Historical Significance of Egypt
Egypt’s rich history is renowned for its extraordinary contributions to human civilization, particularly through its ancient monuments and cultural achievements. The pyramids stand as iconic symbols of Egypt’s historical significance, reflecting the advanced architectural skills and spiritual beliefs of the ancient Egyptians. These awe-inspiring structures not only served as monumental tombs for pharaohs but also exemplify Egypt’s prominent role in early history and its lasting influence on art, religion, and culture worldwide.
Ancient Egyptian Civilization
The ancient Egyptian civilization holds a profound historical significance due to its remarkable contributions to human culture, innovation, and architecture, particularly the construction of the iconic pyramids. These monumental structures symbolize the Egyptians’ advanced engineering skills and their religious beliefs centered around the afterlife. The pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, serve as enduring symbols of Egypt’s political power and spiritual devotion during the Old Kingdom period.
Furthermore, ancient Egypt’s advancements in writing, with the development of hieroglyphics, and in fields such as mathematics, astronomy, and medicine, have left a lasting legacy that influenced subsequent civilizations. The preservation of tombs and artifacts through the practice of mummification and elaborate burial rituals reflects their complex beliefs about death and the afterlife, highlighting the importance of religion in shaping their society.
The historical significance of Egypt is also evident in its contributions to art, literature, and governance, which have been studied and admired for thousands of years. The enduring mystery and grandeur of the pyramids continue to attract scholars, explorers, and tourists, reinforcing Egypt’s vital role in world history as a cradle of civilization and a testament to human ingenuity.
Major Dynasties and Rulers
Egypt, renowned for its ancient civilization, holds immense historical significance due to its advancements in culture, architecture, and governance, notably exemplified by the construction of the pyramids. These monumental structures reflect the ingenuity and religious devotion of the Egyptians, serving as tombs for pharaohs and symbols of their divine authority.
Throughout its history, Egypt was ruled by several major dynasties that contributed to its development. The most prominent include the Old Kingdom, Middle Kingdom, and New Kingdom, each marked by unique achievements and influential rulers.
- Old Kingdom (c. 2686–2181 BC): Known as the “Age of the Pyramids,” this period saw the construction of the Pyramids of Giza under the reign of Pharaoh Khufu.
- Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BC): A time of stability and reunification, with Pharaoh Mentuhotep II establishing a strong centralized government.
- New Kingdom (c. 1550–1070 BC): Egypt reached its greatest territorial extent under powerful rulers like Thutmose III and Ramses II, and saw the construction of iconic temples and monuments.
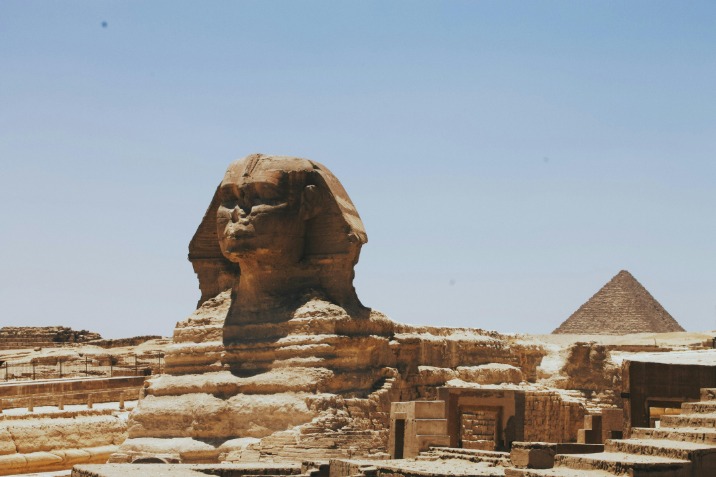
- Sphinx of Giza: Believed to represent Pharaoh Khafre, it exemplifies the grandeur of Egyptian sculpture.
- Pharaoh Ramses II: Known as Ramses the Great, he expanded Egypt through military campaigns and commissioned numerous architectural projects.
- Queen Hatshepsut: One of the few female pharaohs, she is remembered for her prosperous reign and monumental building works at Deir el-Bahari.
Historical Landmarks and Sites
Egypt holds a profound historical significance as one of the world’s earliest cradles of civilization, renowned for its contributions to writing, architecture, and culture. The ancient Egyptians developed sophisticated systems of governance, religion, and art that continue to influence the modern world. Their achievements in engineering and construction are exemplified by the iconic pyramids, which serve as enduring symbols of their technological prowess and spiritual beliefs.
Among the numerous historical landmarks and sites in Egypt, the Great Pyramid of Giza stands out as the most famous. Built during the Fourth Dynasty for Pharaoh Khufu, it is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World and epitomizes the Egyptians’ architectural ingenuity. Besides the pyramids, other significant sites include the Valley of the Kings, the Sphinx, Luxor Temple, and Abu Simbel, each reflecting Egypt’s rich history and cultural legacy. These monuments not only symbolize Egypt’s grandeur but also continue to attract scholars and tourists, offering insight into the civilization’s ancient achievements and beliefs.
The Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is one of the most iconic symbols of ancient Egypt and a marvel of engineering. Located on the Giza Plateau near Cairo, this grand structure was built as a tomb for Pharaoh Khufu and exemplifies the sophistication of ancient Egyptian civilization. Its impressive size and precise construction continue to fascinate historians and visitors alike, making it a timeless testament to Egypt’s rich cultural heritage.
Construction and Architecture
The Great Pyramid of Giza, located in Egypt, is one of the most remarkable achievements of ancient engineering and architecture. Constructed during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom around 2580–2560 BC, it served as a tomb for the Pharaoh Khufu, also known as Cheops. The pyramid’s impressive scale and precise construction reflect the advanced skills of ancient Egyptian builders and their sophisticated understanding of mathematics and astronomy.
The pyramid was built using millions of limestone blocks, each weighing several tons. It originally stood at 146.6 meters (481 feet), but today it reaches about 138.8 meters (455 feet) due to the loss of outer casing stones. The construction process involved meticulous planning, organization, and labor, which likely included a large workforce of skilled laborers and craftsmen. The limestone core was covered with smooth, white Tura limestone casing stones, which gave the pyramid its characteristic gleam.
Architecturally, the Great Pyramid features a complex internal layout with ascending galleries, a descending corridor, and the Grand Gallery, leading to the burial chamber that housed Khufu’s sarcophagus. The alignment of the pyramid is remarkably precise, with its sides aligned closely to the cardinal points, showcasing the Egyptians’ advanced knowledge of astronomy and geometry. Its construction methods continue to intrigue scholars, with theories ranging from the use of straight or spiral ramps to other innovative techniques.
As a marvel of ancient Egyptian ingenuity, the Great Pyramid of Giza not only served as a royal tomb but also symbolized the divine authority of the Pharaoh and the architectural prowess of Egypt. Its enduring legacy reflects the civilization’s sophisticated culture and technological achievements, making it a timeless wonder of human history.
Purpose and Function
The Great Pyramid of Giza, located in Egypt, is one of the most iconic and monumental structures from ancient history. Its purpose and function have fascinated scholars and visitors alike for centuries. Built during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, it served as a tomb for the Pharaoh Khufu and was designed to ensure hisJourney into the afterlife.
The primary purpose of the Great Pyramid was to serve as a final resting place for Pharaoh Khufu, reflecting his divine status and power. It was also believed to aid in his transformation into an eternal afterlife, a common goal in ancient Egyptian religion. The pyramid’s impressive size and precise construction were intended to demonstrate the strength and stability of the Pharaoh’s rule, as well as to honor the gods.
In addition to its function as a tomb, the pyramid complex had religious and ceremonial significance. It was part of a larger mortuary complex that included temples, causeways, and subsidiary structures, all aligned with celestial events. The pyramid’s design and orientation were meant to facilitate the Pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife and to reinforce the divine order.
- To house the tomb of Pharaoh Khufu, ensuring his preservation after death.
- To serve as a symbol of the Pharaoh’s divine authority and power.
- To act as a spiritual gateway for the Pharaoh’s soul to ascend to the afterworld.
- To reflect the religious beliefs and cosmology of ancient Egypt.
- To demonstrate the technological and organizational capabilities of ancient Egyptian society.
Construction Techniques and Materials
The Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the most remarkable achievements of ancient Egypt, was constructed using advanced techniques and durable materials rooted in the civilization’s ingenuity. The pyramid’s core was built with large limestone blocks that were quarried locally, while the outer casing was originally covered with smooth, white Tura limestone to give it a brilliant finish visible from miles around. The core stones were precisely shaped and fitted together to create a stable, enduring structure, demonstrating sophisticated engineering skills.
Construction techniques relied heavily on a massive workforce of skilled laborers and engineers who used simple tools such as copper chisels and wooden sledges to transport and position the enormous stones. Ramps, either straight or spiral, are believed to have been used to move the stones upward as the pyramid ascended in height, allowing for efficient placement of blocks. Precise planning and organization were crucial to align the pyramid accurately with the cardinal points and ensure the structural integrity of the monument.
The materials used were primarily limestone for the bulk of the structure, with higher-quality Tura limestone for the outer casing and granite for internal chambers and corridors. The granite, quarried from Aswan, was chosen for its hardness and durability, especially in areas exposed to greater stress. These construction materials and techniques exemplify the ancient Egyptians’ mastery in building enduring monuments that have withstood thousands of years.
Archaeological Discoveries
Egypt is renowned for its incredible archaeological discoveries, particularly the ancient pyramids that stand as enduring symbols of its rich history. These remarkable structures have fascinated historians and explorers for centuries, revealing valuable insights into the civilization that built them. The pyramids of Egypt, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, continue to captivate the world with their architectural ingenuity and historical significance, offering a glimpse into the grandeur of ancient Egypt.
Unveiled Tombs and Artifacts
Egypt’s rich history is underscored by its extraordinary archaeological discoveries, particularly in the realm of tombs and artifacts that reveal the grandeur of ancient civilization. These discoveries provide valuable insights into the cultural, religious, and daily lives of the Egyptians, shedding light on their complex society and beliefs about the afterlife.
- The tomb of Tutankhamun, uncovered in the Valley of the Kings, remains one of the most famous archaeological finds, offering an unparalleled collection of treasures and golden artifacts that illuminate Egypt’s craftsmanship and spiritual practices.
- Recently discovered tombs in Saqqara have unveiled intricate wall paintings and burial chambers, connecting modern researchers with Egypt’s earliest dynasties and revealing evolving funerary customs over centuries.
- Famous for their monumental architecture, the pyramids—particularly the Great Pyramid of Giza—serve as enduring symbols of Egypt’s ancient ingenuity and religious devotion. These pyramids were originally built as elaborate tombs for pharaohs, illustrating their importance in spiritual beliefs and governance.
- Excavations around the pyramids have uncovered hidden chambers and passages, sparking new theories about their construction and purpose.
- Artifacts such as carved statues, jewelry, and religious texts found within the pyramids provide clues to the rituals and beliefs surrounding death and the divine authority of the pharaohs.
- Ongoing archaeological efforts continue to unearth new sequences of pyramids and tombs, expanding our understanding of ancient Egypt’s architectural and cultural achievements.
Recent Excavations and Findings
Recent archaeological excavations in Egypt continue to shed new light on the ancient civilization that built the iconic pyramids. Scientists and archaeologists have uncovered hidden chambers within the Great Pyramid of Giza, revealing complex construction techniques and offering clues about the burial practices of the Old Kingdom Pharaohs. Excavations in Saqqara have unearthed well-preserved funerary structures, statues, and inscriptions that provide valuable insights into the religious beliefs and daily life of ancient Egyptians.
In recent discoveries, a team of archaeologists announced the discovery of a vast burial site dating back to the reign of Pharaoh Pepi II, containing thousands of artifacts and mummies. These findings help to fill gaps in our understanding of pyramid construction, the administration of resources, and the evolution of Egyptian religious practices over centuries. The ongoing excavations continue to emphasize Egypt’s significance as a hub of ancient innovation and spirituality, with each new discovery adding layers to its rich historical narrative.
Significance of Discoveries
Archaeological discoveries in Egypt, particularly those related to the pyramids, hold immense significance in understanding ancient Egyptian civilization. The pyramids serve as extraordinary monuments that reveal the ingenuity, religious beliefs, and social organization of the Egyptians during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. Discovering new tombs and artifacts within or near these structures provides valuable insights into burial practices, hieroglyphic writing, and artistry of the time. Such findings help scholars piece together the cultural and historical context of one of the world’s most influential ancient societies. Moreover, these discoveries inspire a deeper appreciation of human achievement and the enduring legacy of Egypt’s architectural and artistic innovations.
Cultural and Religious Importance
Egypt is a land rich in cultural heritage and religious significance, embodying a history that dates back thousands of years. The ancient civilization of Egypt has left an indelible mark on the world through its remarkable pyramids, which are not only architectural marvels but also symbols of spiritual beliefs and cultural identity. These structures reflect the deep reverence for the divine and the importance of religion in shaping Egypt’s history and society.
Religious Beliefs and Practices
Egyptian culture and religion have historically played a central role in shaping the nation’s identity, with the pyramids standing as iconic symbols of their spiritual and cultural beliefs. These monumental structures are more than just historical landmarks; they embody the profound religious convictions of the ancient Egyptians regarding the afterlife and divine power.
The religious beliefs of ancient Egypt centered around a pantheon of gods, immortality, and the divine authority of pharaohs, who were seen as gods on earth. These beliefs influenced many practices, including burial rituals and the construction of pyramids, which served as tombs designed to ensure the safe passage of the deceased into the afterlife.
- Belief in an afterlife: Egyptians believed that life continued after death, necessitating elaborate burial preparations and preservation of the body.
- Worship of gods: Deities such as Osiris, Isis, and Ra played vital roles in religious ceremonies and were believed to influence all aspects of life and death.
- Pharaohs as divine rulers: The pharaoh was considered a living god responsible for maintaining order and harmony under divine guidance.
- Rituals and offerings: Religious practices included daily offerings, prayers, and ceremonies to appease gods and secure spiritual favor.
- The pyramids, especially the Great Pyramid of Giza, were constructed as eternal homes for pharaohs, reflecting their divine status and religious significance.
- Trainings and knowledge of priests: A specialized class of priests conducted rites and maintained temples as centers of worship and spiritual learning.
- Festivals and religious events: Public celebrations, such as the Opet Festival, reinforced societal cohesion and religious devotion.

Symbolism of the Pyramids
The pyramids of Egypt hold profound cultural and religious significance, symbolizing the divine connection between the pharaohs and the gods. These monumental structures were designed as grand tombs to ensure the safe passage of the pharaohs’ souls into the afterlife, reflecting ancient Egyptian beliefs about immortality and spiritual continuity. The pyramids also serve as a testament to the advanced engineering skills and religious devotion of the civilization, embodying their view of eternity and divine authority.
Influence on Modern Culture
The pyramids of Egypt hold profound cultural and religious significance that dates back thousands of years. They were originally constructed as grand tombs for Pharaohs, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ beliefs in the afterlife and the divine status of their rulers. These structures served not only as burial sites but also as symbols of the divine power and eternal life, reinforcing the religious worldview of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Throughout history, the pyramids have influenced various aspects of modern culture, inspiring art, literature, and architecture worldwide. Their iconic shapes and mysterious origins continue to captivate people’s imaginations, fostering interest in Egypt’s rich heritage. Many modern buildings and monuments draw inspiration from their geometric design, showcasing the enduring legacy of Egyptian culture. The pyramids remain a powerful symbol of human ingenuity and spiritual aspiration, bridging ancient traditions with contemporary cultural identity.
Tourism and Preservation
Tourism plays a vital role in Egypt’s economy, attracting millions of visitors eager to explore its rich history and iconic landmarks. Among these, the pyramids stand as timeless symbols of ancient ingenuity and cultural heritage. Preserving these archaeological treasures is essential to maintaining Egypt’s historical legacy while ensuring that future generations can continue to marvel at their grandeur and significance.
Visitor Attractions and Experience
Egypt’s rich cultural heritage and historic monuments, such as the iconic pyramids, play a crucial role in attracting tourists from around the world. Preservation of these ancient wonders is essential to maintain their integrity for future generations, ensuring that their historical and archaeological significance remains intact. Careful management and conservation efforts help protect the pyramids from natural weathering, pollution, and human impact.
Visitor attractions in Egypt, especially the pyramids of Giza, offer a unique glimpse into ancient Egyptian civilization. Tourists have the opportunity to explore the awe-inspiring structures, learn about their historical context, and marvel at the engineering marvels of the past. Cultural sites are complemented by museums, boat rides on the Nile, and vibrant markets, creating diverse experiences that immerse visitors in Egypt’s heritage.
Enhancing the visitor experience involves balancing accessibility with preservation. Guided tours, augmented reality, and informative displays enrich understanding and appreciation of Egypt’s archaeological treasures. Responsible tourism practices ensure that the preservation of the pyramids and other archaeological sites remains sustainable, allowing future generations to enjoy these extraordinary landmarks while respecting their cultural significance.
Preservation Challenges
Egypt, renowned for its ancient pyramids, faces the ongoing challenge of balancing tourism with the preservation of these iconic structures. As millions of visitors flock to see the monumental feats of the Pharaohs, the wear and tear on the pyramids and surrounding sites increase, risking irreversible damage. Preservation efforts must therefore address both environmental factors, such as erosion and pollution, and human impacts from foot traffic and souvenir collection.
One of the primary preservation challenges is managing the high volume of tourism. Overexposure can lead to surface erosion, structural weakening, and loss of historical integrity. Efforts like limiting visitor access, implementing strict conservation protocols, and promoting responsible tourism are essential to safeguard these monuments for future generations.
Additionally, environmental threats such as rising temperatures, desert sands, and groundwater fluctuations contribute to the deterioration of the pyramids. Preservation initiatives include environmental monitoring, structural reinforcement, and research into sustainable preservation techniques. International cooperation and local community involvement are crucial to ensure that Egypt’s cultural heritage remains intact amidst the pressures of modern tourism.
Efforts to Protect the Pyramids
Tourism plays a significant role in Egypt’s economy, with the iconic pyramids drawing millions of visitors from around the world each year. However, the increasing influx of tourists has posed challenges to the preservation of these ancient monuments. To protect Egypt’s cultural heritage, numerous efforts have been implemented to ensure the longevity of the pyramids while maintaining their historical integrity.
- Strict regulations and guidelines are enforced to limit access to the most vulnerable areas of the pyramids, reducing physical wear and tear.
- Advanced conservation techniques and technologies, such as 3D scanning and restoration, help repair and stabilize the structures without compromising their authenticity.
- Monitoring systems are installed to detect environmental threats like humidity, pollution, and vibrations caused by nearby tourism activities.
- Public awareness campaigns educate visitors about the importance of respecting and preserving the site for future generations.
- International collaborations and funding support innovative preservation projects and research efforts targeting pyramid conservation.




0 Comments