Geographical Location and Landscape
Cape Cross in Namibia is a remarkable destination characterized by its unique geographical location and diverse landscape. Situated along the Atlantic coast, it features dramatic cliffs, expansive beaches, and rugged terrain that create a stunning natural environment. The region’s landscape is shaped by the powerful ocean currents and wind patterns, offering a captivating backdrop for visitors and local wildlife alike. This distinctive setting plays a significant role in shaping the area’s ecological and cultural significance.
Position along the Skeleton Coast
Cape Cross in Namibia is situated along the rugged and remote Skeleton Coast, renowned for its dramatic coastal landscape and striking natural beauty. The location is positioned on the Atlantic Ocean’s edge, offering breathtaking views of the endless ocean and rocky shoreline. The Skeleton Coast itself extends along the northwestern part of Namibia, characterized by vast deserts, towering sand dunes, and cliffs that create a stark yet mesmerizing scenery. Cape Cross lies approximately 60 kilometers north of Henties Bay, serving as a prominent landmark along this isolated stretch of coast. Its geographical setting plays a significant role in shaping the unique environment, with the confluence of desert and ocean creating a habitat rich in wildlife, including the famous Cape Cross colonies of Cape fur seals that inhabit the area.
Physical Features and Coastal Environment
Cape Cross in Namibia is located along the Atlantic Ocean coastline in the northern part of the country. It is situated near the Skeleton Coast, an area known for its dramatic scenery and remote wilderness. The landscape surrounding Cape Cross features a combination of rugged cliffs, sandy beaches, and vast desert plains, creating a striking contrast between land and sea.
The physical features of Cape Cross include a prominent headland that extends into the ocean, providing a natural vantage point. The region is characterized by its arid environment, with sparse vegetation adapted to the desert climate. The landscape is shaped by strong ocean currents and frequent fog, which contribute to its unique coastal environment.
The coastal environment of Cape Cross is notable for its extensive seal colony, which attracts visitors and researchers alike. The area experiences rough seas and powerful waves, influenced by the Atlantic Ocean’s fetch. This combination of physical and environmental features creates a distinctive coastal ecosystem rich in marine life, supporting a variety of seabirds and marine mammals.
Climate and Weather Patterns
Cape Cross in Namibia is located along the rugged Atlantic coast in the northern part of the country, within the Kunene Region. It is situated approximately 125 kilometers south of the town of Henties Bay, offering a striking coastal landscape characterized by cliffs, rocky outcrops, and expansive beaches. The area is renowned for its dramatic scenery where the desert meets the ocean, creating a unique and picturesque environment.
The landscape surrounding Cape Cross features a combination of barren deserts, sparse vegetation, and rocky formations that have been shaped over centuries by natural processes. The coastline is marked by prominent headlands and cliffs, providing critical habitats for various seabirds and marine mammals. The vast, open spaces and rugged terrain are typical of Namibia’s arid coastal regions.
The climate in Cape Cross is classified as semi-arid with a coastal influence, resulting in mild to warm temperatures throughout the year. Summers are generally hot, with daytime temperatures often exceeding 30°C (86°F), while winters tend to be cooler but still relatively mild, with daytime temperatures averaging around 15°C to 20°C (59°F to 68°F). The region experiences low annual rainfall, mostly falling during the winter months from May to August, contributing to its dry and arid environment.
Weather patterns are predominantly influenced by the cold Benguela Current along the Atlantic Ocean, which leads to frequent fogs, especially in the mornings. These fogs provide moisture to the otherwise dry landscape and are an important ecological feature of the area. Wind conditions can be strong and persistent, shaping the coastal landscape and impacting weather patterns, making Cape Cross a region of stark beauty with a climate that reflects its remote, rugged character.
Wildlife and Marine Life
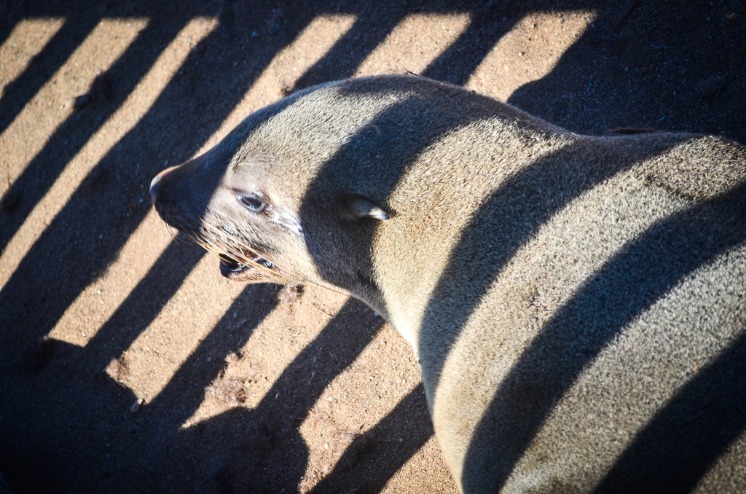
Cape Cross in Namibia is a renowned destination for wildlife and marine life enthusiasts. This rugged coastal area offers a unique glimpse into the thriving ecosystems that exist along the Atlantic Ocean, home to a diverse array of species. From massive fur seals to migratory seabirds, Cape Cross provides an extraordinary opportunity to observe the beauty and complexity of marine and terrestrial wildlife in their natural habitat.
Seabird Colonies and Bird Species
Cape Cross in Namibia is renowned for its rich biodiversity, particularly its thriving seabird colonies and diverse bird species. The area provides a crucial habitat for numerous seabirds, including the iconic Cape Gannets, which nest on the cliffs and are easily observed from viewing platforms. These colonies are vital breeding sites that support a variety of species such as cormorants, terns, and gulls, forming a vibrant ecosystem sustained by the abundant fish stocks in the surrounding waters. The marine life around Cape Cross is equally impressive, with schools of sardines, anchovies, and other small fish attracting larger predators like seals, dolphins, and sharks, creating a dynamic marine environment. The coastal waters act as a feeding ground for these species, contributing to the overall health of the region’s marine and avian populations. Efforts to preserve this delicate balance are essential to maintaining Cape Cross’s status as a significant sanctuary for both terrestrial and marine wildlife in Namibia.
Marine Mammals and Aquatic Species
Cape Cross, located along the rugged Atlantic coast of Namibia, is renowned for its rich diversity of wildlife and marine life, especially marine mammals and aquatic species. The area is a vital breeding ground for thousands of Cape fur seals, making it one of the world’s largest colonies of this species. These seals attract numerous seabirds, such as cormorants and gulls, creating a bustling ecosystem rich in avian and marine biodiversity.
The waters surrounding Cape Cross are teeming with marine species, including various fish, sharks, and rays that support the local food chain. The region’s nutrient-rich waters are driven by upwellings, which bring nutrients to the surface, fostering a thriving habitat for phytoplankton, which forms the base of the marine food web.
Marine mammals such as dolphins, whales, and seals are frequently observed in these waters, with species like the Heaviside’s dolphin, bottlenose dolphin, and even occasional sightings of migrant whales passing through during migration seasons. The area offers unique opportunities for eco-tourism centered on observing these incredible creatures in their natural environment.
Overall, Cape Cross represents a vital sanctuary for marine and aquatic species, highlighting the importance of conservation efforts in maintaining Namibia’s extraordinary biodiversity and supporting sustainable tourism initiatives.
Terrestrial Wildlife in the Area
Cape Cross in Namibia is renowned for its diverse wildlife and vibrant marine life, making it a significant area for both terrestrial and marine ecosystems. The region offers a unique habitat where various species of animals coexist, contributing to the area’s ecological richness.
Terrestrial wildlife around Cape Cross includes a variety of mammals such as the Cape fur seals, which are the main attraction and inhabit the coastal rocks in large numbers. Besides seals, the area is home to desert-adapted species like oryx, springbok, and jackals that have evolved to survive in this arid environment. Bird species such as cormorants, gulls, and pelicans are also prominent, often seen nesting on cliffs and hunting along the shoreline.
The marine life in the waters off Cape Cross is equally abundant and diverse. The region is an important breeding ground for numerous fish species, while the ocean supports a wide array of marine mammals including whales, dolphins, and other seal species. Seasonal migrations bring large pods of dolphins and whales, providing spectacular sightings for visitors. The nutrient-rich waters foster a thriving ecosystem that sustains these diverse terrestrial and marine species, highlighting Cape Cross as a vital ecological hotspot in Namibia.
Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony
Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony, situated along the rugged coast of Namibia, is one of the world’s most significant and accessible breeding sites for elephant seals. This remote and stunning location attracts visitors and researchers alike, offering a unique opportunity to observe these magnificent marine mammals in their natural habitat. The colony’s dramatic scenery and wildlife make it a must-visit destination for nature enthusiasts exploring the Cape Cross area in Namibia.
History and Significance of the Colony
The Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony, located along the Skeleton Coast of Namibia, is renowned as one of the world’s largest and most important elephant seal rookeries. Established in 1913, the colony has played a significant role in the conservation of the species, which faced near extinction due to overhunting in the early 20th century. Today, it serves as a vital breeding ground where thousands of southern elephant seals gather annually to mate and give birth.
The colony’s history is marked by efforts to protect and restore elephant seal populations, which dramatically declined due to the fur trade and hunting for oil and blubber. Recognizing its ecological importance, the site was designated a protected area, allowing the seals to thrive and expanding their population. The colony has become a symbol of successful wildlife conservation, illustrating the importance of safeguarding marine mammals and their habitats.
In addition to its ecological significance, Cape Cross holds cultural and tourism value, attracting visitors from around the world eager to witness the massive seals in their natural environment. The colony’s prominence continues to grow as a key attraction along Namibia’s coast, highlighting the country’s commitment to conserving its unique biodiversity and promoting sustainable tourism. The Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony remains a vital part of Namibia’s natural heritage and a testament to the resilience of marine life when given proper protection.
Elephant Seal Behavior and Life Cycle
The Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony in Namibia is renowned for hosting one of the world’s largest gatherings of elephant seals. This impressive colony attracts both researchers and visitors interested in observing the unique behaviors and life cycle of these marine mammals. Elephant seals are known for their remarkable size, with males reaching up to 20 feet in length and weighing over 4 tons.
During the breeding season, dominant males establish territories and gather harems of females, engaging in fierce battles to defend their status. Males large territories and make loud vocalizations to attract females, showcasing their strength and dominance. Females give birth to their pups after a gestation period of approximately 11 months, usually around December or January, and nurse their young for about a month. This period is critical for the pups’ survival, as they gain essential fat reserves to sustain them through the months of fasting during the breeding season.
Elephant seals exhibit a highly synchronized life cycle, with breeding, molting, and migration occurring in specific seasons. After the breeding period, males and females leave the colony to go on long migrations for feeding, often in productive fishing grounds across the South Pacific. Pups grow rapidly during lactation, and weaning marks the end of their dependence on maternal milk. The entire life cycle is characterized by a cycle of intense social interactions, vocal displays, and strategic movements driven by environmental conditions and reproductive needs.
Visitor Facilities and Eco-tourism
Cape Cross Elephant Seal Colony in Namibia is a remarkable natural attraction that showcases one of the largest concentrations of elephant seals in the world. Visitors can observe these majestic creatures in their natural habitat, especially during the breeding season when thousands gather on the rocky beaches. The site provides a unique opportunity to witness seal behavior up close and learn about their conservation efforts.
Visitor facilities at Cape Cross include a visitor center that offers educational displays, informative signage, and guided tours to enhance the experience. There are designated viewing platforms that allow visitors to observe the seals safely and respectfully, minimizing disturbance to the animals. Additionally, amenities such as restrooms, parking areas, and small gift shops are available for visitor convenience.
Eco-tourism at Cape Cross emphasizes sustainable and responsible tourism practices that prioritize the protection of the environment and wildlife. Visitors are encouraged to follow guidelines to avoid disturbing the seals and to respect their natural habitat. This eco-friendly approach promotes awareness of marine conservation issues while providing an enriching experience that highlights Namibia’s unique coastal ecosystem. The site is a prime example of how tourism can support conservation efforts while offering a memorable nature experience.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Cape Cross in Namibia holds a rich historical and cultural significance, serving as a testament to the region’s ancient maritime heritage and its importance in trade and exploration. The area is renowned for its historical lighthouse and the nearby colony of Cape Cross Seal Reserve, which highlights the enduring relationship between the local communities and the natural environment. This site not only offers insight into Namibia’s past but also reflects the cultural diversity and resilience of its people.
Origins of the Name “Cape Cross”
Cape Cross in Namibia holds both historical and cultural significance, serving as a notable landmark along the country’s coastline. Known for its towering lighthouse and the famous colony of over 80,000 Cape fur seals, the site has been a vital point for maritime navigation and local traditions. The cape’s name derives from the Portuguese explorers who arrived in the 15th century, referring to the dangerous waters and the prominent rocky outcrop. The name “Cape Cross” is believed to originate from a prominent cross established by Portuguese explorers during their voyage, symbolizing their claim and marking a significant navigation point on the route to the East. Over the centuries, Cape Cross has become a symbol of Namibia’s maritime history and a reminder of early European exploration in Africa.
Historical Exploration and Shipping Routes
Cape Cross in Namibia holds a prominent place in both historical and cultural contexts, as well as in the exploration of ancient shipping routes. Recognized for its historical significance, Cape Cross is famously known as the site where Portuguese explorers, including Diego Cao in the late 15th century, first made landfall on the Namibian coast during their navigation along Africa’s southwestern shoreline. This event marked the beginning of European interest and subsequent interactions with local communities, shaping the region’s colonial history.
Beyond its historical exploration, Cape Cross is renowned for its cultural importance, particularly as a site of heritage for the local Himba and other indigenous peoples. The area reflects a rich tapestry of traditions and their enduring connection to the sea and land, which is integral to their identity and livelihood.
In terms of shipping routes, Cape Cross served as a crucial navigational point for early explorers and traders venturing around the Cape of Good Hope. Its strategic position facilitated maritime trade routes connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa. The anchorage provided a vital stopping point for ships on their way to the lucrative markets of the East, influencing global trade patterns during the Age of Exploration.
- Early European explorers established routes around the Cape, using it as a landmark for navigation.
- The site became a key location for sealing and whaling activities in the 19th and early 20th centuries.
- Today, Cape Cross is a significant waypoint for maritime routes along the western coast of Africa, supporting modern shipping and tourism industries.
Cultural Interactions and Heritage
Cape Cross in Namibia holds profound historical and cultural significance as a site deeply connected to maritime history and indigenous heritage. It is renowned for the Cape Cross Seal Reserve, which supports one of the largest colonies of Cape fur seals, highlighting its importance in ecological and economic contexts. Historically, the area was a key point for explorers and traders navigating the Atlantic coast, and it played a role in the region’s contact with European explorers during the age of discovery. Culturally, it is sacred to the local indigenous communities who have lived in harmony with the natural environment for generations.
Through centuries, Cape Cross has served as a crossroads of cultural interactions, where indigenous groups such as the Himba and the Nama interacted with European explorers, missionaries, and traders. These encounters facilitated exchanges of knowledge, goods, and cultural practices, leaving a lasting imprint on the local heritage. The site is also marked by the historic Portuguese cross erected in 1486 by King John II of Portugal, symbolizing early European exploration efforts and the longstanding maritime connections between Africa and Europe.
Today, Cape Cross stands as an important heritage site that embodies the rich tapestry of Namibia’s cultural history and natural wonders. It not only preserves the memory of past explorers and indigenous traditions but also promotes awareness of conservation efforts and intercultural understanding, making it a pivotal location for cultural tourism and heritage preservation in Namibia.
Conservation and Environmental Efforts
Cape Cross in Namibia is a vital location for conservation and environmental efforts, serving as a significant habitat for various marine and terrestrial species. Efforts to preserve this unique ecosystem focus on protecting its diverse wildlife, including the famous Cape fur seals that breed and thrive in the area. These conservation initiatives aim to maintain the delicate balance of the environment, ensuring that future generations can continue to experience the remarkable biodiversity of Cape Cross and contribute to the global effort to safeguard our planet’s natural heritage.
Protection of Wildlife and Habitats
Cape Cross in Namibia is a vital site for conservation and environmental efforts, primarily due to its significance as a habitat for the Cape Cross seal colony, which is one of the largest in the world. Protecting this habitat is essential for maintaining the biodiversity of the region and supporting various marine and coastal species. Conservation initiatives focus on preventing habitat destruction caused by overfishing, pollution, and human interference, ensuring the long-term survival of the seals and other wildlife inhabiting the area.
Efforts also include the establishment of protected areas and wildlife reserves around Cape Cross, which help preserve the natural environment and reduce illegal poaching. Education and local community involvement are key components, promoting sustainable tourism and responsible interaction with wildlife. These measures contribute to the broader goal of safeguarding Namibia’s unique coastal ecosystems, ensuring that future generations can enjoy and learn from this remarkable region.
Impact of Tourism on the Ecosystem
Cape Cross, Namibia, is renowned for its rich marine biodiversity and the iconic Cape Cross Seal Reserve, which hosts thousands of Cape fur seals. Conservation efforts in this region aim to protect these vital species and preserve the delicate ecosystem that sustains them. Local authorities and conservation organizations work diligently to monitor seal populations, prevent illegal fishing, and promote awareness about marine conservation.
The impact of tourism on the ecosystem at Cape Cross is significant yet manageable when carefully regulated. Visitors who come to see the seals and enjoy the natural beauty contribute to the local economy but must do so responsibly to avoid disturbing the wildlife or damaging the environment. Initiatives such as guided tours, educational programs, and designated viewing areas help minimize human impact while fostering appreciation and understanding of the importance of conservation. Maintaining a balance between tourism and ecological preservation is crucial for the ongoing health of Cape Cross’s ecosystem.
Role of National and Local Conservation Programs
Cape Cross in Namibia is a significant site for conservation and environmental efforts, particularly due to its diverse marine and coastal ecosystems. The region is home to a large colony of Cape fur seals, and preserving these populations is essential for maintaining ecological balance. National and local conservation programs play a vital role in protecting this area and promoting sustainable practices to ensure the long-term health of its natural resources.
Role of conservation programs includes wildlife protection, habitat restoration, and community engagement. National initiatives often establish protected areas, enforce anti-poaching laws, and fund research to monitor biodiversity. Local programs focus on educating communities, promoting eco-tourism, and implementing sustainable fishing practices that minimize environmental impact.
- Protection of marine species such as the Cape fur seals and seabirds.
- Habitat preservation through marine protected areas around Cape Cross.
- Research and monitoring efforts to track ecological changes and threats.
- Community involvement in conservation activities and sustainable resource use.
- Promotion of eco-tourism that benefits local economies while conserving natural assets.
Tourism and Visiting Information
Cape Cross in Namibia is a must-visit destination for travelers interested in wildlife and coastal scenery. Located along the Atlantic Ocean, this area is renowned for its impressive population of Cape fur seals and stunning natural landscapes. Visitors can enjoy unique wildlife encounters, explore the rugged coastline, and learn about the region’s ecological significance. Whether you’re an adventure seeker or a nature enthusiast, Cape Cross offers a memorable experience for all ages.
Accessibility and Best Visiting Seasons
Cape Cross in Namibia is a popular destination known for its remarkable population of Cape fur seals and stunning coastal scenery. Visitors can enjoy a unique experience observing thousands of seals lounging on the beaches and swimming in the surrounding waters. Accessibility to Cape Cross is relatively straightforward, with well-maintained roads leading from Swakopmund and other major towns. The site features a visitor center with educational displays, making it suitable for families and nature enthusiasts alike. It is advisable to check local arrangements for guided tours and facilities before planning your visit.
The best visiting seasons for Cape Cross are during Namibia’s cooler months from May to September when the weather is mild, and seal activity is at its peak, especially during the breeding season from November to January. During these months, the weather is pleasant, and wildlife viewing opportunities are optimal. Visiting outside peak seasons can still be rewarding, but be prepared for warmer temperatures and occasional wind. Overall, late winter to early spring offers the best conditions to fully appreciate the natural beauty and wildlife of the area.
Activities and Attractions at Cape Cross
Cape Cross in Namibia is a stunning destination renowned for its fascinating wildlife, unique natural scenery, and historical significance. It is best known for the Cape Cross Seal Reserve, which hosts one of the largest colonies of Cape fur seals in the world, offering visitors a remarkable opportunity to observe these playful marine mammals in their natural habitat.
Tourists visiting Cape Cross can enjoy various activities and attractions such as guided nature walks, photography of the seals and surrounding rugged coastline, and bird watching, as the area is home to numerous seabird species. The scenic landscape features rocky shores, sandy beaches, and salt flats, providing breathtaking views and excellent photo opportunities.
Apart from the wildlife experiences, visitors can explore the historic monument that commemorates the discovery of the Cape by the Portuguese explorer Diego Cao in 1486. The site also offers basic facilities, informative displays, and a nearby lodge for those wishing to extend their stay and enjoy the tranquility of this remote location.
Traveling to Cape Cross involves driving along Namibia’s scenic coastal route, making it ideal for travelers exploring the Skeleton Coast or traveling between Swakopmund and other northern destinations. The best time to visit is during the warmer months from October to April when the seal colonies are most active, and the weather is pleasant.
Facilities, Accommodation, and Visitor Guidelines
Cape Cross in Namibia is a renowned tourist destination famous for its impressive seal colony and rugged coastal scenery. Visitors can enjoy observing thousands of seals up close, providing a unique wildlife experience amid a stunning natural environment. The area offers various facilities to enhance visitor comfort, including a visitor center with informative displays, restrooms, and a small shop selling souvenirs and refreshments. Accommodation options nearby range from basic campsites to more comfortable lodges, catering to different preferences and budgets. Visitors are kindly advised to respect the wildlife and follow guidelines such as maintaining a safe distance from the seals, not disturbing their natural habitat, and adhering to park regulations. It is recommended to visit during daylight hours for the best viewing opportunities and to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience altogether.




0 Comments