Historical Background of Edfu Temple
The Edfu Temple, also known as the Temple of Horus, is one of the most well-preserved and significant religious monuments in Egypt. Located on the west bank of the Nile River in Edfu, it dates back to the Ptolemaic period, approximately 237 BCE to 57 BCE. Built during the Hellenistic era, the temple showcases a blend of traditional Egyptian architecture and Greek influences, reflecting the cultural fusion of the time. Its construction was dedicated to Horus, the falcon-headed god, and it played a vital role as a religious and cultural center in ancient Egypt, contributing to our understanding of Egyptian history and mythology.
Origins and Founding
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is one of the most well-preserved and significant ancient temples dedicated to the falcon-headed god Horus. Its historical background dates back to ancient times, reflecting the religious and cultural achievements of the Ptolemaic period, as well as earlier influences from the New Kingdom era.
The origins of the Edfu Temple can be traced to the Ptolemaic Dynasty, around the 3rd century BCE, when the construction of the current structure was initiated. However, the site itself was sacred long before this period, with earlier temples built on the same location during the Middle and New Kingdoms. The earliest known temple at Edfu was dedicated to Horus and dates back to approximately 237 BCE. Over centuries, successive rulers expanded and renewed the temple, culminating in its grand form seen today.
Founding and Development
- Initial Religious Site: The worship of Horus at Edfu dates back to Pharaonic Egypt, with evidence of earlier structures built during the Middle Kingdom (circa 2000–1700 BCE).
- Hellenistic Period: The predominant construction of the current temple occurred during the Ptolemaic Dynasty (332–30 BCE), emphasizing the importance of Horus and integrating Hellenistic artistic influences.
- Major Renovations: Over the centuries, various Egyptian Pharaohs and Ptolemies contributed to the expansion and decoration of the temple, including intricate reliefs and inscriptions detailing mythological narratives.
Historical Significance in Ancient Egypt
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is one of the most well-preserved and significant ancient Egyptian temples, dedicated primarily to the falcon-headed god Horus. Its construction dates back to the Ptolemaic period, initiated around 237 BCE and completed approximately 57 BCE. The temple’s strategic location along the Nile and its impressive architecture reflect the importance of religious practices during this era.
Historically, the Edfu Temple served as a major religious center in ancient Egypt, symbolizing the divine authority of Horus and integrating local mythologies with state ideology. Its construction expanded upon earlier religious sites devoted to the same deity, emphasizing the continuity and evolution of Egyptian religious traditions.
- Built predominantly during the Ptolemaic Dynasty, representing a fusion of Egyptian tradition and Hellenistic influence.
- Dedicated to Horus, the divine protector of the pharaoh, reinforcing the divine legitimacy of rulers.
- Served as a focal point for religious ceremonies, festivals, and offerings dedicated to Horus and other deities.
- The detailed hieroglyphic inscriptions and extensive reliefs provided valuable insights into religious practices, mythology, and administrative details of ancient Egypt.
- Its construction reflects the technological and artistic achievements of ancient Egyptian civilization during the late period.
Overall, the Edfu Temple’s historical significance lies not only in its architectural grandeur but also in its role as a cultural and religious symbol that exemplifies the enduring spiritual traditions of ancient Egypt. Its preservation offers scholars a window into the religious life and political ideology of a civilization that profoundly influenced subsequent cultures.
Key Historical Events and Renovations
The Edfu Temple in Egypt, dedicated to the falcon god Horus, dates back to the Ptolemaic period, approximately 237 BC to 57 BC. It was constructed during the reign of Ptolemy III and Ptolemy XII, serving as a major religious center in the region. The temple is one of the best-preserved ancient Egyptian temples and provides invaluable insights into religious practices and architecture of the time. Historically, the site was significant as a focal point for the worship of Horus, symbolizing protection and kingship in Egyptian mythology.
Throughout its history, the Edfu Temple underwent several key events and renovations. In antiquity, it was a site of religious festivals dedicated to Horus, attracting pilgrims from across Egypt. The temple was later rediscovered in the 19th century, leading to extensive excavations and restoration efforts. Major renovations occurred during the 20th century, especially after the 1960s when the temple was threatened by the construction of the Aswan High Dam, which led to the relocation of many monuments. Today, Edfu Temple remains a crucial archaeological site, illustrating the grandeur of Ptolemaic Egyptian architecture and religious life.
Architectural Features of Edfu Temple
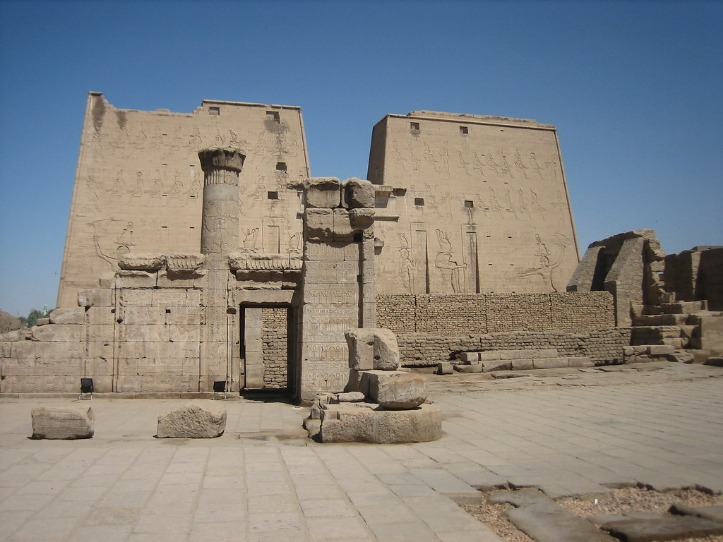
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is a remarkable example of ancient Egyptian architecture, renowned for its well-preserved design and intricate details. This monumental structure showcases the grandeur of classical Egyptian temple construction, featuring massive stone walls, towering pylons, and beautifully carved reliefs. Its strategic layout and elaborate decoration reflect the religious significance and artistic achievements of the period, making it a captivating site for understanding ancient Egyptian architectural prowess.
Overall Layout and Structure
The Temple of Edfu in Egypt is a remarkable example of ancient Egyptian architecture, renowned for its well-preserved structure and intricate design. Its overall layout follows the typical plan of a New Kingdom temple, with a sequence of courtyards, halls, and sanctuaries aligned along a central axis. The temple complex is surrounded by massive mudbrick walls, which enclose the sacred precinct and separate it from the outside world.
The entrance to the Edfu Temple is marked by a colossal pylon adorned with elaborate carvings and inscriptions, leading visitors into the first courtyard. Beyond this, a series of hypostyle halls with tall, closely spaced columns creates a grand procession route towards the inner sanctuaries. The architecture features towering colonnades that support lintels and ceilings decorated with detailed hieroglyphic reliefs and mythological scenes.
The central sanctuary houses the primary cult statue of Horus and is shielded by massive doors, emphasizing its sacred nature. Flanking the main areas are subsidiary chambers, storerooms, and chapels dedicated to various deities. The entire structure is meticulously designed, with drainage systems and specialized architectural elements ensuring stability and durability. Overall, the architecture of Edfu Temple reflects the grandeur, religious significance, and advanced engineering skills of ancient Egypt, making it one of the most impressive and well-preserved temples in Egypt today.
The Path from Outer Courtyard to Inner Sanctum
The pathway from the outer courtyard to the inner sanctum of Edfu Temple showcases remarkable architectural features that emphasize grandeur and religious significance. As visitors proceed inward, they encounter a series of pylons and gateways adorned with detailed hieroglyphic inscriptions and carved reliefs depicting gods, pharaohs, and mythological scenes. The transition along this path highlights the symbolic journey from the mundane world to the sacred inner sanctum, often marked by a narrow, increasingly elaborate corridor that guides worshippers. The construction employs massive sandstone blocks and precise masonry, reflecting the advanced engineering skills of ancient Egypt. Decorative elements such as columns with lotus and papyrus capitals line the pathway, contributing both structural support and aesthetic beauty. Overall, this route exemplifies the careful religious and architectural planning dedicated to creating a spiritual ascent towards the divine within the temple complex.
Notable Architectural Elements and Decorations
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is renowned for its impressive architectural features and elaborate decoration, which reflect the grandeur of ancient Egyptian religious structures. It stands as one of the best-preserved temples and showcases intricate craftsmanship and symbolic artistry.
Notable Architectural Elements and Decorations in Edfu Temple
- Pylon Entrance: A massive gateway with hieroglyphic inscriptions, leading into the temple complex and symbolizing the transition from the mundane to the sacred.
- Hypostyle Halls: Large halls supported by towering columns adorned with detailed carvings and hieroglyphs depicting gods, kings, and mythological scenes.
- Reliefs and Carvings: Extensive stone carvings depicting mythological narratives, rituals, and divine figures, exemplifying high craftsmanship.
- Inner Sanctuary: The most sacred area housing the statue of the god Horus, decorated with inscriptions and symbolic iconography.
- Column Capitals: Capitals designed as lotus, papyrus, and palm motifs, representing fertility and rebirth.
- Obelisks: Tall, tapering stone monuments situated at the entrance, inscribed with hieroglyphs dedicated to the gods and pharaohs.
- Ceiling Decorations: Intricate painted ceiling panels that depict celestial themes and divine symbols, enhancing the sacred atmosphere.
Religious Significance of Edfu Temple
The Edfu Temple in Egypt holds immense religious significance as one of the best-preserved ancient temples dedicated to the falcon-headed god Horus. Serving as a vital site for religious rituals and ceremonies, it reflects the spiritual beliefs and divine worship practices of ancient Egypt. The temple’s intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions and grand architecture exemplify its importance as a center of religious life and devotion for centuries.
Dedication to Horus
The Edfu Temple in Egypt holds immense religious significance as one of the best-preserved and most important temples dedicated to the ancient Egyptian god Horus. Located on the west bank of the Nile, it served as a major center of worship for Horus, symbolizing protection, kingship, and divine authority. The temple’s grand scale and intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions reflect its role in religious rituals and its importance in promoting the mythological lineage of Horus and his father Osiris, reinforcing the divine legitimacy of pharaohs.
The dedication to Horus at Edfu highlights the god’s association with the sky, kingship, and victory over evil. The temple’s architecture, including its massive pylon, hypostyle hall, and sanctuaries, was designed for religious ceremonies and processions honoring Horus. Key mythological themes, such as the reconciliation of Horus and Seth, were reenacted through rituals conducted within the temple, emphasizing its function as a sacred space where divine stories and royal power were reaffirmed.

Throughout ancient history, Edfu Temple served as a vital religious hub, hosting festivals such as the Ptolemaic Festival of Horus, which celebrated the divine birth and kingship of Horus. Its religious significance extended beyond worship, influencing cultural and political aspects of Egyptian society, and cementing its status as a spiritual center that embodied the divine protection and eternal sovereignty represented by Horus.
Role in Ancient Egyptian Religion and Festivals
The Edfu Temple, also known as the Temple of Horus, holds profound religious significance in ancient Egyptian culture. Dedicated to Horus, the falcon-headed god of kingship and protection, it served as a major religious center where rituals and ceremonies honored the divine protector of Egypt. The temple’s design and decorations reflect the theological beliefs of the time, emphasizing the divine authority of the ruler and the everlasting power of Horus.
In ancient Egyptian religion, Edfu Temple played a central role in the worship of Horus, symbolizing the divine connection between the gods and the pharaoh. It was a site for religious festivals, especially the annual Festival of Horus, which celebrated the mythological victory of Horus over Seth, symbolizing the triumph of order over chaos. This festival involved processions, offerings, and rituals performed by priests to ensure the continued favor of the gods and the stability of the land.
Furthermore, the temple was a place for sacred rites related to the coronation of new pharaohs, who would perform purification ceremonies to legitimize their rule. The inscriptions and reliefs inside the temple depict mythological stories, religious rituals, and hymns, reflecting the importance of maintaining maat — cosmic order — through divine worship. Overall, Edfu Temple was not only a religious sanctuary but also a cultural hub that reinforced the divine authority of the Egyptian state and its religious beliefs.
Religious Rituals Performed at the Temple
The Edfu Temple in Egypt holds profound religious significance as a major sanctuary dedicated to the ancient Egyptian god Horus, symbolizing protection, kingship, and divine authority. It served as a vital religious center where the deity was worshipped, embodying the mythological struggle between Horus and Seth, which represented the triumph of order over chaos. The temple’s architecture and inscriptions reflect its role as a sacred site for divine homage and spiritual rites.
Numerous religious rituals were performed at Edfu Temple to honor Horus and seek his blessings. Priests conducted daily ceremonies that included offerings of food, incense, and symbolic objects to the deity’s statues. Major festivals, such as the Heb-Sed festival, involved elaborate processions, prayers, and ritual purification aimed at rejuvenating the divine king and reinforcing cosmic order. Sacred rites also involved chanting of hymns, recitations of sacred texts inscribed on the temple walls, and processions that reinforced the mythological themes central to Horus’s divine reign. These rituals not only maintained the spiritual well-being of the community but also reinforced the divine legitimacy of the pharaoh as Horus incarnate on earth.
Art and Inscriptions within Edfu Temple
Edfu Temple in Egypt is renowned for its exceptional well-preserved architecture and rich cultural heritage, particularly its intricate art and inscriptions. These inscriptions, carved into the temple walls, offer valuable insights into ancient Egyptian religion, mythology, and history. They serve as a vital link to understanding the beliefs and practices of the bygone era, making Edfu Temple a remarkable monument of antiquity.
Reliefs and Wall Paintings
The Temple of Edfu in Egypt is renowned for its intricate Art and Inscriptions that provide a rich visual and textual narrative of ancient Egyptian religion and mythology. These artistic elements are primarily found on reliefs and wall paintings that adorn the temple’s walls, offering insights into religious rituals, deities, and historical events.
The reliefs within Edfu Temple are highly detailed and meticulously carved, depicting scenes of gods, pharaohs, and ceremonial practices. They serve both decorative and informative purposes, illustrating mythological stories such as the battle between Horus and Seth, and highlighting the divine authority of the pharaohs who commissioned the temple.
Wall paintings add a vibrant dimension to the temple’s artwork, utilizing vivid colors and compositional techniques unique to ancient Egyptian artistry. These paintings often depict offerings, processions, and sacred symbols, reinforcing the religious significance of the space and providing instructions for rituals.
- Inscriptions in Edfu are primarily hieroglyphic texts that record religious spells, dedications, and historical accounts, often accompanying the visual reliefs to enhance their meaning.
- The temple’s inscriptions include references to the gods Horus and Hathor, emphasizing their importance in local worship and mythological stories.
- These texts also contain details about the construction, restorations, and the patronage of the temple by various pharaohs.
Hieroglyphic Inscriptions and Their Meanings
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is renowned not only for its impressive architecture but also for the extensive hieroglyphic inscriptions that adorn its walls. These inscriptions provide valuable insights into ancient Egyptian religion, mythology, and history, serving as a record of the gods worshiped and the rituals performed at the temple. The carvings and inscriptions are key to understanding the cultural and spiritual life of ancient Egypt, making Edfu a vital archaeological site.
The hieroglyphic inscriptions within Edfu Temple are composed of sacred texts, prayers, hymns, and descriptions of religious ceremonies. They often depict gods such as Horus and Hathor, along with scenes of offerings and divine ceremonies. These texts were meticulously inscribed by priests and scribes to preserve the sacred knowledge and ensure the proper conduct of rituals.
- The inscriptions serve as a theological vocabulary, illustrating the roles and relationships of various gods in Egyptian mythology.
- They act as historical records, offering dates and accounts of significant events related to the temples and their worshippers.
- The inscriptions include spells and rituals meant to protect the temple and its rituals from evil and chaos, reflecting the spiritual beliefs of the time.
Understanding these inscriptions helps scholars decipher the language, religious practices, and societal organization of ancient Egypt. The inscriptions at Edfu, therefore, are not only artistic expressions but also crucial historical and spiritual documents that deepen our knowledge of Egypt’s rich cultural heritage.
Depictions of Mythological Events
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is renowned for its remarkable artistry and detailed inscriptions that provide valuable insights into ancient Egyptian religion and mythology. The walls and columns are adorned with intricate carvings and hieroglyphic texts that depict various mythological events, emphasizing the divine origins and kingship narratives associated with the gods, particularly Horus and Hathor.
Within the temple, inscriptions narrate mythological stories such as the struggle between Horus and Seth, symbolizing the eternal conflict between order and chaos. These depictions often show gods in symbolic battles, triumphs, and divine interventions, offering a visual and textual representation of myth that was central to Egyptian religious practice and belief systems.
The art within the Edfu Temple serves not only as decoration but as a theological record that communicates complex stories of gods and their interactions with humans. These mythological scenes were designed to convey spiritual truths and ensure the perpetuation of religious traditions, making the temple an essential cultural and religious monument in ancient Egypt.
Archaeological Discoveries and Excavations
The site of Edfu Temple in Egypt is one of the most remarkable archaeological discoveries, revealing the rich history and ancient craftsmanship of the Egyptian civilization. Excavations at Edfu have uncovered well-preserved temples, inscriptions, and artifacts that provide valuable insights into religious practices and societal structures of the time. These archaeological efforts continue to enhance our understanding of Egypt’s ancient legacy and attract historians and tourists alike.
Major Archaeological Finds
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is one of the most well-preserved and significant archaeological sites dating back to the Ptolemaic period. Excavations at the site have revealed intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions, religious artifacts, and stunning architectural details that offer insight into ancient Egyptian religion and culture. The discovery of the temple itself was a major archaeological find, shedding light on the religious practices dedicated to Horus, the falcon-headed god.
Major archaeological excavations at Edfu have uncovered a wealth of relics, including massive stone obelisks, inscribed columns, and religious murals that have helped scholars understand the grandeur of ancient Egyptian temple construction. These excavations also uncovered inscriptions that detail rituals, myths, and the history of the temple’s construction, dating back to the 2nd century BC.
The ongoing excavations and restoration efforts have led to the discovery of lesser-known structures and artifacts such as statues, scarabs, and everyday objects used by priests and worshippers. These findings contribute significantly to the understanding of ancient Egyptian religious practices, social hierarchy, and artistry. Such discoveries at Edfu continue to be invaluable in revealing the spiritual and cultural wealth of ancient Egypt, making it a major site of archaeological importance worldwide.
Recent Excavation Efforts
The Edfu Temple in Egypt, also known as the Temple of Horus, remains one of the most significant archaeological sites, offering valuable insights into ancient Egyptian religion and architecture. Recent excavation efforts have shed new light on the history and preservation of this remarkable monument, revealing previously hidden inscriptions and structural details.
- Ongoing excavation projects around the Edfu Temple have uncovered additional sections of the sacred complex, including underground chambers and ritual spaces that were previously inaccessible.
- Recent efforts have focused on restoring damaged sculptures and inscriptions, allowing scholars to better understand the religious practices and societal structure of the Ptolemaic period.
- Archaeologists have discovered fragments of ancient papyri and pottery nearby, which provide context for the ceremonial activities conducted at the temple.
- Advanced imaging technologies, such as ground-penetrating radar, have been employed to identify undisturbed areas beneath the temple, leading to potential future excavations.
- Further excavation campaigns aim to explore the nearby precincts, revealing more about the urban landscape surrounding the temple during its prime operation.
Preservation and Restoration Projects
The Edfu Temple in Egypt is one of the most well-preserved and significant ancient archaeological sites, offering valuable insights into the religious and architectural practices of the Ptolemaic period. Archaeological excavations at Edfu have uncovered a wealth of detailed carvings, inscriptions, and structural remains that shed light on the worship of the falcon-headed god Horus. These discoveries continue to enhance our understanding of ancient Egyptian beliefs and ceremonial traditions.
Preservation and restoration efforts at the Edfu Temple have been crucial in maintaining its integrity amid environmental challenges and natural deterioration over centuries. Extensive projects have involved cleaning the stone surfaces, consolidating crumbling structures, and restoring fallen architectural elements to ensure the site remains accessible for both research and tourism. Modern techniques such as laser cleaning and non-invasive structural reinforcement have been employed to protect the monument while respecting its historical authenticity.
Ongoing excavations and excavation projects seek to uncover more about the temple complex’s surrounding area, including nearby chapels and courtyards. These efforts aim to complete the site’s reconstruction and provide a more comprehensive understanding of its religious functions. Preservation initiatives are also focused on safeguarding the carved hieroglyphs and inscriptions, which are invaluable for linguistic and cultural studies.
International collaborations and funding have played a vital role in supporting the archaeological and restoration work at Edfu. These projects ensure the safeguarding of this iconic monument against environmental threats and vandalism, allowing future generations to appreciate its historical and cultural significance. Continuous research and conservation efforts are essential for preserving Edfu Temple as a symbol of Egypt’s ancient heritage and a testament to human craftsmanship.
Visiting Edfu Temple Today
Visiting Edfu Temple today offers a fascinating glimpse into ancient Egyptian history and architecture. Located along the Nile River, this well-preserved temple dedicated to the falcon-headed god Horus is one of the most impressive religious sites in Egypt. As you explore its majestic colonnades, intricate carvings, and sacred sanctuaries, you’ll discover the rich cultural and spiritual significance of this ancient monument.
Tourist Information and Access
Visiting the Edfu Temple in Egypt offers an incredible glimpse into ancient Egyptian history and architecture. Located along the Nile River, this well-preserved temple is a major attraction for tourists interested in Egypt’s religious and cultural heritage.
To access Edfu Temple, visitors typically travel from Aswan or Luxor, with guided tours and boat cruises often including a stop at the site. The temple is open daily, allowing tourists ample opportunity to explore its magnificent hieroglyphs, reliefs, and the impressive Horus falcon deity dedication.
- Getting There: Edfu is accessible by train, car, or organized tours from major cities like Aswan and Luxor.
- Entry Fees: There is a standard entrance fee, with additional charges for guided tours or photography.
- Best Time to Visit: The cooler months from October to April are ideal for outdoor explorations.
- Facilities: Basic amenities such as restrooms, a small gift shop, and a café are available near the entrance.
- Tips for Tourists: Wear comfortable shoes, stay hydrated, and consider hiring a local guide for a more enriching experience.
Tips for Visitors
Visiting Edfu Temple in Egypt offers a unique opportunity to explore one of the best-preserved ancient temples of the Ptolemaic period dedicated to Horus, the falcon-headed god. To make the most of your visit, plan your trip early in the morning to avoid crowds and the midday heat. Wearing comfortable clothes, sun protection, and sturdy walking shoes is essential for exploring the expansive site. Remember to carry water and a camera to capture the intricate hieroglyphs and impressive carvings that adorn the temple walls. Guided tours can enhance your understanding of the temple’s rich history and symbolism, so consider hiring a knowledgeable guide. Respect the site by not touching or defacing the monuments, and be mindful of the local customs and regulations. Visiting Edfu Temple promises an unforgettable glimpse into Egypt’s divine past, so take your time to appreciate its detailed architecture and spiritual significance.
Protecting and Preserving the Site
Visiting Edfu Temple in Egypt offers a remarkable glimpse into ancient Egyptian history and architecture. This well-preserved temple, dedicated to the falcon-headed god Horus, attracts numerous travelers eager to explore its impressive hieroglyphs and detailed carvings.
To ensure Edfu Temple remains a historical treasure for future generations, protecting and preserving the site is essential. Restoration efforts are carefully managed by archaeologists and conservation specialists to address weathering, pollution, and tourism-related wear. Visitors are encouraged to follow guidelines, refrain from touching or damaging the carvings, and avoid disturbing the site’s delicate structures.
Educational programs and visitor awareness campaigns play a vital role in promoting respect and understanding of the temple’s cultural significance. Additionally, sustainable tourism practices, such as limiting access to sensitive areas and implementing strict regulations, help safeguard this iconic symbol of Egypt’s ancient civilization.




0 Comments