Historical Significance of Lalibela
Lalibela, a renowned historical site in Ethiopia, holds immense religious and cultural significance. Famous for its breathtaking rock-hewn churches, it is considered a pilgrimage destination and a symbol of Ethiopian Christianity. These extraordinary structures, carved directly into the sandstone cliffs in the 12th century, reflect the ingenuity and spiritual devotion of the Ethiopian people. Lalibela’s historical importance lies in its role as a center of faith, cultural heritage, and architectural marvels that have endured for centuries.
Origins of Lalibela
Lalibela, located in Ethiopia, holds immense historical significance as a sacred pilgrimage site and a masterpiece of medieval Christian architecture. Founded in the 12th century during the reign of King Lalibela, the town is renowned for its rock-hewn churches, which were carved directly from volcanic tuff, showcasing extraordinary craftsmanship and devotion. These structures served as a spiritual refuge and a symbol of Ethiopian Christianity, becoming a center for religious activities and pilgrimage for centuries.
The origins of Lalibela are often linked to the legend of King Lalibela, who is believed to have been divinely inspired to create a “New Jerusalem” after witnessing the suffering of Ethiopian Christians during the Islamic conquests. The creation of the churches was an ambitious project that aimed to establish a holy site that could serve as a spiritual beacon and a place of refuge during periods of persecution. Today, Lalibela remains a living testament to Ethiopia’s rich religious heritage and architectural ingenuity, attracting visitors and pilgrims from around the world who come to admire its historic churches and deep spiritual significance.
Historical Background and Development
Lalibela, located in Ethiopia, holds immense historical significance as the site of a remarkable assembly of rock-hewn churches that are considered one of the world’s greatest architectural and religious achievements. These churches, carved directly into the volcanic rock during the 12th and 13th centuries, serve as a vital pilgrimage destination for Ethiopian Orthodox Christians and symbolize Ethiopia’s rich Christian heritage.
The development of Lalibela is closely tied to the reign of King Lalibela, who is believed to have commissioned the construction of these sacred structures to create a “New Jerusalem” after the Muslim conquests threatened the Christian community in the region. The engineering feat involved excavating eleven monolithic churches and connecting them with a complex system of tunnels and trenches, showcasing advanced skills and devotion. Over the centuries, Lalibela has remained an important spiritual center, with the churches continually maintained and revered, reflecting the resilience of Ethiopian Christianity and its cultural identity.
Role in Ethiopian Christianity
The Lalibela churches in Ethiopia hold profound historical significance as a testament to the resilient spirit of Ethiopian Christianity. Carved entirely out of volcanic rock in the 12th century, these sacred structures symbolize the enduring faith of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church and its pivotal role in the nation’s spiritual identity. Lalibela served as a pilgrimage site and a spiritual center, reinforcing the deep roots of Christianity in Ethiopia and demonstrating the cultural and religious unity of the Ethiopian people.
The complex’s unique architecture, comprising eleven monolithic churches interconnected by tunnels and trenches, exemplifies medieval Ethiopian ingenuity and religious devotion. Lalibela’s churches not only function as places of worship but also as symbols of resistance and preservation of Christian tradition during times of external threats and internal upheaval. As a UNESCO World Heritage site, Lalibela remains a vital hub in Ethiopian Christianity, attracting pilgrims and visitors worldwide, thus continuing to strengthen the faith and cultural heritage of Ethiopia.
Architectural Features of Lalibela
Lalibela, a historic town in Ethiopia, is renowned for its extraordinary architectural features centered around its ancient rock-hewn churches. These remarkable structures, carved directly into the solid volcanic rock, showcase the ingenuity and religious devotion of its creators. The complex is a testament to medieval Ethiopian architecture, blending spiritual symbolism with impressive engineering techniques that continue to fascinate visitors and scholars alike.
Rock-Hewn Churches Overview
The Lalibela Rock-Hewn Churches in Ethiopia are an extraordinary example of medieval Ethiopian architecture, showcasing remarkable craftsmanship and spiritual significance. Carved directly into the volcanic tuff of the Ethiopian Highlands, these churches represent a unique blend of religious devotion and innovative engineering techniques. Each church is a monolithic structure, either cut from a single block of rock or excavated from the ground, forming a complex interconnected network of passageways, courtyards, and tunnels. Architectural features include intricately carved facades, doorways, and windows, often with symbolic designs reflecting Christian themes. The churches are generally designed as cross-shaped structures with multiple levels, demonstrating careful planning and artistic expression. Notable features also include defensive elements like stone walls and moat-like constructions that add to their historical and spiritual importance. Overall, the Lalibela churches stand as a testament to Ethiopia’s architectural ingenuity and unwavering faith, attracting pilgrims and visitors from around the world.
Notable Structures and Their Designs
The Lalibela churches in Ethiopia are renowned for their unique architectural features that blend religious symbolism with innovative engineering. Carved entirely from solid volcanic rock, these structures are monolithic, meaning they were hewn out of a single piece of stone, showcasing remarkable craftsmanship and precision. The layout of the complex resembles a labyrinth, with numerous interconnected tunnels, courtyards, and passageways that facilitate spiritual pilgrimage and ritual activities.
Notable structures within Lalibela include the Church of St. George, which stands out for its cruciform design and intricate interior carvings, and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, dedicated to the burial site of Christ, featuring a cruciform plan with a central nave. The Rock-Hewn Churches of Lalibela are distinguished by their architectural diversity, encompassing monolithic churches, trenches, and compartments that reflect a deep theological symbolism. Many of these structures are characterized by bell towers, facades with detailed reliefs, and sacred windows that cast colorful light into the interiors, enhancing the spiritual atmosphere.
Construction Techniques and Materials
The Lalibela churches in Ethiopia are renowned for their unique architectural features, innovative construction techniques, and use of local materials, reflecting the deep religious and cultural significance of the site.
- The Lalibela churches are carved directly out of volcanic rock, creating monolithic structures that appear to be emerging from the earth itself.
- The architecture features intricate cross-shaped and cave-like structures with tunnels connecting various parts of the complex.
- Most of the churches are built using a method of excavating from the top down, where workers roughly cut the design into the rock and then refine it into detailed structures.
- The use of volcanic tuff stone, a readily available and durable material, has been predominant in construction, allowing for precise carvings and long-lasting structures.
- Structural stability is achieved through clever engineering—such as the thickness of walls, natural drainage systems, and the strategic placement of doors and windows.
- The design incorporates traditional Ethiopian Christian symbolism, with features like domes, arcades, and iconography carefully integrated into the carved forms.
- The entire complex exemplifies a combination of religious function and extraordinary craftsmanship, utilizing local volcanic rock and minimal mortar or binding agents.
Cultural and Religious Importance
The Church of Lalibela in Ethiopia holds profound cultural and religious significance, serving as a spiritual hub for Ethiopian Orthodox Christians. This remarkable site, carved entirely out of rock, exemplifies the deep faith and rich history of the region. Its importance extends beyond religious practices, embodying Ethiopia’s cultural heritage and national identity. Visitors and believers alike revere Lalibela as a symbol of devotion, tradition, and divine connection.
Pilgrimage Traditions
The Church of Lalibela in Ethiopia holds profound cultural and religious significance, serving as a vital pilgrimage site for Ethiopian Orthodox Christians. It is renowned for its remarkable rock-hewn architecture and its role as a spiritual center, symbolizing faith and religious devotion that dates back to the 12th century. The site is an expression of Ethiopia’s rich history of Christianity and its deep-rooted traditions.
Pilgrimage traditions at Lalibela are an essential aspect of spiritual life for many believers. Pilgrims often undertake arduous journeys to reach this sacred place, seeking spiritual renewal, forgiveness, and divine blessings. The pilgrimage period, especially during Ethiopian Orthodox festivals such as Epiphany, attracts thousands of devotees from across the country and beyond, reinforcing Lalibela’s status as a holy sanctuary.
- Visiting sacred churches carved from rock, including the famous Twelve Apostles Church and the Church of St. George.
- Participating in religious ceremonies, processions, and prayers held during major festivals, notably Epiphany (Timket).
- Engaging in traditional rituals and seeking blessings from clergy and monks residing within the complex.
- Exhibiting devotion by offering prayers, lighting candles, and making symbolic rituals in the churches.
- Experiencing Ethiopia’s unique Christian heritage and cultural practices passed down through generations.
Festivals and Religious Events
Church Lalibela in Ethiopia holds significant cultural and religious importance as a symbol of faith and historical heritage. It is renowned for its rock-hewn churches, which are considered a marvel of medieval engineering and deeply rooted in Ethiopian Orthodox Christianity. These churches serve as vital centers for religious worship, pilgrimage, and community gatherings, reflecting the spiritual devotion of the Ethiopian people. The site is also a UNESCO World Heritage site, emphasizing its global cultural significance.
Throughout the year, various festivals and religious events are celebrated at Lalibela, drawing pilgrims from across Ethiopia and the world. One of the most important celebrations is Timket, the Ethiopian Epiphany, held in January. During Timket, believers commemorate the baptism of Jesus Christ with vibrant processions, water blessings, and church services. Another key event is Ethiopian Christmas, celebrated on January 7, which features special liturgies and festive activities. Additionally, the Feast of Saint Lalibela is observed with prayers and processions, honoring the founder of the churches and his spiritual legacy.
Symbolism and Religious Significance
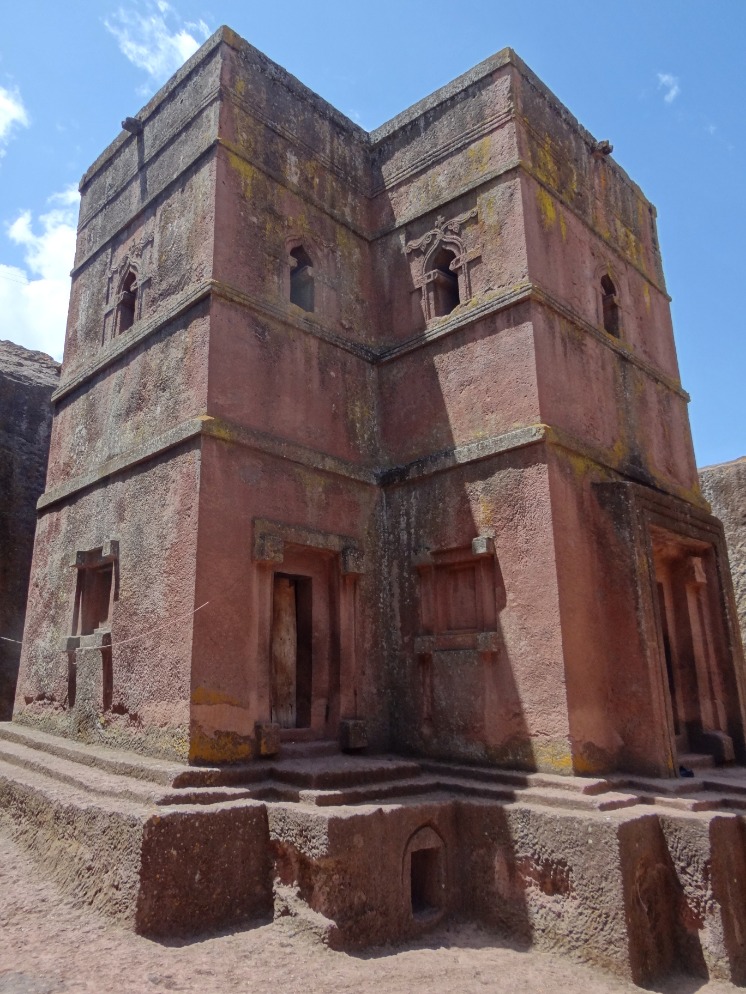

The Church of Lalibela in Ethiopia holds profound cultural and religious significance, symbolizing the enduring faith and spiritual heritage of the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church. These rock-hewn churches are not only architectural marvels but also sacred sites that embody centuries of religious devotion and cultural identity.
- Symbolism of the Churches:
- Representations of heavenly Jerusalem, serving as a terrestrial mirror of divine realms.
- Carved entirely out of solid rock, signifying strength and permanence of faith.
- The arrangement of the churches reflects a spiritual journey from the earthly to the divine.
- Religious Significance:
- Serves as a pilgrimage site for believers, especially during religious festivals such as Timket and Good Friday.
- Functions as a center for worship, prayer, and religious ceremonies for the Ethiopian Orthodox community.
- Houses religious relics and icons that are vital to Ethiopian Christian traditions.
- Cultural Importance:
- Embedment in Ethiopian history and identity, symbolizing resilience and faith.
- Recognition as a UNESCO World Heritage site, highlighting its global cultural significance.
- Inspiration for art, spirituality, and ethical values passed down through generations.
Tourism and Preservation
Tourism plays a vital role in showcasing the rich cultural and historical heritage of destinations around the world. When visiting iconic sites like the Churches of Lalibela in Ethiopia, it is essential to balance tourism with efforts to preserve these precious monuments. Preservation not only protects the architectural and spiritual significance of Lalibela’s rock-hewn churches but also ensures that future generations can experience and learn from this remarkable UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Visitor Information and Access
Church Lalibela in Ethiopia is a renowned pilgrimage site and a remarkable example of medieval Christian architecture. To ensure its preservation and to provide a meaningful experience for visitors, careful management of tourism, visitor information, and access is essential.
- Visitor Information: Visitors are encouraged to learn about the historical and religious significance of the churches before their visit. Informational materials and guided tours are available to enhance understanding and appreciation.
- Access: The site is accessible year-round, with main entry points providing transportation options such as taxis and guided tours. Pathways are maintained to facilitate movement, but some areas require careful navigation due to their carved-in-rock nature.
- Preservation: Efforts are underway to protect the delicate structures from physical wear and environmental damage. Visitors are advised to follow guidelines that prevent harm to the ancient stonework and sculptures.
- Sustainable Tourism: To balance preservation with tourism, visitor numbers are managed through ticketing systems, and educational programs promote respectful behavior among tourists.
- Facilities: Basic facilities, including information centers, rest areas, and sanitation, are provided to enhance visitor comfort while ensuring the site remains pristine.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Tourism at the Lalibela Monolithic Churches in Ethiopia plays a significant role in both cultural preservation and economic development. These ancient rock-hewn structures attract thousands of pilgrims and tourists annually, contributing to the local community’s livelihood. However, managing tourism responsibly is essential to ensure the preservation of this UNESCO World Heritage site for future generations.
- Conservation efforts include regular maintenance, restoration projects, and employing local artisans to repair and preserve the intricate rock carvings.
- Efforts are made to control foot traffic and minimize environmental impact, such as implementing visitor limits and creating designated pathways.
- Local and international organizations collaborate to fund preservation projects and raise awareness about the site’s cultural significance.
- One of the main challenges is environmental degradation, including erosion and damage caused by weathering and pollution.
- Overtourism poses a risk of physical wear on the fragile structures and can dilute the spiritual experience for pilgrims.
- Limited infrastructure and resources hinder comprehensive preservation and visitor management efforts.
- Balancing tourism development with cultural conservation remains an ongoing challenge for stakeholders.
Impact on Local Community
Tourism at Lalibela, Ethiopia, brings significant benefits to the local community by boosting the economy and creating job opportunities. Visitors from around the world come to explore the ancient rock-hewn churches, fostering cultural exchange and local pride. However, increased tourism can also pose challenges, such as environmental degradation and wear-and-tear on the historic structures. The influx of tourists may disrupt the daily lives of residents and lead to commercialization that risks diluting the site’s spiritual and historical significance. It is essential for sustainable tourism practices to be adopted to ensure that Lalibela’s remarkable heritage is preserved while also supporting the well-being of the local community.
UNESCO World Heritage Status
The UNESCO World Heritage Status is an esteemed recognition awarded to sites of cultural, historical, or natural significance around the world. It aims to preserve and protect these treasures for future generations, highlighting their unique value and importance to humanity. One such remarkable site is the Church of Lalibela in Ethiopia, renowned for its extraordinary rock-hewn churches and rich religious history.
Recognition and Criteria
The Church of Lalibela in Ethiopia is a remarkable religious and historical site that has been recognized by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. This designation highlights its global significance and the need to preserve its unique architectural and cultural features. UNESCO’s criteria for such recognition include outstanding universal value, cultural significance, and integrity. Lalibela’s complex of rock-hewn churches exemplifies exceptional craftsmanship and represents a key aspect of Ethiopian Christianity. The site’s inclusion on the World Heritage List emphasizes its importance as a living cultural landscape, attracting pilgrims and visitors from around the world and ensuring its protection for future generations.
Implications for Preservation
The UNESCO World Heritage Status of Lalibela in Ethiopia significantly enhances its preservation efforts by recognizing its cultural and historical importance on a global scale. This designation encourages the protection and maintenance of the rock-hewn churches, ensuring that their unique architectural and archaeological features are conserved for future generations. Additionally, it attracts international attention, funding, and expertise, which can be utilized to implement sustainable preservation strategies. The status also promotes responsible tourism, helping to balance access with conservation, and raises awareness about Lalibela’s spiritual and historical significance. Overall, UNESCO recognition plays a crucial role in safeguarding Lalibela’s rich heritage while fostering cultural pride and educational opportunities for local communities and visitors alike.

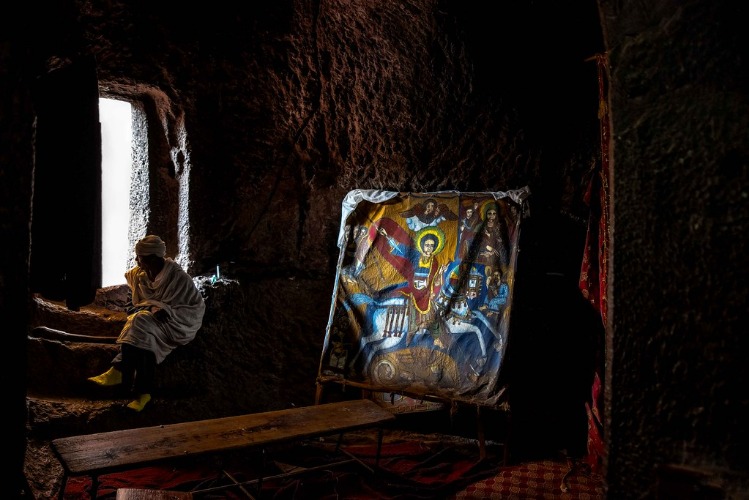



0 Comments