Geography of Nairobi
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a vibrant city situated in the southern part of the country. It is located on the Nairobi River basin and is characterized by a mix of highlands and plains. The city sits at an elevation of approximately 1,795 meters (5,889 feet) above sea level, giving it a mild and temperate climate. Its strategic geographic position makes Nairobi a key economic, political, and cultural hub in East Africa.
Location and Topography
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is situated in the south-central part of the country. It serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of Kenya, with a diverse geographical landscape that influences its climate and topography.
- Nairobi is located at approximately 1.2921° S latitude and 36.8219° E longitude.
- The city lies on the Nairobi Plateau at an elevation of about 1,795 meters (5,889 feet) above sea level.
- The topography of Nairobi is characterized by rolling hills, ridges, and valleys, which create a varied landscape across the city.
- To the south and west, the terrain gradually descends into the surrounding lowlands and savannahs.
- The Nairobi River and several other water bodies flow through the area, contributing to the city’s lush greenery and natural beauty.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is located in the south central part of the country, situated on the highlands of East Africa. It is positioned at an elevation of approximately 1,795 meters (5,889 feet) above sea level, which influences its local climate and weather patterns. The city lies within the Nairobi Basin, surrounded by central Kenyan highlands and is bordered by the Aberdare Range to the northwest and the Ngong Hills to the southwest.
The climate of Nairobi is classified as a subtropical highland climate, characterized by mild temperatures throughout the year due to its elevation. Summers are generally warm, with daytime temperatures averaging around 25-27°C (77-81°F), while winter temperatures can drop to around 10-12°C (50-54°F) at night. The city experiences two main rainy seasons: the long rains from March to May and the shorter, lighter rains from October to December. These seasonal patterns significantly influence agriculture, water availability, and daily life in Nairobi.
Weather patterns in Nairobi tend to be relatively stable, with moderate temperatures and seasonal rainfall. The city’s elevation helps keep temperatures cool compared to other regions at similar latitudes, providing a comfortable climate for residents. The dry months, typically June to September, see less rainfall and cooler temperatures, while the rainy seasons can lead to localized flooding and mudslides in some areas. Overall, Nairobi’s geography and climate make it a unique urban center with a temperate environment amid an African landscape.
Natural Landmarks
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a vibrant city situated in the southern part of the country. It is characterized by its diverse geography, which includes highlands, rolling hills, and savannahs. The city is located on the central highlands of Kenya, approximately 1,795 meters above sea level, providing a mild climate and lush landscapes.
One of the prominent natural landmarks in Nairobi is the Nairobi National Park, a unique wilderness area located just outside the city center. This park offers a rare opportunity to see wildlife such as lions, giraffes, and rhinos against the backdrop of Nairobi’s skyline. Additionally, the Ngong Hills, a series of dramatic ridges nearby, are famous for their scenic views over the city and surrounding plains. These hills are a popular spot for hiking and photography.
Another notable landmark is the Karura Forest, a large urban forest that provides a natural sanctuary within the city. It features waterfalls, walking trails, and diverse flora and fauna. The city’s landscape is also marked by the Mathare River and several smaller streams that contribute to Nairobi’s lush environment. Overall, Nairobi’s natural landmarks blend urban development with rich natural beauty, making it a distinctive and dynamic capital city.
Historical Background
The historical background of Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is deeply rooted in the country’s colonial past and its journey toward independence. Originally a small railway settlement established in the late 19th century, Nairobi grew rapidly due to the construction of the Uganda Railway. Over the years, it transformed into a major commercial and political hub, reflecting Kenya’s broader history of colonization, struggle for independence, and subsequent development. Understanding this history provides valuable insight into the city’s diverse cultural landscape and its significance as the capital of Kenya today.
Founding of Nairobi
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, has a rich historical background that dates back to the late 19th century. Originally, it was established as a railway depot during the construction of the Uganda Railway in 1899. The area was chosen due to its strategic location along the railway route, which connected the coast to the interior of East Africa. Over time, it grew from a small camp into a bustling urban center, attracting settlers, traders, and workers. The founding of Nairobi was closely linked to the development of the railway, which played a crucial role in shaping its growth and positioning it as a major hub in the region. By the early 20th century, Nairobi had officially been recognized as a city, reflecting its importance as a commercial and administrative center in Kenya and East Africa as a whole.
Historical Development
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, has a rich historical background and has developed significantly over the years. Originally a railway depot established in the late 19th century, Nairobi quickly grew as a vital transportation hub during the British colonial period. Its strategic location and economic opportunities attracted a diverse population, leading to rapid urbanization. Over time, Nairobi evolved from a small settlement into Kenya’s political, economic, and cultural center, hosting various government institutions, international organizations, and vibrant neighborhoods. The city’s development has been shaped by both colonial influences and modern advancements, making it a dynamic metropolis in East Africa.
Major Historical Events
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, has a rich historical background shaped by various periods of development and colonial influence. Originally inhabited by indigenous communities, the area was an important trading center long before it became a colonial settlement. During the late 19th century, the arrival of the British railway expansion in East Africa in the 1890s marked a significant turning point. Nairobi grew rapidly as a transportation hub, eventually becoming the administrative and commercial center of British East Africa.
Major historical events include Nairobi’s official founding in 1899 as a depot on the railway line, which attracted settlers and led to urban growth. Kenya gained independence from British colonial rule in 1963, and Nairobi was designated the capital of the newly independent nation. Post-independence, Nairobi developed into a vibrant metropolis, hosting important political, economic, and cultural events. The city played a key role in Kenya’s struggle for independence and continues to be a central player in regional diplomacy and development.
Demographics and Population
The population demographics of Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, encompass a diverse array of communities, cultures, and age groups. Understanding these demographics is essential to grasp the social and economic fabric of the city. With rapid urban growth, Nairobi’s population continues to expand, creating both opportunities and challenges for development and infrastructure planning.
Population Size
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city with a diverse demographic profile and a rapidly growing population. As the economic and political hub of the country, it attracts people from various regions and backgrounds.
Kenya’s population size has been increasing steadily over the years, with Nairobi contributing significantly to this growth. The city is home to several ethnic groups, including Kikuyu, Luo, Luhya, Kalenjin, and others, creating a rich cultural mosaic. Its population is estimated to be over four million residents, but including the metropolitan area, the greater Nairobi region hosts more than four and a half million people, reflecting its importance as an urban center.
This demographic diversity and population expansion present both opportunities and challenges, shaping the city’s development, infrastructure, and social dynamics as it continues to grow as the capital of Kenya.
Ethnic Composition
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city with diverse demographics and a rich ethnic composition. It serves as the political, economic, and cultural hub of the country, attracting people from various backgrounds.
- Kenya’s population is ethnically diverse, consisting of more than 40 ethnic groups.
- The largest communities include Kikuyu, Luo, Luhya, Kalenjin, Maasai, Kisii, and Meru.
- Nairobi’s demographic profile reflects this diversity, with a significant number of residents representing different ethnicities and cultures.
- Urbanization has led to an increased population density in Nairobi, making it a melting pot of different ethnicities and socioeconomic backgrounds.
- The city has a growing expatriate community as well, contributing further to its multicultural environment.
- Despite this diversity, language and cultural practices vary, with Swahili and English serving as official languages in the city.
Languages Spoken
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, has a diverse and vibrant population. As of recent estimates, the city is home to over 4 million residents, making it one of the largest cities in Africa. Nairobi’s demographics reflect a mix of ethnic groups, with Kikuyu, Luo, Luhya, Kamba, and other communities living and working together. The population continues to grow rapidly due to urbanization and migration from rural areas.
Multiple languages are spoken in Nairobi. English and Swahili are the official languages and are widely used in government, business, and education. Additionally, various local languages such as Kikuyu, Luo, and Luhya are spoken by different ethnic communities. The linguistic diversity underscores Nairobi’s role as a melting pot of cultures and peoples from across Kenya and beyond.
Government and Administrative Structure
The government and administrative structure of Kenya play a crucial role in managing the country’s affairs and ensuring effective governance. As the capital of Kenya, Nairobi serves as the political, economic, and administrative hub, reflecting the nation’s organizational framework. Understanding the structure helps in appreciating how various levels of government work together to serve the people and facilitate development across the country.
City Governance
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is governed through a structured administrative system that ensures effective management and delivery of public services. The city governance model combines centralized and decentralized approaches, with various authorities overseeing different aspects of urban administration. Nairobi’s government is led by a City Governor, who is elected by residents and is responsible for local policy implementation, development planning, and city management.
The Nairobi City County government operates under the Constitution of Kenya and United Nations urban policies, overseeing service provision such as roads, health, education, and sanitation. The county assembly, composed of elected Members of County Assembly, legislates on local issues and budgets. Additionally, several specialized departments and agencies support the city’s administration, collaborating with national government ministries to enhance urban development.
Local governance in Nairobi emphasizes citizen participation and transparency, aiming to address urban challenges such as congestion, infrastructure development, and environmental sustainability. Overall, the city’s administrative structure is designed to foster sustainable growth, improve living standards, and ensure efficient service delivery for its residents.
Administrative Divisions
The administrative structure of Kenya is organized into various levels to facilitate effective governance and administration. The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, serves as the central hub for the country’s government and administrative functions. It is not only the political capital but also a major economic and cultural center, hosting key government offices, foreign missions, and regional organizations.
Kenya’s administrative divisions are structured as follows:
- Country Level: Kenya, officially known as the Republic of Kenya
- Regional Level: Divided into 47 counties, each governed by an elected county government
- Sub-Regional Level: Consists of constituencies and sub-counties within each county
- Local Level: Towns, wards, and urban administrative units within counties
Nairobi, as the capital city, integrates these administrative layers and serves as the center of government, hosting the Parliament of Kenya, the Supreme Court, and various ministries and departments that oversee national governance and development initiatives.
Local Government Functions
The capital of Kenya is Nairobi, which serves as the primary political, economic, and administrative center of the country. Kenya’s government operates under a constitutional framework that delineates powers between the national and local governments. The National Government is responsible for important functions such as defense, foreign policy, and national economic planning, while local governments handle municipal services, local infrastructure, and community development projects.
Local government in Kenya is structured into counties, each governed by elected county assemblies and county governors. These local authorities are tasked with providing essential services including education, healthcare, sanitation, and local transportation. The administrative structure aims to promote decentralization, ensuring that local needs are addressed efficiently and effectively. Overall, this organizational setup fosters governance that is closer to the people, enhancing participation and accountability in administrative functions.
Economy of Nairobi
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a vibrant economic hub in East Africa. It plays a crucial role in the country’s overall development, serving as the center for commerce, finance, and industry. With a diverse and growing economy, Nairobi attracts international investments and hosts numerous multinational corporations. Its dynamic business environment and strategic location contribute significantly to Kenya’s economic progress.
Major Industries
The economy of Nairobi, the capital city of Kenya, is a vibrant and dynamic hub that plays a vital role in the country’s overall development. It serves as the primary commercial and financial center, contributing significantly to Kenya’s GDP. Nairobi’s economy is driven by a diverse range of industries that support its status as a major economic hub in East Africa.
Major industries in Nairobi include finance and banking, with numerous banks and financial institutions headquartered in the city. The technology sector, often referred to as “Silicon Savannah,” is rapidly growing, with many tech startups and innovation hubs. The manufacturing industry also thrives, producing textiles, textiles, and consumer goods. Additionally, the city has a robust real estate sector, driven by urban expansion and increased demand for residential and commercial properties. Tourism is another important industry, with Nairobi serving as a gateway to Kenya’s renowned national parks and wildlife reserves. Overall, Nairobi’s diverse economy underpins its importance as the economic heart of Kenya.
Commercial Hubs
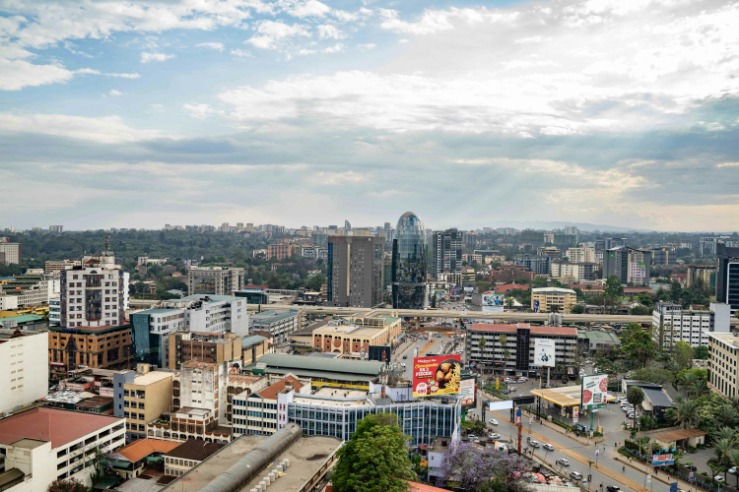

Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a major economic and commercial hub in East Africa. It plays a crucial role in the country’s economy, contributing significantly to GDP through diverse industries such as finance, technology, manufacturing, and trade. The city is home to numerous multinational corporations, Kenyan businesses, and economic institutions that drive growth and innovation.
Commercial hubs within Nairobi include areas like Westlands, Upper Hill, and the Central Business District (CBD). Westlands is known for its vibrant business environment, shopping centers, and entertainment venues, making it a popular location for both local and international companies. Upper Hill hosts numerous financial institutions, corporate offices, and diplomatic missions, serving as the city’s financial heartbeat. The CBD remains the historic and administrative center, hosting government offices, markets, and bustling streets filled with commerce.
These commercial hubs foster a dynamic economy by attracting investment, promoting entrepreneurship, and creating employment opportunities. The development of infrastructure such as office complexes, transport networks, and communication systems continues to enhance Nairobi’s stature as a key economic center in Africa.
Employment Opportunities
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a vibrant economic hub with diverse employment opportunities across various sectors. The city’s economy is driven by finance, technology, manufacturing, tourism, and trade, attracting both local and international investments. Nairobi hosts numerous multinational corporations, banking institutions, and technology startups that create a dynamic job market for residents.
Employment opportunities in Nairobi are continually expanding, especially in sectors like ICT, business process outsourcing, and real estate. The city’s strategic location and developed infrastructure make it an attractive destination for business ventures and employment. Additionally, the growing hospitality and tourism industries offer numerous jobs in hotels, travel agencies, and cultural sites, further contributing to the city’s economic vitality.
Cultural and Tourist Attractions
Nairobi, the vibrant capital of Kenya, is renowned for its rich cultural heritage and diverse tourist attractions. Visitors can explore a fascinating blend of modern city life, natural parks, and historic sites that showcase Kenya’s unique traditions and history. From bustling markets to wildlife reserves, Nairobi offers an exciting array of experiences for travelers seeking both adventure and cultural immersion.
Museums and Galleries
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city known for its diverse cultural and tourist attractions. Visitors can explore a variety of museums and galleries that showcase Kenya’s rich history, arts, and culture. The Nairobi National Museum offers insights into the country’s archaeological and paleontological heritage, while the Karen Blixen Museum provides a glimpse into the life of the famous author. For contemporary art, the Nairobi Gallery displays works by local artists, reflecting the city’s modern creative scene. Additionally, attractions like the Bomas of Kenya provide cultural performances and traditional crafts, making Nairobi a fascinating destination for tourists interested in Kenya’s heritage and artistic achievements.
Historical Sites
Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is a vibrant hub of cultural and tourist attractions, offering a rich blend of history and modernity. Visitors can explore numerous historical sites such as the Karen Blixen Museum, which was once the home of the famous author, and the Nairobi National Museum that showcases Kenya’s diverse cultural and natural heritage. The city is also known for its bustling markets like Maasai Market, where traditional crafts and jewelry are displayed. For wildlife enthusiasts, Nairobi offers a unique experience with the David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust and Giraffe Centre. Additionally, the city’s vibrant neighborhoods, such as Westlands and Karen, boast a variety of restaurants and entertainment venues, making Nairobi a dynamic destination for both history lovers and tourists seeking leisure and adventure.
Festivals and Events
NAIROBI, the vibrant capital of Kenya, offers a diverse range of cultural and tourist attractions, festivals, and events that captivate visitors from around the world. The city is renowned for its rich history, bustling markets, and lively entertainment scene.
Tourists can explore the Nairobi National Park, a unique urban wildlife reserve that hosts lions, giraffes, and rhinos against the backdrop of the city skyline. The David Sheldrick Wildlife Trust provides an inspiring opportunity to see rescued elephants and learn about conservation efforts. The Karen Blixen Museum, located in the former home of the famous author, offers insight into Kenya’s colonial past.
Nairobi boasts vibrant cultural attractions such as the Bomas of Kenya, where visitors can experience traditional music, dance, and crafts from various Kenyan communities. The Maasai Market is a lively hub for local arts and crafts, perfect for purchasing unique souvenirs.
The city hosts numerous festivals and events throughout the year, including the Nairobi International Film Festival, Kenyatta Day celebrations, and the Nairobi Fashion Festival. These events showcase Kenya’s artistic talent, heritage, and modern trends, providing visitors with an immersive experience of the country’s diverse culture.
Transportation and Infrastructure
Transportation and infrastructure play a vital role in shaping the development and accessibility of a city. In Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, a well-established network of roads, railways, and public transit systems connects residents and visitors alike. These systems are essential for economic growth, ease of movement, and improving the overall quality of life in the vibrant urban center.
Road Networks
Transportation and infrastructure play a vital role in the development of Nairobi, the capital of Kenya. A well-developed road network facilitates the movement of people and goods, contributing to economic growth and urban accessibility.
- Nairobi boasts an extensive road network that connects different neighborhoods and suburbs, making commuting easier for residents and visitors.
- The main roads in the city include Kenyatta Avenue, Mombasa Road, and Ngong Road, which serve as arteries for traffic flow and commerce.
- In recent years, efforts have been made to improve road quality and reduce congestion through the construction of bypasses and flyovers.
- Additionally, the city is investing in public transportation systems such as matatus (shared vans) and buses to ease the burden on road infrastructure.
- Infrastructure projects like the Nairobi Expressway have significantly enhanced connectivity and reduced travel time across key areas in the city.
Public Transit Systems
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, boasts a comprehensive transportation and infrastructure network that supports its status as a major economic hub in East Africa. The city’s public transit systems include matatus (minibuses), buses, and commuter trains that facilitate the movement of thousands of residents and visitors daily. Efforts have been made to modernize public transportation with the introduction of Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) services, enabling faster travel between Nairobi and other major cities such as Mombasa. Additionally, ongoing projects aim to improve road infrastructure, reduce congestion, and promote sustainable transport options like cycling and walking. These developments are essential for supporting Nairobi’s growth and maintaining efficient connectivity within the city and beyond.
Airports and Connectivity
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, serves as a vital hub for transportation and infrastructure within the region. It boasts a well-developed network of roads, railways, and air travel facilities that facilitate efficient movement of people and goods. Jomo Kenyatta International Airport, one of Africa’s busiest airports, connects Nairobi to numerous international destinations, enhancing the city’s status as a key gateway to East Africa. Additionally, ongoing improvements in urban infrastructure aim to reduce congestion and improve connectivity across the city, supporting economic growth and development.
Education and Institutions
Education and institutions play a vital role in shaping the social and economic development of a country. They provide the foundation for knowledge, skills, and innovation, fostering growth and progress within communities. In the context of Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, educational institutions are integral to its vibrant culture and dynamic workforce, making it a hub for learning and advancement.
Major Universities
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is not only the largest city in the country but also a major center for education and higher learning institutions. It hosts several prominent universities that attract students from across Africa and beyond, offering a diverse range of academic programs and research opportunities.
- University of Nairobi: Established in 1970, it is Kenya’s oldest and most prestigious university, renowned for its research, law, medicine, and social sciences faculties.
- Kenyatta University: Known for its education, arts, and business programs, it plays a significant role in teacher training and community development.
- Strathmore University: A private university celebrated for its business, information technology, and law faculties, emphasizing entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Inoorero University: Specializes in communication and technology, providing professional training in media, telecommunications, and related fields.
Research Centers
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is renowned not only for its vibrant urban life but also for its significant educational and research institutions. These institutions play a crucial role in fostering innovation, research, and development within the country. Universities such as the University of Nairobi, Kenyatta University, and Strathmore University offer diverse programs and contribute extensively to academic excellence.
Nairobi is also home to numerous research centers and think tanks, including the Kenya Medical Research Institute and the International Livestock Research Institute. These centers focus on health, agriculture, and environmental issues pertinent to Kenya and the broader East African region. They serve as vital hubs for scientific research, policy development, and training, helping to address pressing challenges facing the nation and promoting sustainable development.
Schools and Educational Facilities
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a major center for education and institutions in the region. It hosts numerous schools, universities, and research centers that cater to a diverse student population. Educational facilities in Nairobi include prestigious institutions such as the University of Nairobi, Kenyatta University, and Strathmore University, offering a wide range of academic programs. The city is also home to various primary and secondary schools that emphasize quality education and skill development. These institutions play a crucial role in fostering innovation, leadership, and socio-economic growth in Kenya. Moreover, Nairobi’s educational infrastructure continues to expand, attracting students both locally and internationally, making it a vital hub for learning and development in East Africa.
Environment and Urban Development
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city that plays a crucial role in the country’s environment and urban development. As a rapidly growing metropolis, Nairobi faces unique challenges and opportunities in balancing urban expansion with environmental sustainability. Effective urban planning and development strategies are essential to ensure that the city remains a healthy, sustainable, and livable space for its residents while preserving its natural resources.
Green Spaces and Parks
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city that balances rapid urban development with the preservation of green spaces and parks. As a major economic hub in East Africa, Nairobi faces the challenge of integrating environmental sustainability into its urban planning. Green spaces such as Uhuru Park, Karura Forest, and Nairobi National Park offer residents and visitors opportunities for recreation, relaxation, and connection with nature. These areas play a crucial role in improving air quality, reducing urban heat island effects, and promoting biodiversity within the city. Effective environment and urban development strategies are essential to ensure that Nairobi continues to grow sustainably while maintaining its natural heritage for future generations.
Urban Planning Initiatives
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, is a vibrant city experiencing rapid urban growth and development. In response to increasing population and environmental challenges, numerous urban planning initiatives have been implemented to promote sustainable development and improve the quality of life for residents. These initiatives focus on enhancing green spaces, managing traffic congestion, and ensuring responsible waste management. Efforts are also being made to develop eco-friendly infrastructure, including renewable energy projects and water conservation programs, to minimize the city’s ecological footprint. Through strategic urban planning, Nairobi aims to become a model for sustainable cities in Africa, balancing economic growth with environmental preservation.
Environmental Challenges
The capital of Kenya, Nairobi, faces numerous environmental challenges that threaten its sustainable development. Rapid urbanization has led to increased pollution, deforestation, and strain on natural resources. Traffic congestion and improper waste management contribute to air and water pollution, adversely impacting public health and the surrounding ecosystems. Additionally, encroachment on green spaces and wetlands has resulted in loss of biodiversity and increased vulnerability to climate change effects. Addressing these environmental challenges requires integrated urban planning, sustainable resource management, and community engagement to ensure Nairobi’s growth aligns with environmental preservation and resilience.




0 Comments