Overview of Mount Kilimanjaro
Mount Kilimanjaro, situated in northeastern Tanzania, is Africa’s highest peak and a renowned natural wonder. This majestic mountain stands as a symbol of adventure and exploration, attracting countless climbers and outdoor enthusiasts from around the world. Its snow-capped summit and sprawling glaciers contrast beautifully with the lush surrounding landscapes, making it a significant geographic and cultural landmark in Tanzania.
Geographical Location
Mount Kilimanjaro is the highest peak in Africa and one of the most renowned mountains in the world. It is located in northeastern Tanzania, near the border with Kenya. The mountain forms part of Kilimanjaro National Park, which is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Kilimanjaro’s geographical location places it close to the equator, yet its ice-capped summit creates a striking contrast with the tropical climate surrounding it. The mountain is situated approximately 330 kilometers (205 miles) south of Nairobi, Kenya, and about 420 kilometers (260 miles) northwest of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania’s largest city.
Physical Features and Elevation
Mount Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, is Africa’s highest peak and one of the most iconic mountains in the world. It stands as a symbol of natural beauty and adventure, attracting climbers and trekkers from around the globe. The mountain is part of Kilimanjaro National Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, which is renowned for its stunning landscapes and rich biodiversity.
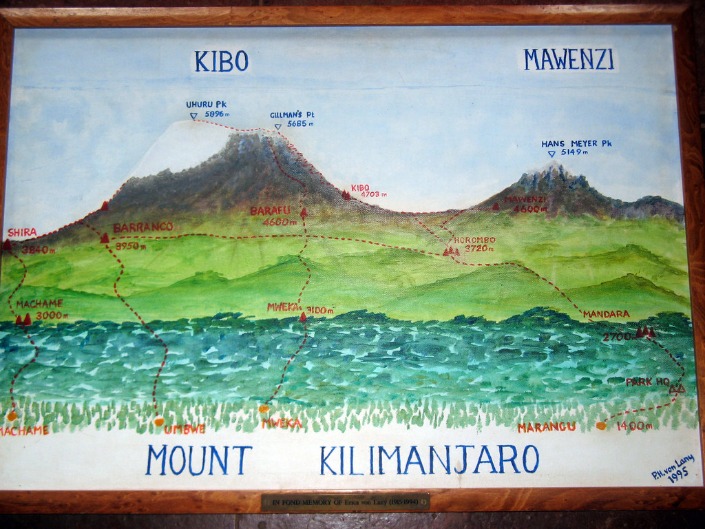
Physically, Mount Kilimanjaro is a dormant volcanic massif composed of three cone-shaped volcanic summits: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. Kibo is the highest of the three and houses Uhuru Peak, the mountain’s summit. Mawenzi and Shira are older volcanic calderas and provide a dramatic backdrop to the mountain’s landscape. The mountain’s base spans approximately 60 kilometers (37 miles) and rises dramatically from the surrounding plains, creating a striking silhouette against the sky.
The elevation of Mount Kilimanjaro is 5,895 meters (19,341 feet) above sea level, making it the tallest free-standing mountain on Earth. Its impressive height and accessible routes make it a popular target for climbers of varying experience levels. The mountain’s summit, Uhuru Peak, offers breathtaking panoramic views and the thrill of standing atop Africa’s highest point, representing an extraordinary achievement for trekkers and mountaineers alike.
Significance to Tanzania and the World
Mount Kilimanjaro, located in northeastern Tanzania, is Africa’s highest peak and one of the most iconic mountains in the world. This majestic mountain stands at 5,895 meters (19,341 feet) above sea level and is renowned for its stunning snow-capped summit and diverse ecological zones. As a prominent feature on the Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania, it attracts thousands of climbers and trekkers each year who seek to conquer its summit through various routes.
More than just a natural wonder, Mount Kilimanjaro holds immense significance for Tanzania and the global community. It is a symbol of natural beauty, biodiversity, and adventure tourism, contributing significantly to the country’s economy through tourism revenue. The mountain also serves as a vital ecological habitat supporting numerous plant and animal species and plays an important role in scientific research related to climate change and elevation ecology. Globally, Kilimanjaro is recognized for its unique geology and the challenge it presents to mountaineers, making it an enduring symbol of human perseverance and natural majesty.
The Kilimanjaro Map
The Kilimanjaro Map in Tanzania offers an invaluable guide for adventurers and travelers seeking to explore Africa’s highest peak. It provides detailed information about the mountain’s various routes, elevation points, and surrounding landmarks, making it easier for visitors to plan their ascent or sightseeing trips. This map is essential for both mountaineers aiming to reach the summit and tourists wishing to appreciate the breathtaking scenery of Kilimanjaro and its national park.
Details and Scale of the Map
The Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania provides a detailed representation of the region surrounding Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest peak in Africa. It highlights key features such as trekking routes, wildlife parks, and nearby towns, offering valuable information for travelers and explorers. The map helps users navigate the area, showing elevation levels, terrain types, and significant landmarks associated with Kilimanjaro and its environment.
The scale of the Kilimanjaro map is typically designed to give a clear understanding of distances and relative sizes of features within the region. Common scales used are 1:100,000 or 1:50,000, which allow for detailed viewing of trails, campsites, and geographical features while maintaining manageable map dimensions. Such scale facilitates planning for trekking expeditions or eco-tourism activities by providing accurate spatial context within the Tanzanian landscape surrounding Kilimanjaro.
Types of Maps Available
The Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania provides detailed information about the region surrounding Africa’s highest peak. It helps travelers and climbers understand the terrain, routes, and key landmarks associated with Mount Kilimanjaro. Different types of maps are available to suit various needs, including topographic maps that showcase elevation and terrain features, navigational maps designed for safe trekking, and simplified route maps highlighting the main ascent paths. Additionally, there are tourist maps that feature attractions, accommodations, and transportation options around Kilimanjaro. Each map type serves a specific purpose, whether for planning a climb, exploring the area, or gaining geographic insights into this iconic mountain in Tanzania.
Uses of the Kilimanjaro Map
The Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania is an essential tool for travelers, trekkers, and geographers interested in exploring the region around Mount Kilimanjaro. It provides detailed information about the mountain’s terrain, hiking routes, and surrounding areas, making navigation easier for those planning an ascent or a sightseeing visit. The map is also useful for educational purposes, helping students and researchers understand the geography and topography of this iconic mountain. Additionally, the Kilimanjaro map aids local authorities and tourism operators in managing the region effectively by highlighting key locations, facilities, and conservation zones. Overall, it serves as a vital resource for anyone seeking to understand or explore the natural beauty of Kilimanjaro and its environment in Tanzania.
Regions and Routes on Kilimanjaro
Kilimanjaro, the tallest mountain in Africa, offers a diverse range of regions and routes for climbers and trekkers. Its landscape comprises lush rainforests, alpine meadows, and icy summit glaciers, each providing unique scenery and challenges. Exploring the various routes and regions on Kilimanjaro is essential for understanding the mountain’s geography and planning a successful ascent. A detailed map of Kilimanjaro in Tanzania helps adventurers navigate these routes and appreciate the mountain’s stunning natural features.
Machame Route
The Machame Route is one of the most popular and scenic pathways to reach the summit of Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania. This route passes through diverse regions, offering travelers a chance to experience different ecological zones and breathtaking landscapes. Navigating the Machame Route involves traversing various terrains and regions, each with unique features and challenges.
- Starting Region: Machame Gate (Shira Gate) – The journey begins in the southern foothills of Kilimanjaro, where trekkers register at the entrance and begin their ascent through lush rainforests.
- Rainforest Zone: The initial part of the route takes hikers through dense tropical rainforest, home to vibrant flora and fauna, providing a humid environment rich in biodiversity.
- Heath and Moorland Regions: As elevation increases, the landscape transitions into heath and moorland zones characterized by heather, giant groundsels, and lobelias, offering stunning views and a change in climate.
- Alpine Desert: Higher up, the route enters the alpine desert region, which is arid and rocky, with sparse vegetation and spectacular views of the surrounding volcanic landscape.
- The Summit Region: The final ascent leads to the Uhuru Peak on the Kibo Crater Rim, where trekkers are rewarded with panoramic views from the summit of Africa’s highest mountain.
Lemosho Route
The Lemosho Route is one of the most popular and scenic trekking routes on Mount Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania. It offers hikers a stunning journey through diverse landscapes, including lush rainforests, heath moorlands, alpine deserts, and icy summits. The route begins on the western side of Kilimanjaro and then traverses around the mountain, providing excellent acclimatization opportunities and a higher success rate for reaching Uhuru Peak.
The Lemosho Route covers several key regions on Kilimanjaro. Starting from the Londorossi Gate, trekkers pass through the lush rainforest region, where they encounter rich flora and fauna. As the route progresses, it enters the health moorlands, characterized by unique vegetation and high-altitude scenery. Approaching the craters and glaciers near the summit, climbers experience the stark, icy environment of the Alpine Zone before reaching the summit at Uhuru Peak. The route’s flexibility also allows for a gradual acclimatization process, making it a preferred choice for many climbers.
Marangu Route
The Marangu Route, often called the “Coca-Cola Route,” is one of the most popular and accessible ways to climb Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania. This route is known for its relatively straightforward path and the availability of huts, making it suitable for hikers with varying experience levels. Traveling along this route offers a unique chance to experience the diverse regions of Kilimanjaro, from lush rainforests at the base to the alpine desert at higher altitudes.
Starting from the Marangu Gate, the route passes through different ecological zones including the tropical rainforest, the heath and moorland zone, and the alpine desert. These regions provide a scenic and changing landscape that highlights the mountain’s natural beauty. Climbers can enjoy panoramic views and encounter a variety of flora and fauna specific to each zone. The Marangu Route ultimately leads to the summit area, Uhuru Peak, situated on the crater rim, showcasing the rugged terrain and extreme conditions of the mountain’s upper regions.
Rongai Route
The Rongai Route is one of the less crowded and more scenic paths to climb Mount Kilimanjaro, offering a unique experience as it approaches the mountain from the north. This route starts from the northeastern side of the mountain near the town of Nale Moru and traverses through different ecological zones, including rainforest, moorland, and alpine desert. The route is favored for its gradual ascent, which can help climbers acclimatize better and reduce the risk of altitude sickness.
Regions along the Rongai Route include the montane rainforest at the beginning, characterized by lush greenery and diverse wildlife, followed by the moorland zone with its iconic giant groundsels and senecios. As climbers progress, they reach the alpine desert, a stark, breathtaking landscape with vast open spaces and dramatic views of the summit. The route concludes at the Kibo Crater, where climbers prepare for the final ascent to Uhuru Peak.
On the Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania, the Rongai Route is highlighted as a preferred choice for trekkers seeking a quieter and more scenic adventure. Its pathways are well-marked, and the route offers stunning vistas of the surrounding savannah and farmlands. The route’s relatively gentle incline makes it suitable for most climbers, providing a rewarding experience with less congestion compared to more popular routes like Marangu or Machame.
Umbwe Route
The Umbwe Route is one of the shortest and most direct trekking routes to Uhuru Peak on Kilimanjaro, offering a challenging but rewarding ascent for experienced climbers. This route begins in the southern part of the mountain and is known for its steep and rugged terrain, which requires good physical fitness. Throughout the journey, trekkers pass through diverse regions including lush rainforests, bamboo forests, and alpine scree slopes. The route provides spectacular views and a sense of wilderness, making it a popular choice for those seeking an off-the-beaten-path adventure. Navigating on Kilimanjaro map Tanzania, travelers can identify the Umbwe Route as a distinct pathway connecting the initial trailhead to various campsites along the mountain, ultimately leading to the summit of Kilimanjaro’s Uhuru Peak.
Key Landmarks and Features on the Map
Kilimanjaro is one of Africa’s most iconic natural wonders, and its map of Tanzania highlights the key landmarks and features that make this region unique. From the towering snow-capped peak to the surrounding protected areas, the map provides a visual guide to the diverse landscapes and important points of interest. Exploring these landmarks offers insights into the geography, ecology, and cultural significance of this remarkable mountain and its surroundings.
Kibo Crater and Summit
Kilimanjaro, the tallest peak in Africa, is renowned for its diverse geographical features and stunning landmarks. Among these, Kibo Crater stands out as the largest volcanic crater on the mountain, offering a unique geological site surrounded by rugged terrain. The summit of Kilimanjaro, also known as Uhuru Peak, provides breathtaking panoramic views and is a major achievement for climbers. The map of Kilimanjaro in Tanzania highlights these key features, along with glaciers, alpine deserts, and lush rainforests at lower elevations, making it a truly iconic mountain with a variety of natural landmarks.
Gates and Starting Points
Kilimanjaro map Tanzania highlights several key landmarks and features that are essential for explorers and trekkers. The map prominently displays Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa’s highest peak, along with its three volcanic cones: Kibo, Mawenzi, and Shira. Surrounding the mountain are numerous national parks and reserves, such as Kilimanjaro National Park, which protect the rich biodiversity of the region. The map also marks various routes and trails used for ascent, including the Marangu, Machame, Rongai, and Lemosho paths, each offering different perspectives and challenges. Gates and starting points are clearly indicated on the map, such as the Kilimanjaro Gate, Marangu Gate, and Machame Gate, serving as essential access points for climbers beginning their ascent. These gates are situated at different elevations and provide logistical entry points to start the trekking adventures to the summit. Additionally, nearby towns like Moshi and Arusha serve as popular hubs for travelers preparing for their expedition, with transportation links leading to these gateway locations. Overall, the map offers a comprehensive overview of the key geographical and logistical features crucial for anyone planning to explore Kilimanjaro in Tanzania.
Synchronous Landmarks and Campsites
On the Kilimanjaro map of Tanzania, key landmarks and features include the iconic peaks, various campsites, and notable natural formations that guide climbers through their ascent. Synchronous landmarks and campsites are strategically positioned to support safety and navigation during the trek.
- Kibo Summit – the highest point on Kilimanjaro and the ultimate goal for climbers.
- Uhuru Peak – the summit area where climbers celebrate reaching the top.
- Mandara Hut – a popular early campsite on the Marangu Route with distinctive surroundings.
- Barranco Camp – located near the Barranco Wall, offering stunning views and a challenging ascent point.
- Shira Plateau – a high-altitude volcanic plateau providing unique scenery and a key acclimatization site.
- Barafu Camp – the last campsite before the summit assault, known as the “Sting” camp.
- GPS Landmarks – such as the Glacier Rose, and various water streams that are vital for navigation and hydration.
- Natural features like the Furtwangler Glacier and the ice fields, indicating climatic zones and key landmarks for guidance.
- Marangu Route Campsites – Mandara, Horombo, and Kibo Hut serve as essential follow-up points that are synchronized with climbers’ acclimatization schedules.
- Machame Route Campsites – Machame, Shira, Barranco, and Barafu camps are sequential landmarks supporting the trek’s progression.
- Synchronous landmarks include the Lava Tower and the Barranco Wall, which are critical checkpoints for route navigation and safety planning.
Navigation and Map Reading Techniques
Navigation and map reading techniques are essential skills for adventurers and explorers, especially when tackling challenging terrains like Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania. Understanding how to interpret maps, utilize compasses, and plan routes ensures safer and more efficient journeys through the mountain’s diverse landscapes. Mastering these skills allows hikers to navigate confidently, avoid hazards, and fully appreciate the breathtaking scenery of Kilimanjaro.
Understanding Topographical Lines
Understanding navigation and map reading techniques is essential for safely exploring the Kilimanjaro region in Tanzania. Accurate map reading helps in planning routes, estimating distances, and ensuring you stay on the correct path during your ascent. Recognizing topographical lines on maps is fundamental to understanding the terrain’s elevation and slope, which is crucial when navigating the challenging landscape of Kilimanjaro.
Topographical lines, also known as contour lines, represent the elevation and shape of the land on a map. These lines connect points of equal height above sea level, allowing hikers to visualize the terrain’s ups and downs. Closely spaced contour lines indicate steep slopes, while wider spaces show gentler inclines. By studying these lines, climbers can identify potential difficulty points, such as steep ascents or descents, and plan their routes accordingly.
Effective map reading involves interpreting symbols, understanding scale, and recognizing landmarks. When navigating Kilimanjaro, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the specific symbols used for features like campsites, water sources, and trail markers. Using a compass in conjunction with the map enhances navigation accuracy, especially in areas where landmarks are sparse. Developing these skills ensures a safer and more successful ascent on this iconic mountain in Tanzania.
Using a Kilimanjaro Map for Planning
Using a Kilimanjaro map for planning is essential for successful navigation and safe trekking. A detailed map of Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania provides vital information about trail routes, elevation changes, key landmarks, and shelters, helping climbers strategize each stage of their ascent. When reading the map, it is important to identify the various routes such as the Marangu, Machame, Lemosho, and Rongai paths, and understand their difficulty levels and points of interest. Proper map reading techniques include orienting the map with your compass, recognizing contour lines to gauge terrain steepness, and noting distances between landmarks. By carefully analyzing the map, climbers can anticipate challenges, plan rest stops, and ensure they stay on the correct trail, thereby enhancing safety and increasing the likelihood of a successful summit of Kilimanjaro.
Safety and Orientation Tips
Navigating Kilimanjaro requires proper map reading skills, safety precautions, and effective orientation techniques to ensure a successful and secure ascent. Familiarity with terrain features and route markers is essential for climbers venturing into the challenging landscapes of Tanzania’s highest peak.
- Study the Kilimanjaro map carefully before starting your trek to familiarize yourself with key routes, camps, and water sources.
- Use a detailed topographic map that indicates elevation changes, trail markers, and landmarks to navigate effectively.
- Carry a compass and GPS device, and learn how to integrate their readings with your map to maintain accurate orientation.
- Pay close attention to natural features such as ridges, valleys, and glaciers to assist with map reading and route planning.
- Regularly check your position against map references to prevent disorientation in the high-altitude environment.
- Always inform your guide or trekking group of your intended route and estimated checkpoints to enhance safety.
- Follow marked trails and avoid venturing off-route, especially in less visible or poorly marked areas.
- Be aware of weather conditions, as fog or rain can impair visibility and make navigation more difficult.
- Maintain communication devices and have emergency plans in place, including knowledge of rescue routes.
- Ensure you carry sufficient supplies, including water, food, and first aid kits, to handle unexpected situations during your climb.
Conservation and Environmental Zones
Conservation and environmental zones play a crucial role in safeguarding the rich biodiversity and natural beauty of regions like Mount Kilimanjaro in Tanzania. These areas are designated to protect delicate ecosystems, ensure sustainable tourism, and preserve the unique landscapes that attract adventurers and nature enthusiasts from around the world. Understanding these zones helps visitors appreciate the importance of preserving Mount Kilimanjaro’s majestic environment for future generations.
Protected Areas and National Parks
Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, is a prominent symbol of natural beauty and ecological significance. The region surrounding Kilimanjaro is protected by various conservation efforts, including designated environmental zones, protected areas, and national parks. These zones are established to preserve the diverse flora and fauna that inhabit the mountain and its surrounding ecosystems.
Protected areas around Kilimanjaro play a crucial role in conserving the unique biodiversity of the region. The Kilimanjaro National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site known for its stunning landscapes, rare wildlife, and the iconic snow-capped peak. The park encompasses different ecological zones, from cultivated areas at lower elevations to alpine deserts near the summit.
Environmental zones in the Kilimanjaro region are carefully managed to balance conservation with tourism and local community needs. These zones include buffer zones, core protected areas, and transition zones, each serving specific conservation and sustainable use purposes. Maintaining these zones helps prevent habitat degradation, supports endemic species, and sustains the ecological integrity of the mountain.
Overall, the management of conservation and environmental zones around Kilimanjaro is vital for protecting Tanzania’s natural heritage. These efforts ensure that future generations can continue to experience the mountain’s majestic landscape and rich biodiversity while supporting local livelihoods and sustainable tourism activities.
Flora and Fauna Distribution
Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, is a prominent feature in conservation and environmental zones, showcasing diverse flora and fauna. The mountain’s various ecological zones range from tropical rainforest at its base to alpine desert near the summit, each hosting unique plant and animal species. Conservation efforts in this region aim to protect these habitats from deforestation, climate change, and human encroachment. Flora such as bamboo, giant groundsels, and lobelias thrive at different altitudes, while fauna including elephants, buffalo, and numerous bird species contribute to the area’s rich biodiversity. Mapping Kilimanjaro’s environmental zones helps in understanding ecological distributions and promoting sustainable tourism and conservation initiatives throughout Tanzania.
Impact of Tourism and Preservation Efforts
Kilimanjaro, located in Tanzania, is a prominent conservation area that attracts many tourists due to its breathtaking landscapes and unique ecosystem. Environmental zones on the mountain range from lush rainforests at lower altitudes to alpine deserts near the summit, each hosting diverse flora and fauna. The increasing popularity of trekking and climbing expeditions has brought both economic benefits and environmental challenges, such as trail erosion and habitat disturbance. Preservation efforts are crucial to maintaining the mountain’s natural beauty and biodiversity, involving strict regulations, community engagement, and sustainable tourism practices. Conservation initiatives aim to protect Kilimanjaro’s fragile environment while allowing visitors to experience its majestic beauty responsibly, ensuring that future generations can appreciate this iconic landmark in Tanzania.




0 Comments