Historical Background of Capital Cities in Egypt
Egypt’s capital cities have a rich historical background that reflects the country’s long-standing significance as a center of culture, politics, and civilization. Throughout the centuries, various cities have served as political hubs, from ancient capitals like Memphis and Thebes to modern administrative centers such as Cairo. These cities have witnessed the rise and fall of empires, shaping Egypt’s identity and development over millennia. Exploring this historical evolution provides insight into the nation’s dynamic past and its ongoing importance in the region.
Ancient Egyptian Capitals
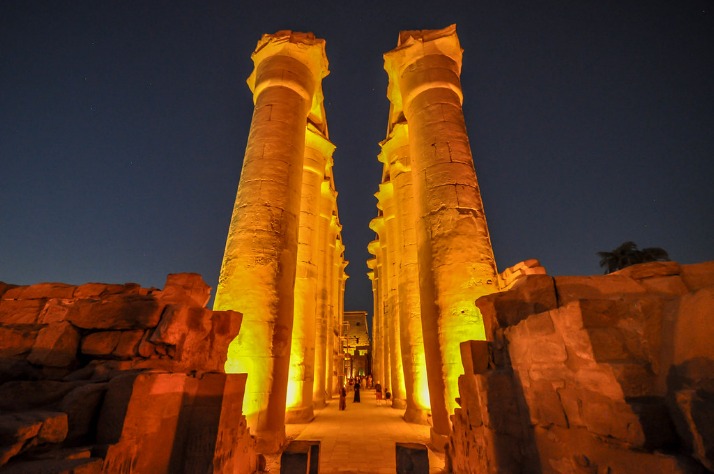
The historical background of capital cities in Egypt reflects the rich and ancient civilization that has flourished along the Nile River for thousands of years. Egypt’s earliest known capitals date back to the prehistoric period, with significant development during the Pharaonic era. The city of Memphis served as a prominent political and cultural center during the Old Kingdom, functioning as a capital for several dynasties and symbolizing the unity of Upper and Lower Egypt. Later, during the New Kingdom, Thebes (modern-day Luxor) became a major religious and political hub, home to monumental temples and tombs for pharaohs. As Egypt evolved through various dynasties, religious centers such as Akhetaten (Amarna) emerged temporarily as capitals under specific rulers. In the later periods, Alexandria was founded by the Greeks and became a major center for culture, trade, and learning, especially during the Hellenistic and Roman periods. The ancient Egyptian capitals were often characterized by their strategic locations, religious significance, and architectural achievements, reflecting the dynamic history of Egypt and its enduring legacy as a cradle of civilization.
Medieval and Ottoman Period Capitals
Egypt’s capital cities have a rich historical background that reflects the country’s diverse civilizations and periods of rule. During the medieval period, the role of cities such as Fustat and Cairo became prominent. Fustat, established in the 7th century by the Arab conquerors, served as an important administrative and commercial center before the founding of Cairo. It was a key city during the Islamic era, known for its vibrant markets and cultural significance. When the Fatimid dynasty founded Cairo in 969 AD, it quickly became the political and cultural heart of Egypt, establishing itself as the capital of the Fatimid Caliphate. Cairo’s strategic location and Islamic architecture contributed to its prominence throughout the medieval period.
Under the Ottoman rule, which began in the early 16th century, Cairo continued to serve as a vital center of administration and commerce. The Ottomans integrated Egypt into their empire, maintaining Cairo’s status as the capital. They constructed fortifications, mosques, and administrative buildings that underscored the city’s importance. Throughout the Ottoman period, Cairo expanded in population and infrastructure, solidifying its position as Egypt’s political and cultural hub. The city’s Ottoman architecture and administrative structures left a lasting impact, shaping Cairo’s development into the modern capital of Egypt.
Modern Capital Development
The historical background of capital cities in Egypt reflects a rich tapestry of cultural, political, and strategic significance that has evolved over millennia. Ancient Egypt’s capital was centered around Thebes (modern-day Luxor) during the New Kingdom, serving as a religious and political hub. Later, Memphis became a prominent capital during the Old Kingdom, symbolizing the unity of Upper and Lower Egypt. With the rise of the Ptolemaic and Roman periods, cities like Alexandria gained prominence as centers of commerce, education, and governance. Cairo, known as Fustat in its early days, eventually emerged as the main capital during the Islamic era, flourishing as a metropolitan hub through centuries of Islamic rule and Ottoman influence.
Modern capital development in Egypt has been characterized by planned urban growth and strategic relocation efforts. The most notable development is the establishment of New Cairo and other satellite cities to accommodate the growing population and ease congestion in historic centers. Recognition of the need for a new administrative capital led to the groundbreaking project of the New Administrative Capital east of Cairo, intended to serve as a modern, sustainable, and administrative hub. This development aims to improve economic growth, urban infrastructure, and governmental efficiency, reflecting Egypt’s ongoing efforts to modernize and diversify its urban landscape while preserving its historical legacy.
Main Capitals of Egypt
Egypt is a country rich in history and culture, with its capital cities playing significant roles throughout its ancient and modern eras. The main capital of Egypt is Cairo, which serves as the political, economic, and cultural center of the nation. Over the centuries, different cities have held importance at various times, reflecting Egypt’s diverse heritage. Exploring these capitals offers insight into the country’s development and historical significance.
Old Cairo (Fostat)
The main capital of Egypt is Cairo, which serves as the country’s political, cultural, and economic center. Within Cairo, there is a historic area known as Old Cairo, or Fostat, which is rich in history and ancient sites. Fostat was once a separate city and later became part of Cairo, offering a glimpse into Egypt’s Islamic and medieval past. Today, Fostat is characterized by its ancient mosques, traditional markets, and narrow winding streets that reflect its historical significance. Cairo itself continues to be the main hub of Egypt, while Old Cairo remains a vital cultural and historical district that attracts many visitors interested in Egypt’s heritage.
Cairo
The main capital of Egypt is Cairo, which is also the largest city in the country. Cairo serves as the political, cultural, and economic center of Egypt, hosting numerous government institutions, historical sites, and vibrant markets. As one of the most populous cities in Africa, Cairo has a rich history dating back to ancient times and is renowned for its proximity to iconic landmarks such as the Giza Pyramids and the Sphinx. The city plays a crucial role in shaping Egypt’s modern identity and continues to be a hub of activity and development.
New Administrative Capital
Egypt has a rich history of capital cities, with Cairo being the most well-known and longstanding center of administration. In recent years, Egypt has developed a new administrative capital to support its growing needs and urban development. This new city aims to reduce congestion in Cairo and promote economic growth across the country.
- Cairo – the historic and current capital of Egypt, known for its ancient monuments and vibrant culture.
- New Administrative Capital – a modern city being constructed east of Cairo, intended to serve as the new government hub and administrative center.
Cairo: The Cultural and Political Hub
Cairo, the vibrant capital of Egypt, stands as a remarkable center of culture, history, and politics. Known for its bustling streets, historic landmarks, and lively markets, Cairo plays a vital role in shaping the nation’s identity. As a hub of innovation and tradition, the city seamlessly blends ancient wonders with modern developments, making it a captivating destination and a crucial political heart of Egypt.
Historical Landmarks in Cairo
Cairo, the capital city of Egypt, stands as a vibrant center for culture, politics, and history, reflecting the rich heritage of the nation. It has long been a hub for scholarly pursuits, political developments, and artistic expression, making it a quintessential example of Egypt’s dynamic history. The city’s unique blend of ancient traditions and modern advancements continues to attract millions of visitors each year.
Among Cairo’s most famous historical landmarks is the iconic Pyramids of Giza, including the Great Pyramid, which is one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The nearby Sphinx, with its mysterious aura, adds to the archaeological significance of the area. Inside the city, the Egyptian Museum houses a vast collection of artifacts from Pharaonic Egypt, providing a glimpse into the civilization that once flourished here.
The Islamic Cairo district is a treasure trove of medieval mosques, markets, and palaces, including the impressive Mosque of Ibn Tulun and the bustling Khan El Khalili bazaar. These sites exemplify Cairo’s role as a center of Islamic culture and history. Additionally, the Citadel of Saladin offers panoramic views of the city and contains impressive structures such as the Muhammad Ali Mosque.
Cairo’s significance as a political hub is evident in its role as the seat of government and national institutions. Its vibrant streets and historic sites embody the spirit of Egypt’s past and present, making it an essential capital city within Africa and the Arab world.
Government and Administrative Centers
Cairo, the capital city of Egypt, stands as a vibrant center of culture, politics, and administration. It is renowned for its rich history, bustling markets, and diverse neighborhoods that reflect the nation’s heritage. As the political heart of Egypt, Cairo hosts numerous government institutions, including the presidential palace, ministries, and parliamentary buildings, serving as the core of national decision-making.
The city functions as the primary administrative hub, where various government agencies operate to manage the country’s affairs. Cairo’s government centers are strategically located across districts like Tahrir Square and Dokki, facilitating effective governance. These centers are not only administrative headquarters but also symbols of Egypt’s political stability and authority.
Beyond politics, Cairo’s cultural scene is distinguished by world-famous landmarks such as the Egyptian Museum and historic mosques, which underscore its significance as a center of ancient civilization and modern Arab culture. The city continues to evolve, blending its historical legacy with contemporary political and administrative functions, making it a pivotal metropolis in Egypt’s national landscape.
Economic Significance
Cairo is the vibrant capital city of Egypt, serving as a central hub for culture, politics, and economics. It has a rich history that dates back over a thousand years, making it one of the most historically significant cities in the Arab world. As the political heart of Egypt, Cairo hosts important government institutions, including the presidential palace and the parliament, shaping the nation’s policies and governance.
Economically, Cairo is Egypt’s largest city and a primary driver of the country’s economy. It is a major center for banking, manufacturing, and trade, with bustling markets and a growing service sector. The city’s strategic location and large population contribute to its role as a pivot for commerce and innovation in the region.
- Rich historical and cultural sites, such as the Egyptian Museum and Islamic Cairo
- Major political institutions and government offices
- Key economic activities including trade, finance, and industry
- Educational and research institutions that attract students and scholars
- A diverse and vibrant population that influences Egyptian culture and society
The New Administrative Capital
The New Administrative Capital of Egypt is a modern development project designed to create a new bustling city near Cairo. It aims to alleviate congestion, improve government infrastructure, and foster economic growth. This ambitious initiative reflects Egypt’s vision for future urban living and strategic expansion, positioning the country as a significant hub in the region.
Design and Planning
The New Administrative Capital of Egypt represents a ambitious urban development project aimed at alleviating congestion in Cairo and creating a modern administrative hub. The design emphasizes sustainable and innovative planning, blending functional zoning with aesthetic landscaping to establish a city that is both efficient and environmentally friendly. The layout incorporates wide avenues, green spaces, and intelligent infrastructure to support the government’s expanding needs.
Architecturally, the city features iconic government buildings, commercial centers, residential complexes, and cultural landmarks designed to showcase modern Egyptian architecture. The planning process carefully considers spatial organization, transportation networks, and integration of smart city technologies to enhance connectivity and urban liveability. Overall, the New Administrative Capital is envisioned as a futuristic urban center that balances form, function, and sustainability, exemplifying Egypt’s commitment to urban development and modernization.
Key Features and Districts
The New Administrative Capital is a planned city in Egypt designed to serve as the new administrative and financial hub, aiming to reduce congestion in Cairo and boost economic development. It features modern infrastructure, intelligent city technologies, and eco-friendly designs to create a sustainable urban environment. The city spans a vast area, encompassing numerous districts each dedicated to specific functions and communities, making it a comprehensive and innovative urban project.
Key features of the New Administrative Capital include its vast government district, which hosts ministries, government offices, and the parliament, all integrated into a state-of-the-art infrastructure. The city also showcases various land-use zones such as residential neighborhoods, commercial areas, educational institutions, and entertainment complexes. Iconic structures like the Iconic Tower, which is among Africa’s tallest, provide a futuristic skyline. Additionally, the city emphasizes green spaces, smart transport systems, and eco-friendly initiatives to promote sustainability and high quality of life.
The districts within the New Administrative Capital are carefully planned to serve specific purposes. The Administrative District is primarily for government buildings and officials. The Business District, also known as the Downtown, contains commercial centers, office spaces, and retail outlets. The Residential Districts offer diverse housing options for different income levels, featuring modern apartments, villas, and gated communities. Other districts include Education City, dedicated to universities and research centers, and New Cairo, which provides additional residential and commercial zones. Parks, cultural centers, and healthcare facilities are integrated throughout the city to support a well-rounded community living experience.
Goals and Expected Outcomes
The New Administrative Capital of Egypt is a major urban development initiative aimed at easing congestion in Cairo and creating a modern, sustainable city center. Its primary goal is to establish a government hub that enhances administrative efficiency and urban planning. The project also seeks to boost economic growth, attract foreign investment, and provide state-of-the-art infrastructure and services to residents and businesses alike.
Expected outcomes include the reduction of Cairo’s overcrowding and pollution, improved quality of life for citizens, and the development of a vibrant economic zone. The new capital is designed to feature advanced transportation networks, green spaces, smart city technologies, and modern residential and commercial areas. Ultimately, the project aims to position Egypt as a competitive regional hub and exemplify the country’s commitment to innovative urban development.
Other Notable Cities with Administrative Functions
Egypt is renowned for its rich history and vibrant culture, but beyond Cairo, several other cities play crucial roles in the country’s administrative landscape. These cities serve as regional hubs, administrative centers, and key locations for governance and development. Exploring these notable urban areas provides a broader understanding of Egypt’s diverse urban landscape and the important functions they serve within the nation’s framework.
Alexandria
Alexandria is one of the notable cities in Egypt that holds significant administrative importance. Although Cairo is the nation’s capital, Alexandria serves as a vital administrative hub and a major economic center, especially in the fields of trade, logistics, and culture. The city functions as the administrative center for various government offices and regional authorities, contributing to the governance and development of Egypt. Its strategic location on the Mediterranean coast also enhances its role in international commerce and maritime activities.
Suez and Canal Zone
Suez and the Canal Zone are significant areas in Egypt that hold notable administrative functions beyond the country’s primary capital cities. Suez serves as an important strategic and industrial hub, primarily due to its proximity to the Suez Canal, one of the world’s most vital waterways for international maritime trade. The Canal Zone encompasses the region surrounding the Suez Canal, which has historically been under special administrative status, reflecting its importance in Egypt’s economy and national security. These regions are key to Egypt’s transportation, logistics, and economic infrastructure, and they operate under distinct administrative arrangements to support their specialized functions.
Port Said
Port Said is a significant city in Egypt that holds notable administrative functions, especially due to its strategic location at the northern entrance of the Suez Canal. As a major port, it serves as a vital hub for maritime trade and logistics, contributing to Egypt’s economy and international connectivity. The city also functions as an administrative center for the Suez Governorate, overseeing various regional governance and development initiatives. Its importance extends beyond commerce, with cultural and historical sites that attract tourists and serve as a testament to Egypt’s rich heritage.




0 Comments