Historical Overview of Dendera Temple
The Dendera Temple, located in Egypt, is an extraordinary ancient religious complex renowned for its remarkable architecture and well-preserved reliefs. Constructed during the Ptolemaic period, it is dedicated to the goddess Hathor and has served as a significant center of worship for centuries. Its history reflects Egypt’s rich cultural and religious heritage, making it a vital site for understanding ancient Egyptian civilization.
Origins and Construction Phases
The Dendera Temple, located in Upper Egypt, is one of the most well-preserved and significant ancient Egyptian religious sites. Its origins date back to the Ptolemaic period, around the 1st century BCE, although the site itself has a history that stretches back to earlier periods, possibly as far as the late Pharaonic era. The temple complex was primarily dedicated to Hathor, the goddess of love, music, and motherhood, and it served as a major religious center for centuries.
The construction of the Dendera Temple evolved over multiple phases, beginning with the original foundation during the late Ptolemaic period. Subsequent rulers, including the Romans, contributed to its expansion and renovation. The temple’s architecture reflects a blend of local Egyptian design with Hellenistic influences, evident in its detailed reliefs, pylons, and sanctuaries. Major construction phases occurred during the reigns of Ptolemy VI, Ptolemy XII, and later Roman emperors, each adding structures or restoring existing ones. Noteworthy features include the Hypostyle Hall, the iced treasury, and the distinctive ceiling carvings illustrating ancient cosmology and mythological scenes. The temple’s construction and renovations showcase the enduring religious significance and architectural ingenuity of ancient Egypt across different dynastic and imperial periods.
Deities and Religious Significance
The Dendera Temple, located in Upper Egypt, is one of the most well-preserved and significant religious sites of ancient Egypt. Its construction began during the late Pharaonic period, primarily during the Ptolemaic era, around the 1st century BCE, although some structures date back to earlier periods, including the New Kingdom. The temple complex was dedicated to Hathor, the goddess of love, beauty, fertility, and motherhood, which is reflected in its intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions and stunning carvings. Over centuries, the temple served as a major center for worship and pilgrimage, blending earlier Egyptian religious traditions with Greco-Roman influences that characterized the Ptolemaic period.
The religious significance of Dendera is closely associated with Hathor, who was worshipped as a nurturing mother goddess and a symbol of joy and music. The temple also depicts several other deities, including Hathor’s consort, Horus of Dendera, a form of the falcon-headed god associated with kingship and protection. The temple’s facade features detailed astronomical and mythological motifs, illustrating the Egyptians’ sophisticated understanding of cosmology and divine mythology. Rituals conducted here included fertility rites, offerings, and ceremonies aimed at ensuring fertility of the land and well-being of the pharaoh and the people. The complex’s architecture and artistic decoration provide invaluable insights into the religious beliefs, practices, and artistic achievements of ancient Egypt, cementing its importance as a cultural and spiritual hub for millennia.
The Role in Ancient Egyptian Religion
The Dendera Temple, located in Upper Egypt, is a remarkable example of ancient Egyptian religious architecture and art. Constructed primarily during the Ptolemaic period, it is dedicated to Hathor, the goddess of love, joy, and motherhood. The temple complex features well-preserved reliefs, inscriptions, and a unique hypostyle hall that exemplifies the grandeur of Egyptian temple design.
Throughout its history, the Dendera Temple played a significant role in the religious life of the ancient Egyptians. It served as a center for worshiping Hathor and other deities, hosting numerous rituals, festivals, and ceremonies. The temple was also associated with the Sun god Ra, with several inscriptions and carvings indicating its importance in solar worship, reflecting the integration of different deities within the Egyptian pantheon.
In addition to its religious functions, the temple served as a political and economic hub, influencing regional power and wealth. Its intricate artwork and hieroglyphic inscriptions provide valuable insights into ancient Egyptian mythology, religious beliefs, and daily life. Over centuries, the Dendera Temple remained a symbol of divine authority and spiritual significance, illustrating the enduring legacy of Egyptian religion and culture.
Architectural Features of Dendera Temple
The Dendera Temple, located in Egypt, is renowned for its stunning architectural features that exemplify ancient Egyptian craftsmanship and religious significance. This ancient complex showcases intricate carvings, grand pylons, and beautifully decorated hypostyle halls that highlight the architectural ingenuity of its builders. Its well-preserved structures provide a fascinating glimpse into the religious practices and artistic achievements of ancient Egypt.

Main Temple Structure
The main temple structure of Dendera Temple is a remarkable example of ancient Egyptian religious architecture, showcasing intricate design and elaborate symbolism. It was constructed primarily during the Greco-Roman period, yet retains elements from earlier Egyptian traditions, reflecting a blend of styles and functions.
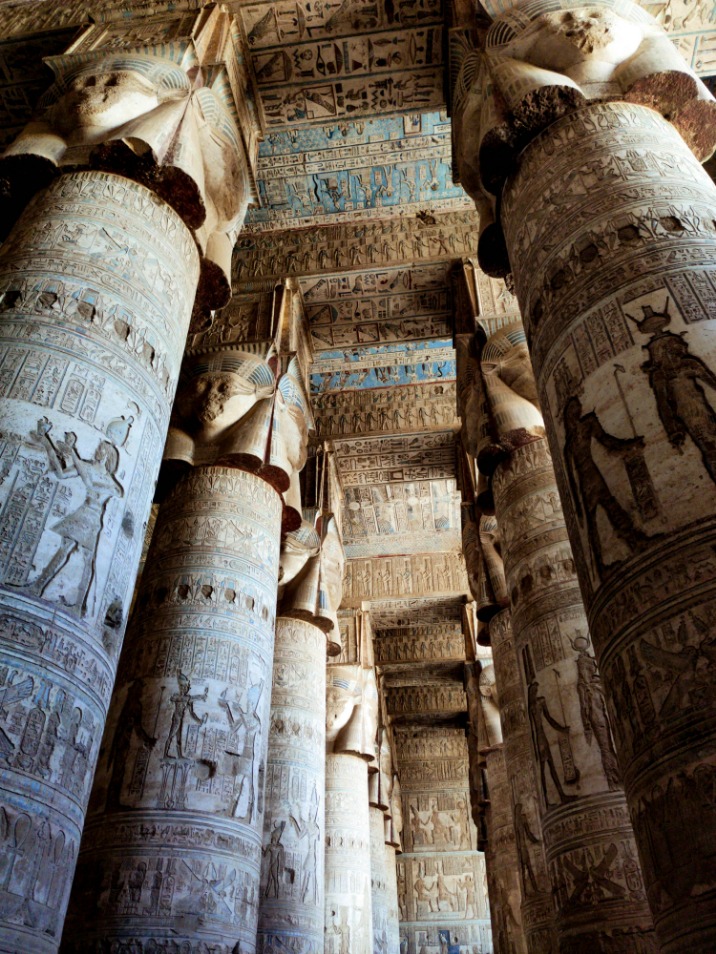
- Vaulted Roofs and Hypostyle Hall: The temple features a hypostyle hall with massive columns supporting large stone roofs, creating a grand space for rituals and ceremonies.
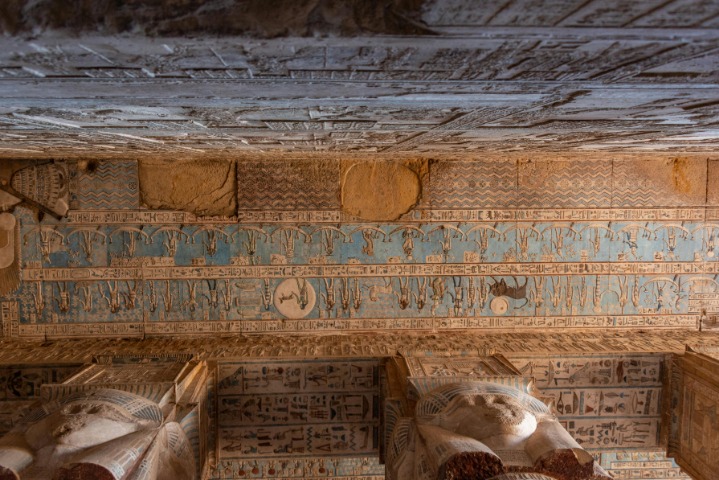
- Ceiling Decorations and Carvings: The ceilings are richly decorated with astronomical and mythological scenes, including representations of the heavens and the goddess Hathor.
- Orientation and Axial Layout: The temple is aligned along a precise axis, with a series of corridors and chambers leading to the innermost sanctuary, emphasizing symmetry and purposefulness.
- Heavily Decorated Walls and Facades: The walls are covered with detailed reliefs, hieroglyphic inscriptions, and images of gods, emphasizing religious storytelling and divine protection.
- Pylon Gateways: The entrance to the temple is marked by grand pylon gateways, adorned with colossal statues and inscriptions, serving as symbolic thresholds between the sacred and the profane.
- Sanctuaries and Shrines: The innermost sanctuary houses the cult statue of Hathor, and surrounding chapels dedicated to various deities add to the temple’s complex architecture.
Decorative Reliefs and Hieroglyphs
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt is renowned for its exquisite architectural features, including finely crafted columns, monumental gateways, and intricately carved walls that showcase the skill of ancient Egyptian builders. The temple’s layout reflects a sophisticated design, with interconnected courtyards, sanctuaries, and a series of corridors that guide visitors through a spiritual journey.
Decorative reliefs within the Dendera Temple are among its most striking elements, illustrating gods, pharaohs, and mythological scenes. These reliefs are rendered with incredible detail and depth, often utilizing low and high relief techniques to create a sense of dimension. The artwork is characterized by scenes depicting religious rituals, offerings, and divine symbols, emphasizing the temple’s sacred purpose.
The hieroglyphs adorning the walls of the Dendera Temple serve both decorative and informative functions, illustrating episodes from Egyptian mythology and royal titulary. The hieroglyphic inscriptions are meticulously carved and painted, offering valuable insights into ancient Egyptian religion and history. They often accompany the reliefs, providing context and enhancing the spiritual atmosphere of the sanctuary.
Hypostyle Hall and Sacred Lake
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt showcases remarkable architectural features that reflect the grandeur of ancient Egyptian religious constructions. Central to the site is the Hypostyle Hall, distinguished by its massive sandstone columns topped with intricate capitals, often depicting lotus and papyrus motifs symbolizing Upper and Lower Egypt. These columns are arranged in a grid-like pattern, creating a vast interior space that impresses visitors with its scale and detailed carvings. The Sacred Lake within the temple precinct served both ritualistic and symbolic purposes. It is a rectangular, man-made water basin that was used for sacred cleansing and offerings, and it also represents the primordial waters of creation in Egyptian mythology. The temple’s architecture emphasizes harmony, symmetry, and the use of symbolic imagery, which together convey the spiritual grandeur and religious significance of the site. Intricately carved Reliefs and inscriptions adorn the walls, illustrating mythological scenes, deities, and royal figures, reinforcing the temple’s role as a powerful religious and cultural monument in ancient Egypt.
Mythological and Cultural Significance
The Dendera Temple in Egypt holds profound mythological and cultural significance, serving as a remarkable testament to ancient Egyptian religion and artistry. This revered site is intricately connected to mythological stories of gods and cosmic forces, reflecting the spiritual beliefs that shaped Egyptian civilization. Its detailed carvings and architectural features illuminate the rich cultural heritage and religious practices central to ancient Egyptian society, making it an essential symbol of their mythological world view.
Connection to Hathor Goddess
Dendera Temple in Egypt holds profound mythological and cultural significance, deeply intertwined with ancient Egyptian religion and mythology. Its design and artwork reflect the worship of deities, notably Hathor, the goddess of love, music, motherhood, and joy. The temple complex showcases elaborate reliefs and sculptures that emphasize Hathor’s central role in Egyptian spiritual life, symbolizing fertility and divine protection.
- Hathor is often depicted within the temple as a cow goddess, embodying motherhood and nurturing qualities, which are integral to Egyptian beliefs about fertility and cosmic order.
- The hypostyle hall and ceilings are adorned with astronomical and mythological motifs that connect Hathor to celestial events, highlighting her association with the sky and the stars.
- Many reliefs depict Hathor as a guide and protector of the pharaoh, reinforcing her significance in the divine kingship and religious practices of ancient Egypt.
- The temple’s architecture and ritual inscriptions emphasize her role as a nurturing mother goddess, reflecting the cultural values placed on fertility, vitality, and cosmic harmony in Egyptian society.
Mythical Narratives Depicted in Reliefs
The Dendera Temple in Egypt is renowned for its rich mythological and cultural significance, which is vividly expressed through its intricate reliefs. These reliefs depict a variety of mythical narratives that reveal the religious beliefs and stories central to ancient Egyptian civilization. Among the prominent themes are the creation myths, gods such as Hathor, Osiris, and Horus, and their legendary interactions that symbolize divine authority and cosmic order. The visual storytelling in these carvings offers insight into the spiritual worldview of the ancient Egyptians, illustrating divine battles, miraculous events, and the journey of the soul. Through these detailed depictions, the temple serves as a mythological archive, preserving stories that conveyed moral lessons, religious duties, and the divine legitimacy of the pharaohs. Overall, the reliefs at Dendera embody a profound connection between myth and culture, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ reverence for their gods and their understanding of the universe.
Festivals and Rituals Celebrated at Dendera
The Dendera Temple in Egypt holds remarkable mythological and cultural significance, reflecting the rich spiritual history of ancient Egypt. It is dedicated to Hathor, the goddess of love, music, and motherhood, and serves as a testament to the religious practices that were deeply embedded in Egyptian society. The temple’s intricate carvings and reliefs depict mythological stories, gods, and rituals that illustrate the beliefs and ceremonial customs of the ancient Egyptians. These elements reveal the importance of mythological narratives in understanding their worldview and religious devotion.
Among the festivals celebrated at Dendera, the most prominent is the Hathor Festival, which honored the goddess and involved intricate rituals, offerings, and processions. This festival was believed to promote fertility, prosperity, and spiritual harmony. During special occasions, priests performed elaborate rituals to invoke Hathor’s blessings, often involving music, dance, and symbolic offerings to ensure the divine favor of the goddess. The temple also played a vital role during the festival of the New Year, marking the rebirth of the sun god and the renewal of life that aligned with the ancient Egyptian calendar.
The rituals conducted at Dendera were deeply rooted in ancient Egyptian religious practices, emphasizing harmony between the divine and the mortal world. These included daily ceremonies and special rites during significant festivals, often performed by priests wearing distinctive garments and utilizing sacred objects. Celebrations at Dendera were not only religious events but also cultural gatherings that reinforced community bonds and spiritual beliefs, leaving a lasting legacy of Egypt’s rich mythological and cultural traditions.
Artistic and Symbolic Elements
The Dendera Temple in Egypt is renowned not only for its historical significance but also for its rich artistic and symbolic elements that adorn its walls and ceilings. These intricate designs and carvings offer a glimpse into ancient Egyptian religious beliefs, mythology, and cultural practices. Through vivid imagery and detailed hieroglyphs, the temple reveals a universe of meaning, blending artistry with symbolism to convey profound spiritual concepts and stories from the past.
Iconography and Artistic Style
The Dendera Temple in Egypt is renowned for its rich artistic and symbolic elements that reflect the religious and cultural beliefs of ancient Egypt. Its intricate carvings and painted reliefs depict gods, mythological scenes, and sacred symbols that convey spiritual significance and cosmological concepts. The temple’s iconography includes depictions of Hathor, the goddess of love and motherhood, often shown with a set of horns and a solar disk, emphasizing her divine status. Artistic style in the Dendera Temple features detailed and highly stylized figures, with an emphasis on clarity, symmetry, and elaborate ornamentation, typical of the Ptolemaic period. These stylistic choices serve not only aesthetic purposes but also reinforce the religious narratives and the divine authority of the pharaohs and gods represented within the temple’s walls.
Symbolic Motifs and Their Meanings
The Dendera Temple in Egypt is renowned for its rich artistic and symbolic elements that convey profound spiritual and cultural meanings. The intricate carvings and reliefs depict a variety of motifs that intertwine religious beliefs, mythological stories, and celestial symbolism. These artistic features serve not only as decoration but also as a language through which the ancient Egyptians expressed their understanding of the cosmos, divine power, and the cycle of life and death.
One of the most prominent symbolic motifs in the Dendera Temple is the depiction of Hathor, the sky goddess associated with fertility, motherhood, and music. Her image, often shown with cow horns and a solar disk, symbolizes nourishment and the divine feminine. The sacred lotus and papyrus plants found in the carvings represent creation, rebirth, and the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt. These motifs emphasize the importance of harmony and balance in the universe.
Additionally, the temple features representations of cosmic phenomena, such as star symbols and celestial deities, which highlight the Egyptians’ fascination with astronomy and the belief that divine forces governed the heavens. The serpent, often associated with protection and eternity, appears in various forms, symbolizing both danger and everlasting life. The use of hieroglyphs alongside these motifs adds layers of meaning, transforming the temple walls into a sacred narrative with spiritual and cosmological significance.
Overall, the artistic and symbolic elements of the Dendera Temple reflect a sophisticated worldview where art served as a conduit for divine communication. The motifs and their meanings reveal the Egyptians’ deep spiritual connection to the cosmos, their reverence for gods and nature, and their commitment to preserving sacred knowledge through their intricate symbolism.
Unique Features of the Zodiac Ceiling
The Zodiac Ceiling of the Dendera Temple is renowned for its exquisite artistic and symbolic elements, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ deep connection with astronomy and spirituality. This masterpiece combines complex iconography, vibrant imagery, and detailed craftsmanship to convey astronomical and mythological themes.
- Intricate Depictions of Zodiac Signs: The ceiling features twelve panel representations of the zodiac animals and symbols, each carefully rendered to align with celestial phenomena and Egyptian cosmology.
- Vivid Colors and Fine Detailing: Bright pigments and meticulous artistry highlight the signs and deities, emphasizing their importance in Egyptian religion and celestial mechanics.
- Symbolic Use of Hieroglyphs and Deities: The artwork integrates hieroglyphic inscriptions and images of gods such as Hathor and Osiris, imbuing the celestial scenes with divine significance.
- Alignment with Celestial Events: The placement and orientation of the zodiac signs reflect astronomical knowledge, aligning with key celestial events like solstices and equinoxes.
- Unique Artistic Style: The ceiling showcases a distinctive blend of Egyptian geometric patterns and mythological motifs, creating a harmonious visual narrative of the cosmos.
Archaeological Discoveries and Conservation
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt is one of the most remarkable archaeological sites, offering a glimpse into ancient Egyptian religion and artistry. Its intricate carvings, well-preserved structures, and rich history attract researchers and explorers worldwide. The ongoing efforts in archaeological discovery and conservation play a crucial role in preserving this invaluable cultural heritage for future generations to study and appreciate.
Excavations and Key Discoveries
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt is renowned for its remarkable archaeological significance, offering invaluable insights into ancient Egyptian religion and culture. Excavations at Dendera have uncovered a wealth of artifacts, elaborate reliefs, and well-preserved structures that shed light on the architectural and artistic achievements of the Ptolemaic and Roman periods. Conservation efforts have been crucial in preserving these artifacts from environmental damage and human interference, ensuring that future generations can continue to study and appreciate this historical site. Key discoveries at Dendera include the magnificent Hathor Temple, intricate frescoes depicting mythological scenes, and the famous zodiac ceiling, which provides vital information about ancient Egyptian astronomy and calendar systems. Ongoing archaeological excavations continue to reveal new chambers, carvings, and relics that deepen understanding of the complex’s religious and ceremonial significance. These discoveries not only enhance our knowledge of ancient Egypt but also highlight the importance of meticulous conservation in safeguarding cultural heritage.
Preservation Efforts and Challenges
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt is one of the most significant archaeological sites, renowned for its striking Egyptian temple architecture and detailed hieroglyphic carvings. Preserving such an ancient monument presents numerous challenges, but ongoing efforts aim to protect its intricate artwork and structural integrity for future generations.
Archaeological discoveries at Dendera have continually shed light on ancient Egyptian religious practices, art, and architecture. These find significant importance in understanding Egypt’s cultural history and spiritual life. However, the delicate nature of the temple’s carvings and the effects of natural weathering, pollution, and human activity threaten its preservation.
Efforts to conserve Dendera involve a combination of modern technology and traditional techniques. Restoration projects aim to stabilize the structures, while advanced imaging helps document and analyze carvings to prevent further deterioration. Conservationists also work to control environmental conditions around the site to minimize damage from humidity, temperature fluctuations, and nearby urban development.
Challenges faced in preserving Dendera include:
- Environmental degradation caused by pollution and climate change
- Tourist traffic leading to physical wear and accidental damage
- Limited funding for extensive restoration and maintenance projects
- Balancing public access with preservation needs
- Addressing structural vulnerabilities due to age and previous restorations
Restoration Projects and Modern Access
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt is one of the most significant archaeological sites, renowned for its well-preserved reliefs and intricate hieroglyphic inscriptions. Over the years, extensive archaeological discoveries have shed light on ancient Egyptian religious practices and artistic achievements, making it a vital part of Egypt’s cultural heritage. Conservation and restoration projects have played a crucial role in preserving these invaluable structures, ensuring their survival against environmental and human-induced threats. Modern access to the site has been enhanced through careful restoration of pathways and visitor facilities, allowing researchers and tourists to experience the grandeur of the temple while maintaining its integrity for future generations.
- Archaeological Discoveries: Excavations at Dendera have revealed numerous artifacts, including statues, temple reliefs, and inscriptions that illuminate ancient Egyptian religious beliefs and artistic techniques.
- Conservation and Restoration Projects: Efforts have included cleaning beneath layers of dirt and grime, reinforcing deteriorated stonework, and stabilizing structural elements to prevent further damage.
- Modern Access: Improved pathways, informational signage, and visitor centers have been established to facilitate safer and more educational visits, ensuring sustainable tourism and ongoing research opportunities.
Modern Significance and Tourism
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt exemplifies the remarkable blend of ancient history and modern tourism, attracting visitors from around the world. As a well-preserved monument of the Greco-Rassan period, it offers insight into Egypt’s rich cultural heritage while serving as a popular destination for travelers seeking historical exploration. Its significance extends beyond its historical value, playing a vital role in contemporary tourism and cultural appreciation.
Visitor Attractions and Tours
The Dendera Temple complex in Egypt holds significant modern relevance as a prominent tourist destination, attracting visitors from around the world eager to explore its ancient history and stunning architecture. Its well-preserved temple structures and intricate hieroglyphic carvings offer a unique glimpse into Egypt’s rich cultural heritage, making it a vital part of Egypt’s tourism industry today.
Visitors to Dendera can enjoy a variety of attractions and tours that enhance their experience of this historic site:
- Guide-led archaeological tours that explain the symbolism and history of the temple’s reliefs and inscriptions.
- Visits to the Hathor Temple, renowned for its detailed carvings and celestial motifs.
- Exploration of the hypostyle halls and the astronomical ceiling, highlighting ancient Egyptian knowledge of astronomy.
- Photography tours offering opportunities to capture the intricate artwork and stunning temple architecture.
- Nighttime visits and light shows that illuminate the temple, showcasing its details in a different ambiance.
- Combined tour packages that include nearby sites such as the Dendera Museum and other ancient ruins in the region.
Importance for Cultural Heritage
The Dendera Temple in Egypt holds profound modern significance as a symbol of ancient Egyptian civilization and its enduring cultural legacy. It attracts numerous tourists from around the world who seek to explore its impressive architecture and intricate reliefs, fostering cultural exchange and economic growth in the region. The site plays a vital role in promoting awareness of Egypt’s rich history and prehistoric achievements, helping to preserve its importance for future generations. Additionally, tourism to Dendera Temple supports local communities by generating employment opportunities and encouraging the appreciation of Egypt’s archaeological heritage. Overall, the temple remains a crucial link between the past and present, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding cultural landmarks for global cultural heritage.
Research and Educational Initiatives
The Dendera Temple in Egypt holds significant modern importance due to its status as a major archaeological site and cultural landmark. It attracts numerous tourists eager to explore its well-preserved hieroglyphic inscriptions and intricate carvings, contributing substantially to Egypt’s tourism industry. The site provides a captivating glimpse into ancient Egyptian religion and artistry, fostering a deeper appreciation for the civilization’s achievements. Additionally, ongoing research initiatives aim to uncover more about its historical context, preservation techniques, and architectural innovations, ensuring its legacy for future generations.
Educational programs and research projects centered around Dendera Temple serve to enhance public understanding of ancient Egyptian history and culture. Universities and archaeological institutes frequently organize excavations, internships, and seminars at the site, promoting scholarly activity and interdisciplinary studies. These initiatives not only support conservation efforts but also inspire new generations of Egyptologists and historians. Overall, Dendera Temple’s role in modern tourism, research, and education underscores its ongoing significance as a vital link to Egypt’s rich heritage.




0 Comments