Overview of Lions in Namibia
Namibia is renowned for its thriving lion populations, which play a crucial role in the country’s diverse ecosystems. These majestic predators are a symbol of strength and wilderness, signifying Namibia’s rich natural heritage. Efforts to conserve and protect lions in Namibia have gained momentum, ensuring that future generations can continue to experience the awe-inspiring presence of these iconic animals.
Habitat and Range
The lion population in Namibia is a vital part of the country’s diverse ecosystems, primarily residing in the savannas and arid regions. These majestic predators are known for their strength and social structures, often living in prides that offer protection and cooperation in hunting. Namibia’s unique landscape provides an ideal habitat for lions, supporting their dietary and territorial needs.
Habitat and Range of Lions in Namibia include:
- Namibia’s extensive savannas and scrublands, providing open spaces for hunting and roaming.
- Desert-adjacent areas such as the Namib Desert, where lions adapt to harsher conditions.
- Protected areas like Etosha National Park, which serve as crucial habitats for lion populations.
- Regions in western Namibia, where lions are often seen near water sources and game-rich zones.
- Increased conservation efforts have helped maintain and expand their range within the country.
Population Status
The lion in Namibia is a significant and iconic species, playing a crucial role in the country’s biodiversity and ecosystem. Namibia is home to one of the largest populations of desert-adapted lions, which have uniquely evolved to survive in arid environments. These lions are known for their resilience and adaptability in harsh desert conditions, making Namibia a vital habitat for their conservation.
The population status of lions in Namibia is relatively stable compared to other regions in Africa, thanks to effective conservation efforts and protected areas such as Etosha National Park and Botswana border transfrontier parks. However, despite these positive developments, lions face ongoing threats from human-wildlife conflict, poaching, and habitat loss. Conservation programs are actively working to ensure sustainable coexistence between lions and local communities, emphasizing eco-tourism and habitat preservation to maintain healthy lion populations across Namibia.
Historical Distribution
Lions in Namibia are a significant part of the country’s wildlife heritage, renowned for their majestic presence and vital role in the ecosystem. Historically, lions once roamed across vast areas of Africa, including regions that now form Namibia, reflecting a wide distribution across grasslands, savannas, and open woodlands.
In the past, the historical distribution of lions in Namibia was extensive, covering much of the national territory. They inhabited the Namibian desert regions, the Etosha Pan, and surrounding plains, thriving in ecosystems that provided ample prey and suitable cover. Over time, however, their range has become more restricted due to human activities such as agriculture, settlement expansion, and hunting.
Today, lions are primarily found in protected areas like Etosha National Park, where conservation efforts help maintain their populations. Despite these efforts, their historical range has diminished, making them a focal point for conservation initiatives aimed at restoring and preserving their presence throughout Namibia. The historical distribution of lions in Namibia underscores their importance and the need for ongoing efforts to ensure their survival in the wild.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts in Namibia play a vital role in protecting the majestic lion populations that roam its diverse landscapes. These initiatives aim to preserve the natural habitats of lions, prevent poaching, and promote coexistence between wildlife and local communities. Through dedicated programs and community involvement, Namibia strives to ensure that future generations can continue to witness the awe-inspiring presence of lions in the wild.
Protected Areas
Conservation efforts in Namibia have been instrumental in protecting the lion populations that roam its vast landscapes. Numerous protected areas, including Etosha National Park, serve as critical habitats for lions, ensuring their survival amidst increasing threats from poaching and habitat loss. These regions are managed with a focus on maintaining ecological balance and promoting coexistence between wildlife and local communities. Community-based conservation programs and eco-tourism initiatives have further strengthened protection efforts, providing sustainable economic incentives for local residents to preserve lion populations. Continuous research and monitoring are vital components of these efforts, helping authorities to adapt strategies and safeguard Namibia’s iconic lions for future generations.
Conservation Programs and Initiatives
Conservation efforts in Namibia play a crucial role in protecting the endangered lion populations and ensuring their long-term survival. These initiatives aim to balance ecological sustainability with the needs of local communities, promoting coexistence between humans and wildlife.
- Namibia established community-based conservation programs that involve local residents in safeguarding lion habitats and reducing human-wildlife conflicts. This approach empowers communities to become stewards of the lions and benefit economically from eco-tourism.
- Numerous national parks and protected areas, such as the Etosha National Park, serve as vital habitats for lions. These areas are managed by the Namibian government with strict anti-poaching measures and habitat preservation strategies.
- Conservation organizations like the Namibia Conservation Foundation implement initiatives focused on research, wildlife monitoring, and habitat restoration to understand lion behavior and ensure effective protection measures.
- Community outreach and education programs are essential components of conservation efforts, raising awareness about the importance of lions to Namibia’s ecosystem and promoting sustainable practices among local populations.
- Partnerships with international agencies and NGOs help supply funding, expertise, and innovative technologies for lion conservation projects, enhancing the effectiveness of national strategies.
Community Involvement
Conservation efforts in Namibia play a crucial role in protecting the lion population, which is vital to maintaining the country’s rich biodiversity. Community involvement is at the heart of these initiatives, encouraging local residents to participate actively in preserving their natural heritage. Many programs offer incentives for communities to adopt sustainable practices, ensuring lions and other wildlife are safeguarded from poaching and habitat destruction. Education campaigns raise awareness about the importance of lions to the ecosystem and promote coexistence between humans and wildlife. By fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among local communities, Namibia enhances its conservation success and secures a future where lions continue to thrive naturally in their habitat.
Lion Behavior and Ecology
Lions in Namibia exhibit fascinating behaviors and ecological patterns that are vital to understanding their role in the environment. As apex predators, they play a crucial part in maintaining the balance of the local ecosystem. Their social structures, hunting strategies, and interactions with prey and rivals provide insight into their adaptive strategies in the diverse landscapes of Namibia. Studying lion behavior and ecology helps conservation efforts and ensures the survival of these majestic animals in the wild.
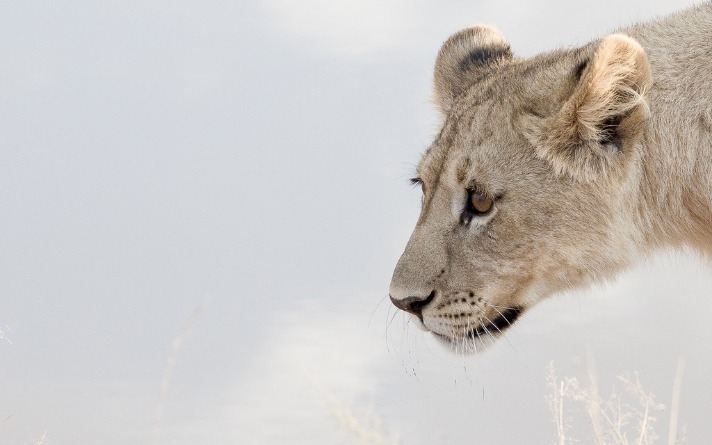

Diet and Hunting Patterns
Lions in Namibia exhibit distinct behavioral and ecological traits that are closely linked to their environment. They are social animals, typically living in prides composed of related females, their offspring, and a few males. These prides display cooperative behaviors, especially during hunting and defending territory. Namibia’s lion populations are adapted to the arid, open landscapes of the Namib Desert and surrounding savannas, which influence their movement and activity patterns.
The diet of Namibian lions primarily consists of large prey species such as zebras, wildebeests, oryx, springboks, and sometimes larger animals like elephants or buffalo, depending on the availability. Their hunting behavior is largely nocturnal or during cooler parts of the day to conserve energy and avoid the intense daytime heat. Lions employ various strategies, including stalking and coordinated group pursuits, to capture prey effectively in the vast, open terrain of Namibia.
The hunting patterns of lions in Namibia are shaped by environmental conditions and prey distribution. They often establish patrols along territorial boundaries and adapt their hunting times and tactics based on prey movement and availability. The scarcity of water and prey in desert regions forces lions to expand their ranges and be opportunistic, emphasizing their resilience and adaptability in harsh environments. Their ability to hunt efficiently is vital for their survival in the challenging ecosystems of Namibia.
Social Structure and Pride Dynamics
Lions in Namibia exhibit complex behaviors and ecological patterns that are integral to their survival in the savannah and desert environments. They are apex predators, primarily hunting large herbivores such as wildebeest, zebras, and antelopes, which influences the structure of the ecosystem. Territoriality plays a significant role, with male lions defending the pride’s territory to ensure access to food resources and mating rights. These territories can range widely and are marked with scent markings and vocalizations to communicate with rival prides.
The social structure of lions in Namibia revolves around prides, which typically consist of related females, their offspring, and a coalition of male lions. Female lions are the core of the pride, cooperative in hunting and raising cubs, forming tight-knit social bonds. Male coalitions, often brothers or close allies, maintain control over the pride by defending against rival males and attempting to establish or take over prides. Pride dynamics involve frequent pride fusions and dispersals, especially among males, to avoid inbreeding and increase genetic diversity.
In Namibia, lion behavior and pride dynamics are also influenced by environmental factors such as water availability and prey distribution. During dry seasons, lions tend to be more nomadic, following herds to water sources. The balance of pride stability, territory defense, and resource availability reflects their adaptive strategies to thrive in arid regions. Additionally, conservation efforts focus on maintaining healthy pride structures, recognizing their importance for the species’ long-term survival in the region’s evolving landscapes.
Reproduction and Lifespan
Lions in Namibia are iconic predators known for their complex social structures, behaviors, and adaptability to their environment. They predominantly reside in the country’s desert and savanna habitats, engaging in behaviors that optimize their survival and reproduction.
In terms of behavior and ecology, Namibian lions are highly social animals living in groups called prides, which typically consist of related females, their offspring, and a few dominant males. These prides defend their territory through scent marking and vocalizations, such as roaring, which can be heard over long distances. They are apex predators, primarily hunting large herbivores like zebras, hartebeests, and wildebeest, often cooperating during hunts to increase success rates.
Reproduction among Namibia’s lions is characterized by high pride turnover. Female lions usually reach sexual maturity around 2 to 3 years of age and give birth to litters of 1 to 4 cubs after a gestation period of approximately 110 days. Cubs are born blind and rely heavily on their mothers and pride members for protection and nourishment. Male lions may challenge for pride dominance, engaging in fierce battles to establish or take over a pride.
The lifespan of lions in Namibia varies but generally ranges from 10 to 14 years in the wild. Factors influencing lifespan include resource availability, human-wildlife conflict, and disease. Male lions tend to have shorter lifespans due to the stresses of maintaining dominance, while females often live longer, especially if they are part of a thriving pride with consistent access to resources.
Challenges Facing Lions in Namibia
Namibia’s lions face numerous challenges in their natural habitat, threatening their survival and the delicate ecosystem they inhabit. Human-wildlife conflict, habitat loss due to agricultural expansion, and poaching are among the primary concerns that endanger lion populations in the region. Efforts to conserve these majestic animals must address these pressing issues to ensure their continued existence in Namibia’s wild landscapes.
Human-Wildlife Conflict
Lions in Namibia face numerous challenges that threaten their survival, with human-wildlife conflict being one of the most significant. As human populations expand and agricultural activities increase, lions often venture into livestock areas, leading to conflicts with local communities. This results in retaliation killings by farmers who seek to protect their livestock, further reducing the already vulnerable lion populations. Additionally, habitat loss caused by expanding settlements, mining, and infrastructure development diminishes suitable living spaces for lions, forcing them into smaller territories and increasing encounters with humans. Poaching and illegal wildlife trade also pose serious threats, targeting lions for trophies or traditional medicine. Conservation efforts in Namibia must therefore address these challenges through community engagement, effective land-use planning, and enforcement of anti-poaching laws to ensure the long-term survival of lions in the region.
Poaching and Illegal Trade
Lions in Namibia face several significant challenges, with poaching and illegal trade being among the most critical threats. Despite conservation efforts, poachers target lions for their valuable body parts, such as bones and skins, which are in high demand in illegal markets. This illegal trade is driven by the lucrative international demand for wildlife products, often fueled by traditional medicine and trophy hunting. The threat of poaching not only reduces lion populations directly but also disrupts social structures within lion prides, impacting their long-term survival. Additionally, habitat loss due to human-wildlife conflict, agriculture, and infrastructure development further pressures lion populations in Namibia. Addressing these challenges requires robust anti-poaching measures, strengthened law enforcement, community engagement, and international cooperation to curb illegal trafficking and ensure the preservation of Namibia’s iconic lions.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Lion populations in Namibia are increasingly threatened by habitat loss and fragmentation, primarily driven by human activities such as agriculture, infrastructure development, and settlement expansion. As large areas of land are converted for farming or urban use, lions lose their natural hunting grounds and territories, making it difficult for them to find sufficient food and shelter. This fragmentation also isolates lion populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of inbreeding, which can threaten their long-term survival. Additionally, reduced habitat connectivity leads to conflicts with local communities, as lions venture into human settlements in search of prey or new territories, often resulting in retaliatory killings. Addressing these challenges requires concerted conservation efforts focused on habitat preservation, creating wildlife corridors, and engaging local communities to ensure sustainable coexistence between lions and humans in Namibia.
Ecotourism and Economic Impact
Ecotourism has become an important aspect of sustainable travel, promoting responsible interactions with natural environments while supporting local economies. In Namibia, this form of tourism is particularly significant due to its rich biodiversity and iconic wildlife, such as lions. The economic impact of ecotourism in Namibia not only helps conserve vital ecosystems but also provides livelihoods for local communities, making it a crucial component of the country’s sustainable development strategies focused on preserving its unique wildlife heritage.
Tourist Attractions and Safaris
Ecotourism in Namibia, centered around its iconic lion populations, significantly contributes to the local economy by attracting eco-conscious travelers eager to experience the country’s unique wildlife. Tourism related to safaris and lion viewing offers a sustainable way to generate revenue while supporting conservation efforts. Tourist attractions like Etosha National Park and private game reserves provide natural habitats for lions and other wildlife, drawing visitors from around the world. These safaris not only provide extraordinary wildlife encounters but also foster awareness about the importance of protecting Namibia’s rich biodiversity, ultimately fueling economic growth through job creation, infrastructure development, and local businesses.
Economic Benefits to Local Communities
Ecotourism in Namibia, particularly centered around lions, offers significant economic benefits to local communities. By attracting tourists interested in wildlife and conservation, ecotourism creates alternative income sources beyond traditional industries like agriculture or mining. Local residents often participate as guides, hospitality providers, and artisans, thereby generating employment opportunities and fostering entrepreneurship. This influx of visitors boosts small businesses and enhances infrastructure development, directly contributing to community development. Additionally, revenue generated through park entrance fees and tours can be reinvested into conservation efforts and community projects, ensuring sustainable benefits. Overall, ecotourism in Namibia’s lion habitats creates a positive economic loop that supports both conservation and local livelihoods.
Sustainable Tourism Practices
Ecotourism in Namibia, particularly around the habitats of lions, plays a significant role in promoting sustainable tourism practices that benefit both wildlife conservation and local economies. By focusing on responsible travel, ecotourism helps protect Namibia’s unique ecosystem while providing economic opportunities for communities living near lion habitats.
The economic impact of lion ecotourism in Namibia is substantial, attracting travelers from around the world who are eager to witness these majestic animals in their natural environment. Revenue generated from tourism supports conservation efforts, fund local development projects, and create jobs, contributing to a sustainable and resilient economy.
Sustainable tourism practices in Namibia emphasize minimizing environmental footprints, engaging local communities in conservation activities, and educating visitors about the importance of protecting lion populations. Initiatives such as community-based conservation projects ensure that tourism benefits are equitably distributed, fostering a sense of ownership and stewardship among residents and fostering long-term ecological sustainability.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
The future outlook for lions in Namibia presents both opportunities and challenges that will shape conservation efforts moving forward. As one of Africa’s key habitats for wild lions, Namibia holds a crucial role in sustaining these majestic predators. Strategic recommendations focus on strengthening protected areas, fostering community involvement, and implementing innovative conservation techniques to ensure the long-term survival of lion populations in the region.
Research and Monitoring Needs
The future outlook for lions in Namibia presents both opportunities and challenges that require strategic planning and sustained conservation efforts. As habitat loss and human-wildlife conflict continue to pose threats, implementing adaptive management practices and expanding protected areas are essential to ensure the long-term viability of lion populations. Promoting community-based conservation programs can foster local stewardship and reduce negative interactions with livestock, helping to secure ecological balance.
Recommendations for future actions include strengthening anti-poaching initiatives, enhancing habitat connectivity through wildlife corridors, and supporting research that informs evidence-based policies. Collaboration among government agencies, non-governmental organizations, local communities, and international partners is vital for advancing conservation goals. Engaging in public awareness campaigns can also garner support and promote coexistence strategies.
Research and monitoring needs must focus on understanding lion population dynamics, their genetic diversity, and ecological requirements within Namibian landscapes. Establishing comprehensive monitoring systems using technology such as GPS collaring and camera traps will enable real-time data collection. Additionally, studying the impacts of climate change on prey availability and habitat conditions can inform adaptive management strategies to mitigate future risks. Continuous research efforts are crucial to adapt conservation practices effectively and ensure the sustainable future of lions in Namibia.
Policy and Management Strategies
The future outlook for lions in Namibia remains cautiously optimistic, provided that effective conservation efforts are sustained and enhanced. As one of Africa’s key lion habitats, Namibia has made significant progress in protected area management, but threats such as poaching, human-wildlife conflict, and habitat degradation continue to pose challenges. Addressing these issues through innovative policies and community engagement is essential to ensure the long-term survival of lion populations in the region.
Policy strategies should prioritize the strengthening of anti-poaching measures, including increased patrols and technological surveillance. Implementing strict enforcement of wildlife laws and promoting regional cooperation can help curb illegal hunting and trafficking. Additionally, fostering community-based conservation programs that benefit local communities economically and socially can reduce human-wildlife conflict and incentivize residents to participate in safeguarding lions.
Management strategies should focus on habitat preservation and connectivity, ensuring lions have access to sufficient prey and territory. Integrating scientific research with adaptive management practices can enhance decision-making processes. Moreover, promoting ecotourism and sustainable utilization of lion-related resources can generate revenue that supports conservation initiatives while providing alternative livelihoods for local populations.
Overall, a coordinated approach involving government policy, community participation, scientific research, and international support is critical for securing a resilient future for lions in Namibia. Continued commitment and proactive management will be key to maintaining healthy lion populations and preserving Namibia’s rich biodiversity for generations to come.
Community Engagement and Education
The future outlook for lion conservation in Namibia remains cautiously optimistic, provided that ongoing efforts to protect habitats and mitigate human-wildlife conflict are sustained and strengthened. Recommendations include expanding protected areas, enhancing anti-poaching measures, and fostering partnerships with local communities to promote coexistence. Community engagement is vital, as involving residents in conservation initiatives can lead to more effective safeguarding of lion populations. Education programs should focus on raising awareness about the ecological importance of lions and promoting community-led initiatives that benefit both wildlife and local livelihoods. By fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility among communities, Namibia can ensure the long-term survival of its iconic lions for future generations.




0 Comments