to convey power and divine authority. Iconography often incorporated motifs of gods, pharaohs, and religious symbols, emphasizing their connection to the divine realm. Alignment and orientation played a crucial role, with many structures carefully aligned with cardinal points, solstices, or specific stars, illustrating the Egyptians’ sophisticated understanding of astronomy and their desire to align their architecture with cosmic principles. This meticulous attention to orientation and symbolic iconography helped reinforce the sacred purpose of their temples, tombs, and monuments, making their architecture enduring symbols of divine order and stability.
Legacy and Influence of Ancient Egyptian Architecture
Ancient Egyptian architecture stands as a testament to the ingenuity and spiritual devotion of one of history’s most remarkable civilizations. Its enduring structures, from majestic temples to grand pyramids, have influenced architectural design for centuries and continue to captivate the world. The legacy of these monumental constructions reflects advanced engineering skills, religious beliefs, and a keen sense of aesthetics that have shaped architectural practices throughout history.
Impact on Later Cultures
Ancient Egyptian architecture, driven by a deep connection to spirituality and the divine, has left a lasting legacy that profoundly influenced subsequent cultures and architectural practices. The grandeur of temples, tombs, and pyramids exemplifies their advanced engineering skills and aesthetic sensibilities, which set a standard for monumental construction. The use of massive stone blocks, precise alignment with celestial bodies, and intricate decorative motifs became benchmarks for grandeur and permanence that many future civilizations sought to emulate.
In particular, the architectural techniques developed by the Egyptians, such as the creation of columned halls, corbeling, and the use of hieroglyphic carvings, significantly impacted later cultures in the Mediterranean and beyond. These elements were adopted and adapted by civilizations such as the Greeks and Romans, influencing their own temple designs, religious structures, and decorative arts. Moreover, the symbolic and spiritual significance embedded in Egyptian architecture contributed to the emphasizing of sacred spaces across subsequent architectural traditions. Overall, the enduring influence of ancient Egyptian architecture reflects its innovative spirit and the universality of its aesthetic and spiritual expressions, echoing through centuries of architectural evolution.
Preservation and Study of Ancient Structures
Architects in ancient Egypt played a crucial role in shaping the enduring legacy and influence of Egyptian architecture, demonstrating mastery in monumentality, symmetry, and religious symbolism. Their expertise led to the creation of iconic structures such as pyramids, temples, and tombs that have stood the test of time, reflecting sophisticated engineering techniques and spiritual beliefs. These architects not only contributed to the aesthetic and functional aspects of their constructions but also established architectural principles that influenced subsequent civilizations.
The preservation and study of ancient Egyptian structures are essential for understanding their engineering innovations, cultural significance, and religious practices. Efforts have been made to conserve these monuments through complex restoration projects and protective measures, ensuring that future generations can appreciate their grandeur. Archaeological research continues to uncover new insights into ancient Egyptian architectural methods, material use, and the social organization behind their construction endeavors.
Through scholarly examination and meticulous preservation, the legacy of ancient Egyptian architects endures, offering a window into a civilization renowned for its architectural ingenuity and spiritual symbolism. Their work continues to inspire modern architecture and remains a testament to human ingenuity and the enduring power of cultural expression.




0 Comments