Geographical Overview of the Algerian Desert
The Algerian Desert, a vast and captivating landscape, forms a significant part of the Sahara Desert, extending across southern Algeria. Characterized by sprawling sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and remote oases, this arid region boasts extreme temperatures and minimal precipitation. Its diverse terrain supports unique ecosystems and traditional nomadic lifestyles, making it a crucial aspect of Algeria’s geographical identity and natural heritage.
Location and Extent
The Algerian Desert, part of the vast Sahara Desert, covers a significant portion of southern Algeria and plays a crucial role in the country’s geographical landscape. It is characterized by its expansive arid plains, towering sand dunes, and rugged mountain ranges, creating a diverse and challenging environment. This desert region extends across a large area, influencing the climate, ecosystem, and human activities within Algeria.
- The Algerian Desert is primarily situated in the southern part of the country, bordering Libya, Niger, Mali, and Mauritania.
- It spans approximately 1.3 million square kilometers, making it one of the largest deserts in Africa and the world.
- The region includes notable features such as the Grand Erg Oriental, a vast sea of sand dunes, and the Tademait Plateau.
- Its geographical extent is marked by extreme temperatures, scarce rainfall, and unique geological formations that vary from flat plains to mountainous zones.
- The desert’s location influences strategic, economic, and ecological aspects of Algeria, serving as a vital but inhospitable landscape.
Topographical Features
The Algerian desert, primarily part of the vast Sahara, spans a significant portion of southern Algeria, showcasing an expansive arid landscape characterized by diverse topographical features. This region features extensive sand dunes, rocky plateaus, mountain ranges, and vast gravel plains, creating a unique and rugged terrain. The Sahara’s massive sand dunes, some reaching heights of over 180 meters, dominate the landscape and are among the most iconic features of the Algerian desert. Surrounding these dunes are rugged mountainous areas, including the Ahaggar Mountains with the impressive Mount Tahat, which is the highest point in Algeria. The Tassili n’Ajjer plateau, renowned for its extraordinary rock formations and prehistoric cave paintings, adds to the topographical diversity. Additionally, the landscape encompasses vast gravel plains, such as the Grand Erg Oriental and Grand Erg Occidental, which are huge dune seas that stretch across the desert. These features contribute to the desert’s extreme climatic conditions and make it a region of significant geographical interest and variety.
Climate and Temperature Ranges
The Algerian Desert, predominantly part of the Sahara Desert, covers a vast expanse in southern Algeria, representing one of the most expansive arid regions in the world. It features a diverse landscape composed of sand dunes, rocky plateaus, gravel plains, and occasional oases that provide vital water sources for local flora, fauna, and human settlements. The desert’s geography varies from high mountain ranges and depressions to expansive flat plains, creating a uniquely striking environment.
The climate in the Algerian Desert is characterized by extreme aridity and significant temperature fluctuations. It experiences very low annual rainfall, often less than 100 millimeters, contributing to its desert classification. Summers are intensely hot, with daytime temperatures frequently soaring above 40°C (104°F), while nights can be markedly cooler. In contrast, winter temperatures can drop significantly, especially in elevated areas, sometimes approaching 0°C or below during cold spells. This combination of high daytime heat and cooler nights defines the harsh, yet fascinating, climate of the Algerian Desert.
Major Deserts and Regions
Algeria is home to some of the most extensive and diverse desert regions in the world, primarily dominated by the Sahara Desert. These major deserts feature vast, arid landscapes characterized by towering dunes, rocky plateaus, and unique ecosystems. Understanding the key desert areas within Algeria provides insight into the country’s geographic and climatic diversity, highlighting both natural beauty and environmental challenges.
Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert is the largest hot desert in the world, covering much of North Africa, including a significant portion of Algeria. It stretches across multiple countries and is renowned for its vast, arid landscape, extreme temperatures, and unique ecosystems. In Algeria, the Sahara dominates the southern part of the country, forming a key feature of the region’s geography. The desert region is characterized by extensive sand dunes, rocky plateaus, and sparse vegetation, making it one of the most inhospitable yet captivating environments on Earth. Despite its harsh conditions, the Sahara in Algeria is home to various adapted wildlife and nomadic communities who have historically thrived in this challenging landscape. The desert also holds important cultural and historical significance, with ancient caravan routes and archaeological sites dotted across its vast expanses.
Grand Erg
The Algeria desert is renowned for its vast and diverse arid landscapes, primarily dominated by major deserts and regions that define its geographical identity. One of the most significant features is the Grand Erg, a massive field of sand dunes stretching over large parts of the Sahara desert within Algeria. The Grand Erg is characterized by towering, golden dunes that can reach heights of over 180 meters, creating a mesmerizing and iconic desert scenery. Alongside the Grand Erg, Algeria hosts other notable desert regions such as the Sahara proper, which encompasses a variety of terrains including rocky plateaus, gravel plains, and sparse oases. These deserts play a crucial role in shaping the climate, ecology, and culture of the region, attracting explorers, researchers, and tourists eager to experience their stark beauty and vastness.
Fezzan and Tanezrouft
Algeria is home to some of the most extensive and challenging desert regions in the world, with the Sahara Desert covering the vast majority of its territory. Within this immense desert landscape, several major desert regions stand out for their unique geographical and cultural significance, including Fezzan and Tanezrouft. Fezzan, located in the southwestern part of Libya but closely associated with Algeria’s southern desert regions, is a desert basin characterized by sparse settlements, ancient ruins, and valuable archaeological sites. Tanezrouft, often referred to as the “Land of Thirst,” is known for its extreme aridity and one of the hottest, driest parts of the Sahara, stretching across southern Algeria and neighboring countries. These regions epitomize the harsh yet fascinating environment of the Algerian desert, showcasing its stark beauty and enduring human resilience amidst extreme conditions.

Unique Landforms and Landmarks
Algeria’s desert region is home to some of the most striking and unique landforms and landmarks found in the world. The vast Sahara Desert covers a significant portion of the country, showcasing awe-inspiring natural features such as towering sand dunes, rugged mountain ranges, and unusual rock formations. These extraordinary landforms not only define the landscape but also hold cultural and historical significance, making Algeria’s desert a fascinating destination for explorers and nature enthusiasts alike.
Ergs, Hamadas, and Oases
Algeria’s desert landscape is rich with diverse landforms and landmarks that highlight the beauty and complexity of the Sahara. Unique features such as ergs, hamadas, and oases are prominent in shaping the region’s geography and cultural significance. Ergs are vast seas of sand dunes that stretch across the desert, creating mesmerizing patterns and shifting shapes shaped by wind. Hamadas are elevated, flat, rocky plateaus that serve as stable surfaces amid the sandy terrain, often acting as natural barriers and habitats. Oases are lush, fertile spots scattered throughout the desert, providing vital water sources and supporting life in an otherwise arid environment. These landforms not only define Algeria’s desert scenery but also play crucial roles in the ecology and human settlements within this harsh yet captivating landscape.
Ajjer Mountain Range
The Ajjer Mountain Range, located in southeastern Algeria, is renowned for its stunning unique landforms and ancient landmarks. Rising dramatically from the desert landscape, Ajjer features striking sandstone formations, towering cliffs, and deep gorges that create a surreal and awe-inspiring scenery. This mountain range is also famous for its rich collection of prehistoric rock art, which depicts early human life and animals, providing valuable insights into ancient history. The landscape’s distinctive shapes and archaeological significance make Ajjer a vital natural landmark within the Algerian desert, attracting explorers, historians, and nature enthusiasts alike.
Richat Structure (Eye of the Sahara)
The Richat Structure, also known as the Eye of the Sahara, is a striking and unique landform located in the Sahara Desert of Algeria. This massive circular formation spans approximately 50 kilometers in diameter and is easily visible from space, making it a prominent landmark in the region. Its distinctive concentric rings are the result of geological processes involving erosion and uplift, revealing ancient rock layers and sedimentary formations. The structure’s unusual appearance has long intrigued scientists and explorers, serving as a natural landmark in the vast Algerian desert. As a notable geological feature, the Eye of the Sahara contributes to the desert’s diverse landscape, highlighting its rich natural history and the dynamic processes that shape landforms in extreme environments.
Hydrology and Water Resources
Hydrology and water resources play a vital role in shaping the environment and supporting life, especially in arid regions like the Algerian desert. In such harsh and dry landscapes, understanding the movement, distribution, and management of water is essential for sustainable development and survival. Despite the extreme dryness, innovative techniques and natural water systems help communities and ecosystems adapt to the challenging conditions of the Algerian desert.
Oases and Their Significance
In the vast and arid deserts of Algeria, hydrology and water resources play a crucial role in sustaining life and supporting human activities. The scarcity of surface water has led to the development of various techniques for managing underground aquifers and utilizing limited water sources efficiently. Oases are vital ecological and social hubs within the desert environment, acting as natural reservoirs of water that sustain plant, animal, and human populations. These green areas provide refuge from the harsh desert conditions, enabling agriculture, settlement, and trade to thrive. The significance of oases in Algeria extends beyond their ecological importance, as they are cultural landmarks with historical value, facilitating connectivity across desert regions. Effective management of water resources and the protection of oases are essential for ensuring sustainable development and resilience against desertification, contributing to the overall stability and well-being of communities in Algeria’s desert zones.
Underground Water Reserves
Algeria’s desert regions are characterized by vast, arid landscapes with limited surface water sources, making underground water reserves essential for sustaining ecosystems and human activities. These underground reserves, also known as aquifers, play a crucial role in providing water for agriculture, industry, and domestic use in the desert areas of Algeria.
In Algeria’s desert, groundwater is often the primary source of water due to the scarcity of surface water like rivers and lakes. The major underground water reserves are found in deep aquifers, which can span extensive areas and contain significant volumes of water stored in porous rock formations and sediments.
Management and sustainable use of these underground water resources are vital to prevent over-extraction, which can lead to issues such as land subsidence, groundwater salinization, and depletion of aquifer reserves. Techniques such as groundwater recharge and conservation practices are implemented to help preserve these vital resources.
- Importance of underground water reserves in sustaining desert ecosystems and human settlements
- Challenges of over-extraction leading to environmental and structural issues
- Need for sustainable water management practices in arid regions
- Use of geophysical surveys and drilling technology to locate and assess aquifer capacity
- Impact of climate variability and prolonged droughts on underground water levels
Impact of Drought and Climate Change
In Algeria, the vast deserts are significantly impacted by drought and climate change, leading to serious challenges in water resource management. The increasing variability in rainfall patterns causes prolonged dry spells, depleting surface water sources and reducing groundwater recharge. This results in water scarcity for both local communities and agricultural activities, threatening livelihoods and regional development.
Climate change intensifies these effects by raising temperatures and altering precipitation regimes, which accelerates evaporation rates and diminishes available freshwater supplies. Desert regions in Algeria face heightened risks of soil degradation and desertification, further diminishing the natural water retention capacity of the land. As a consequence, there is an urgent need for sustainable water management strategies, such as improved conservation, rainwater harvesting, and the development of resilient infrastructure to adapt to these environmental challenges.
Flora and Fauna
The deserts of Algeria are home to a diverse array of flora and fauna uniquely adapted to the harsh, arid environment. Despite the extreme conditions, many plants and animals have evolved fascinating survival strategies to thrive in this rocky landscape. Exploring the rich biodiversity of Algeria’s desert reveals a remarkable balance of life that sustains itself amid extreme heat, scarce water, and expansive sand dunes.
Adapted Plant Species
Deserts in Algeria, such as the Sahara, host a unique array of flora and fauna that have adapted to extreme conditions like high temperatures, arid soils, and scarce water resources. Many plant species have evolved to survive with minimal water, including drought-resistant shrubs and succulents such as Acacia trees, Date palms, and various cacti that store water in their tissues. These plants typically have deep root systems or protective features to reduce water loss.
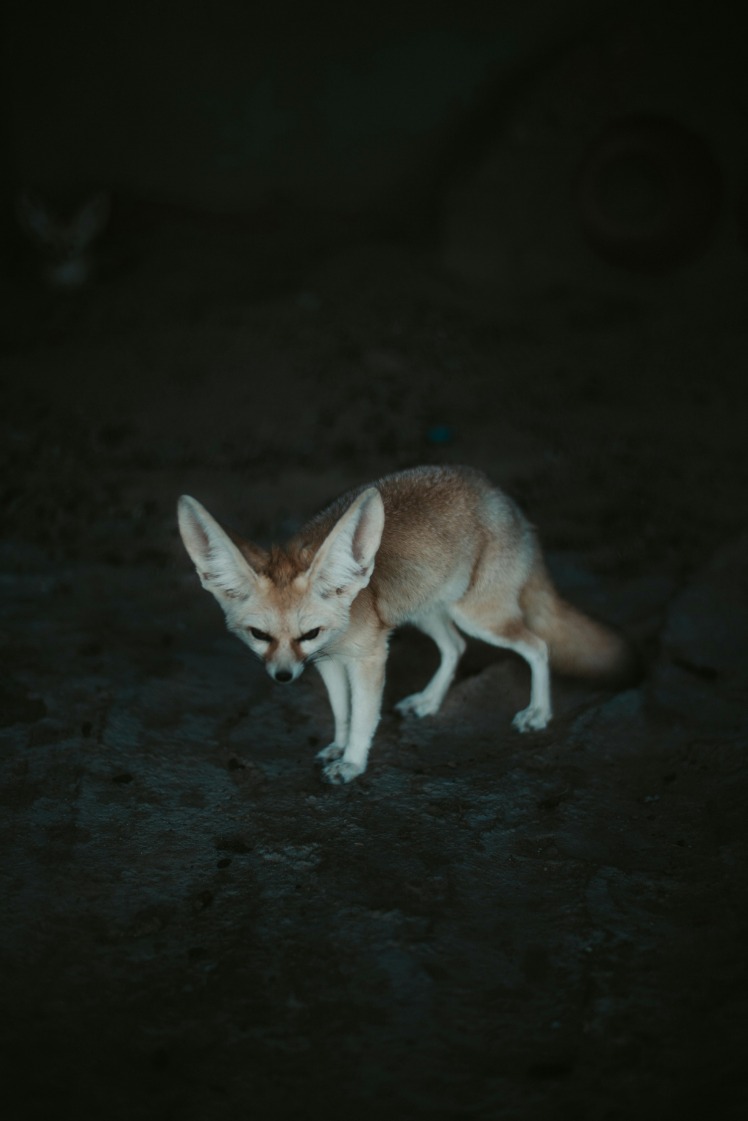
Fauna in the Algerian desert has also developed remarkable adaptations. For example, the fennec fox has large ears to dissipate heat and is active primarily at night to avoid daytime heat. The Saharan horned viper burrows underground to escape high surface temperatures and is capable of conserving water efficiently. Additionally, various insects, lizards, and small mammals have adapted to the harsh desert conditions by being nocturnal and conserving energy during the hottest periods.
Wildlife in the Desert Ecosystem
The Algerian desert, part of the vast Sahara region, hosts a unique and diverse range of flora and fauna adapted to the harsh arid environment. Vegetation is sparse and consists mainly of drought-resistant plants such as succulents, shrubs, and grasses that can survive extreme temperatures and minimal water availability. These plants play a vital role in preventing soil erosion and providing Shelter for various small animals.
The desert ecosystem of Algeria supports a variety of wildlife specially adapted to survive the extreme conditions. Notable species include the dromedary camel, which is well-suited for transportation and carrying loads across the desert. Small mammals like jerboas and fennec foxes have evolved to stay active during cooler nights, avoiding the heat of the day. Reptiles such as desert lizards and snakes are common, often blending into their surroundings for protection. Additionally, several bird species like desert hawks and sandgrouse are attracted to the oasis and scattered water sources, playing essential roles in the ecological balance.
Despite the extreme environment, the desert ecosystem in Algeria is rich with specialized wildlife that has evolved unique adaptations to thrive in this challenging landscape. Conservation efforts are crucial to preserve this fragile environment and sustain the biodiversity it supports.
Conservation Efforts
Algeria’s deserts are home to a unique array of flora and fauna adapted to the harsh, arid environment. Vegetation such as Acacia trees, Date palms, and drought-resistant shrubs sustain various animal species while preventing erosion and maintaining the ecosystem balance. Fauna includes uniquely adapted animals like the Addax antelope, desert foxes, and various reptile species, all of which play crucial roles in the desert’s ecological dynamics.
Conservation efforts in Algeria aim to protect these fragile ecosystems from threats such as desertification, overgrazing, and illegal hunting. Initiatives include establishing protected areas like the Ahaggar and Tassili n’Ajjer national parks, which serve as refuges for rare and endangered species. Additionally, environmental awareness campaigns and research programs help promote sustainable practices and restore degraded habitats, ensuring that the desert’s rich biodiversity endures for future generations.
Economic and Cultural Significance
The Algeria desert holds immense economic and cultural significance, serving as a vital region for the country’s natural resources and heritage. Its vast expanse not only contributes to Algeria’s economy through activities such as mineral extraction and tourism but also preserves a rich tapestry of cultural traditions and historical sites. Understanding the importance of this desert region offers insights into Algeria’s diverse identity and economic potential.
Tourism and Desert Expeditions
The deserts of Algeria hold substantial Economic and Cultural Significance, serving as vital resources and cultural heritage sites. Their unique landscapes attract a diverse range of tourists and explorers, contributing significantly to the country’s economy through tourism and desert expeditions.
Economically, the Algerian deserts are important for mineral and fossil fuel extraction, supporting local industries and providing employment. Culturally, they are home to ancient archaeological sites, traditional nomadic communities, and indigenous art, preserving the rich history and traditions of the region.
Tourism and desert expeditions play a crucial role in showcasing the natural beauty and cultural heritage of Algeria’s deserts. Visitors are drawn to the vast sand dunes, rocky formations, and historic sites, fueling local businesses and fostering international interest in the region.
- Desert safaris and guided tours exploring the Sahara and Hoggar Mountains
- Visits to historic sites such as Timgad and Djemila, showcasing Roman-era ruins
- Experiences with nomadic cultures and their traditional lifestyles
- Adventure activities including camel trekking, sandboarding, and stargazing
- Ecotourism initiatives aimed at preserving the fragile desert ecosystem
Nomadic Cultures and Traditions
The deserts of Algeria, particularly the Sahara, hold profound economic and cultural significance rooted in the nomadic cultures that have thrived there for centuries. These regions serve as vital zones for pastoralism, enabling nomadic tribes to sustainably graze livestock such as camels and goats, which are integral to their livelihood and sustenance. The desert economy is also complemented by mineral and fossil fuel resources, which contribute to Algeria’s broader economic framework. Culturally, the nomadic tribes of the Algerian desert uphold rich traditions, including intricate embroidery, music, dance, and oral storytelling, that reflect their history, values, and relationship with the harsh environment. Their customs emphasize mobility, resourcefulness, and resilience, which continue to be passed down through generations, preserving a unique cultural identity deeply intertwined with the desert landscape. These nomadic cultures not only symbolize the enduring spirit of adaptation but also contribute to Algeria’s diverse cultural heritage, attracting interest from scholars and travelers worldwide.
Mining and Natural Resources
The Algerian Desert, primarily composed of the vast Sahara, holds substantial economic and cultural significance due to its abundant natural resources and historical heritage. Rich in minerals such as zinc, lead, iron ore, and vermiculite, the desert region contributes significantly to Algeria’s mining sector, supporting both local industries and export markets. Additionally, the desert’s vast oil and gas reserves underpin the country’s economy, making Algeria one of Africa’s leading energy producers.
Culturally, the Algerian Desert is home to ancient Berber and Arab communities, whose traditions and lifestyles have been shaped by the harsh yet captivating environment. The desert’s archaeological sites, including rock art and historic trade routes, offer insights into early nomadic cultures and their interactions across North Africa. These cultural elements, combined with the region’s stunning landscapes, attract tourism and foster national identity tied to resilience and heritage.
Challenges and Preservation
The vast and captivating Algerian desert presents unique challenges for language preservation, as the diverse communities living in this harsh environment rely on their linguistic heritage to maintain cultural identity. Harsh conditions and geographic isolation often threaten the continuity of traditional languages and dialects, making preservation efforts crucial. Exploring these challenges highlights the importance of safeguarding linguistic diversity amid the evolving landscape of the Algerian desert region.

Environmental Concerns
The Algerian desert presents unique challenges and opportunities for preservation amid growing environmental concerns. The vast Sahara region in Algeria faces threats from climate change, desertification, and human activities such as mining and infrastructure development. These issues threaten the delicate ecosystems and the traditional lifestyles of indigenous communities. Preservation of the desert’s natural landscapes and biodiversity requires coordinated efforts to combat land degradation and promote sustainable practices. Additionally, protecting archaeological sites and cultural heritage within the desert is vital to maintaining Algeria’s historical identity. Environmental concerns necessitate a balance between economic development and conservation, ensuring the desert’s ecological integrity is maintained for future generations.
Desertification and Human Impact
The Algerian desert faces significant challenges related to desertification and human impact, threatening its fragile ecosystem and local communities. Human activities such as overgrazing, deforestation, and unsustainable agricultural practices exacerbate soil degradation and reduce vegetation cover, accelerating the process of desertification. Climate change also plays a role, causing irregular rainfall and rising temperatures that further dry out the land. This ongoing deterioration not only endangers native flora and fauna but also compromises the livelihoods of populations dependent on the land for grazing and agriculture. Preservation efforts focus on implementing sustainable land management practices, reforestation projects, and raising awareness to combat desertification. It is essential to balance development with environmental conservation to ensure the resilience of Algeria’s desert regions for future generations.
Strategies for Sustainable Management
The Algerian desert faces numerous challenges in balancing development and conservation efforts. Increasing industrial activity, urban expansion, and tourism put additional pressure on fragile ecosystems, leading to habitat loss, desertification, and biodiversity decline. Climate change exacerbates these issues by causing unpredictable weather patterns, reducing water availability, and intensifying droughts. Preserving this unique environment requires strategic approaches that promote sustainable management practices.
Implementing environmental protection policies is essential to mitigate degradation. This includes establishing protected areas and restoring degraded lands through afforestation and soil conservation techniques. Promoting renewable energy projects, such as solar power, can reduce reliance on non-renewable resources and minimize environmental impacts. Education and awareness campaigns are vital to engaging local communities in conservation efforts and fostering sustainable tourism practices.
Furthermore, integrating traditional knowledge with modern scientific approaches offers innovative solutions for managing desert ecosystems. Developing sustainable water management systems, such as drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, can enhance resource efficiency. Regional cooperation and international support are also crucial in funding conservation initiatives and facilitating knowledge exchange. Ultimately, a comprehensive strategy that combines ecological, social, and economic considerations will help preserve Algeria’s desert for future generations while supporting sustainable development.




0 Comments