Overview of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological feature that spans across the eastern part of the country, offering stunning landscapes and diverse wildlife. Known for its deep trenches, volcanic formations, and expansive lakes, the valley is a significant part of the East African Rift System. It attracts travelers, researchers, and adventurers alike who are eager to explore its unique terrain and learn about Earth’s geological history. A map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya provides valuable insights into its size, location, and the various attractions within this awe-inspiring landscape.
Geographical Location and Extent
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a significant geographical feature that stretches across the country, forming part of the larger East African Rift System. This vast and dynamic valley is renowned for its stunning landscapes, rich wildlife, and geological importance, making it a prominent subject in the Great Rift Valley map of Kenya.
- The Great Rift Valley extends approximately 6,000 kilometers from Lebanon in the Middle East down to Mozambique in Southeastern Africa.
- In Kenya, the rift valley runs from the northern border with Ethiopia through central Kenya towards the southern border with Tanzania.
- It features a series of deep lakes, escarpments, volcanoes, and fossil-rich sedimentary deposits, which are prominent on the Great Rift Valley map of Kenya.
- The valley is approximately 50 to 80 kilometers wide in Kenya, with its depth reaching up to 1,000 meters below the surrounding highlands.
- This geographical feature not only shapes the physical landscape but also influences the climate, agriculture, and biodiversity of the region.
Formation and Geological Significance
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geographical feature that extends over 6,000 kilometers from Lebanon to Mozambique, with a significant section running through Kenya. It is famous for its breathtaking landscapes, diverse wildlife, and geological importance, making it a popular destination for tourists and scientists alike.
- Formation: The Great Rift Valley was formed as a result of tectonic plate movements where the African Plate is splitting into the Somali and Nubian plates. This process began around 30 million years ago and continues today, causing the land to slowly fracture and create the rift.
- Geological Significance: The valley is a key area for understanding continental rifting and plate tectonics. It contains features such as rift escarpments, volcanoes, and lakes, which provide valuable insights into Earth’s geological processes. The volcanic activity has also resulted in rich soil, supporting diverse ecosystems and agriculture in the region.
Impact on Kenya’s Topography
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geological feature that stretches across the country, forming a significant part of the East African Rift System. This lengthy valley is characterized by deep valleys, volcanoes, lakes, and diverse landscapes that shape Kenya’s topography. It has played a crucial role in shaping the country’s physical landscape, influencing its elevation, terrain, and natural resources. The valley’s presence creates a series of highlands and lowlands, with spectacular features such as the Rift Valley Lakes and volcanic mountains that attract numerous tourists and researchers alike. Overall, the Great Rift Valley is a defining element in Kenya’s topographical diversity, contributing to the country’s unique geographic identity and ecosystem diversity.
Key Features of the Great Rift Valley
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological feature known for its stunning landscapes and diverse ecosystems. Characterized by deep valleys, volcanic mountains, and expansive lakes, it provides a unique glimpse into the Earth’s tectonic processes. The valley’s key features include towering escarpments, fertile plains, and rich wildlife habitats, making it a significant area for both science and tourism. Exploring the Great Rift Valley map of Kenya reveals the intricate network of rifts that shape the region’s dramatic scenery and vibrant biodiversity.
Major Rift Valleys and Segments
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geographical feature characterized by its extensive series of rift valleys, which stretch from the northern part of the country down to the south. These valleys are marked by dramatic escarpments, lakes, and volcanic landscapes, making them significant both geologically and ecologically. The key features of this rift include its tectonic origin, large lakes such as Lake Turkana and Lake Naivasha, and its diverse wildlife habitat.
Major Rift Valleys are segmented parts of the entire rift system, each with distinct characteristics. These segments include the northern, central, and southern sections, each featuring unique volcanic activities, escarpments, and ecosystems. The northern segment, for example, is known for its arid landscapes and Lake Turkana, while the central segment is more fertile and densely populated with lakes and forests. The southern segment extends towards Tanzania, merging into other rift systems.
The segments are further divided into smaller segments or fault lines that define the geological boundaries of the rift. These fault lines are responsible for the formation of the rift valleys and influence seismic activity in the region. The great rift is also characterized by numerous volcanic features, including calderas and volcanic cones, which are prominent along the segments like the Menengai and Olkaria volcanoes. Overall, the Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a dynamic geological zone vital to understanding tectonic activity, regional ecology, and human settlement patterns.
Crater Lakes and Excavations
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological feature characterized by a series of deep trenches, escarpments, and volcanic formations that run through the landscape. It is renowned for its impressive crater lakes, which are formed within volcanic calderas and offer stunning scenery and ecological diversity. The valley’s excavations and fossil sites provide valuable insights into early human history, making it a crucial area for archaeological research. These features contribute to the valley’s significance as a major geological and biological region, attracting tourists, scientists, and nature enthusiasts alike.
Active Volcanic Sites
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is renowned for its striking geological features and vibrant volcanic activity. It stretches across the country, creating a dramatic landscape characterized by deep trenches, escarpments, and a series of lakes and grasslands. The valley is a key feature of the East African Rift System, which is an active divergent tectonic boundary.
One of the main features of the Great Rift Valley is its extensive network of fault lines and rift valleys that have been formed over millions of years through tectonic movements. These formations have resulted in a series of escarpments and depressions that make the landscape unique. The valley is also home to several notable lakes, including Lake Naivasha, Lake Nakuru, and Lake Bogoria, which are important ecological zones.
Active volcanic sites are prominent within the Great Rift Valley. These include Mount Longonot, a dormant stratovolcano with ongoing geothermal activity; Mount Suswa, known for its lava caves and volcanic features; and Mount Eburru, which is part of a volcanic complex. The area around these volcanoes is characterized by hot springs, geysers, and fumaroles, indicating active geothermal processes.
The volcanic activity in the region has contributed to fertile soils, supporting rich biodiversity and agriculture, especially in regions surrounding the volcanoes. The ongoing geological processes continue to shape the landscape, making the Great Rift Valley a dynamic and fascinating area for both scientists and tourists alike.
Major Landmarks and Points of Interest
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a region rich in natural beauty and historical significance, attracting travelers and explorers from around the world. This expansive valley features a variety of major landmarks and points of interest that showcase the diverse ecosystems, geological formations, and cultural heritage of the area. Exploring these sites provides a unique glimpse into the Earth’s geological processes and Kenya’s vibrant history.
Lake Turkana
Lake Turkana is one of the most significant landmarks in the Great Rift Valley of Kenya. Known as the world’s largest desert lake, it is locally called “Jade Sea” due to its striking turquoise color. The lake extends over 250 kilometers and is renowned for its unique ecosystem, including numerous bird species and crocodiles. Nearby, the Loiyangalani town offers cultural insights into the indigenous communities, such as the Turkana people. Lake Turkana’s landscape features striking volcanic formations and the Chalbi Desert, making it a fascinating point of interest for travelers exploring the Great Rift Valley map of Kenya. It also holds archaeological importance, with numerous ancient fossils discoverable in the surrounding area, shedding light on human evolution history.
Lake Naivasha
Lake Naivasha, situated in the Great Rift Valley of Kenya, is one of the most notable landmarks in the region. Surrounded by lush vegetation and vibrant wildlife, it serves as a key point of interest for visitors exploring the Rift Valley. The lake is renowned for its abundant birdlife, including pelicans, kingfishers, and herons, making it a paradise for birdwatchers.
Nearby attractions include Crescent Island Game Sanctuary, where visitors can enjoy guided walks among giraffes, zebras, and buffalos. Hell’s Gate National Park, close to Lake Naivasha, offers striking landscapes, geothermal activity, and opportunities for rock climbing and cycling. Additionally, the flower farms around the lake are famous for their vibrant blooms and are a vital part of Kenya’s horticultural industry.
These landmarks and points of interest make Lake Naivasha a must-visit destination within the Great Rift Valley map of Kenya, showcasing the region’s diverse ecosystems and natural beauty.
Hell’s Gate National Park
Hell’s Gate National Park, located in the Great Rift Valley of Kenya, is renowned for its striking landscapes and diverse wildlife. This park offers visitors a unique opportunity to experience the breathtaking scenery of the Rift Valley, characterized by dramatic cliffs, geothermal activity, and expansive savannahs. Major landmarks within the park include Fischer’s Tower, a towering volcanic plug that provides panoramic views of the area, and the prominent Olkaria Geothermal Power Station, showcasing the region’s geothermal energy development. The park is also famous for its natural geysers, hot springs, and the stunning Central Tower, a volcanic formation that adds to the park’s allure. Visitors can explore the park through walking or cycling safaris, and it is a popular spot for birdwatching, rock climbing, and game viewing, with animals such as zebras, giraffes, and buffalos regularly sighted in the area. Hell’s Gate National Park is an essential stop for anyone interested in exploring the natural beauty and geological wonders of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya.
Masai Mara and Surrounding Ecosystems
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is renowned for its diverse landmarks and rich ecosystems that attract travelers and nature enthusiasts alike. One of the most famous attractions within the area is the Masai Mara National Reserve, a renowned wildlife haven home to the “Big Five” animals and millions of migratory wildebeests. Surrounding ecosystems include savannahs, acacia woodlands, and riverine forests that support a wide variety of flora and fauna. These ecosystems are interconnected, creating a vibrant landscape that plays a vital role in Kenya’s ecological health. Visitors can explore breathtaking viewpoints such as the Escarpment, the Olololaim10s, and the Mara River, which are integral to understanding the region’s natural beauty and biodiversity. The Great Rift Valley map of Kenya highlights these key landmarks, showcasing their significance in both conservation and tourism.”
Map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological and scenic feature that stretches across the landscape, offering breathtaking views and diverse wildlife. The map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya provides a detailed overview of this historic and natural wonder, highlighting key locations, lakes, volcanic regions, and wildlife reserves. Exploring the map helps visitors and researchers understand the valley’s vast expanse and significance in both natural history and tourism.
Legend and Symbols Explanation
The map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya features a detailed representation of this significant geological formation, highlighting key geographic and geological features. The legend included on the map explains the various symbols and colors used to identify major landmarks, fault lines, lakes, and volcanic formations within the valley area. Symbols such as dashed lines typically denote fault lines, while solid lines mark the main rift edges. Different colors are used to distinguish between lakes, volcanic regions, and highlands. For example, blue areas indicate lakes like Lake Naivasha and Lake Nakuru, and volcanic symbols mark active or dormant volcanoes like Mount Longonot and Mount Suswa. The legend helps users interpret the map accurately, providing essential information about the terrain and geological features of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya.
Topographical Features on the Map
The map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya highlights the extensive topographical features that define this remarkable geological formation. It showcases the deep chasms and valleys formed by tectonic movements, with prominent features such as the Gregory Rift and the Kenyian Rift Valley. The map illustrates the elevation variations, including highlands, lowlands, volcanoes, and lakes that are characteristic of this region. Notable topographical features include the presence of escarpments, volcanic cones, and expansive plains, which contribute to the area’s diverse landscape. Overall, the map provides a detailed view of the intricate topography that makes the Great Rift Valley in Kenya a significant geographical and ecological region.
Major Cities and Settlements
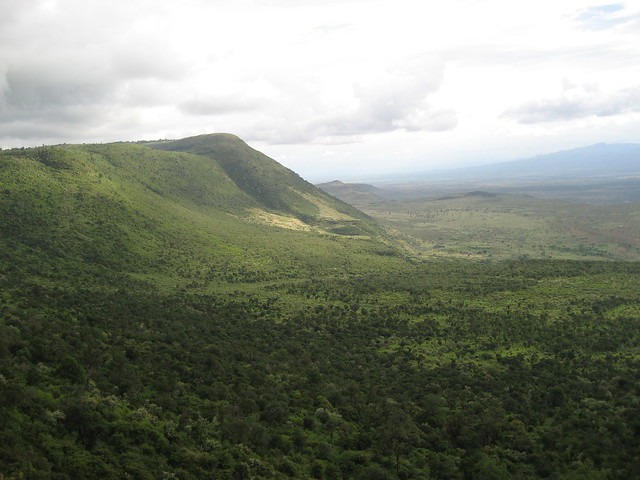

The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geological and geographical feature that stretches from the northern part of the country to the south, forming a deep and scenic trench. The map of the Great Rift Valley in Kenya highlights this extensive rift and its surrounding areas, showcasing the diverse landscapes and ecosystems. Major cities and settlements along the Rift Valley include Nairobi, the capital city of Kenya, which is located towards the southern part of the valley. Other significant towns are Nakuru, famous for its flamingos and nearby Lake Nakuru, and Eldoret, a key economic hub in western Kenya. Along the rift, you will also find Kisumu, situated near Lake Victoria, and Naivasha, known for its freshwater lake and surrounding wetlands. These cities and settlements are vital centers of culture, commerce, and tourism, offering visitors a glimpse into the unique geography and vibrant communities within the Great Rift Valley in Kenya.
Ecological and Cultural Significance
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds immense ecological and cultural significance, serving as a vital cradle of biodiversity and a crossroads of diverse human communities. This iconic landscape not only supports a wide variety of wildlife and unique ecosystems but also reflects the rich history and traditions of the indigenous peoples. Understanding its ecological and cultural importance enhances appreciation for this remarkable region and highlights the need for its conservation.
Biodiversity and Wildlife
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds exceptional ecological and cultural significance, serving as a vital habitat for diverse biodiversity and a region rich in cultural heritage. Its landscapes support a wide variety of flora and fauna, making it an important area for wildlife conservation and ecological research.
- Home to numerous endemic species such as the graceful flamingos at Lake Nakuru and the rare white rhinos at Lewa Wildlife Conservancy.
- Provides critical breeding and feeding grounds for migratory birds, contributing to global avian biodiversity.
- Contains diverse ecosystems including lakes, volcanoes, grasslands, and forests, supporting a wide range of plant and animal life.
- Enables local communities to sustain their cultural practices and traditional livelihoods, which are often intertwined with conservation efforts.
- Acts as a living cultural landscape where archaeological sites reveal insights into ancient human history and migration patterns.
Traditional Communities and Cultures
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds immense ecological and cultural significance, serving as a vital habitat for diverse flora and fauna while also being a cradle of traditional communities. Its landscapes, ranging from lakes and volcanoes to savannahs, support unique ecosystems that are crucial for maintaining regional biodiversity.
- Ecologically, the valley hosts important wetlands, lakes, and forests that provide breeding grounds for countless bird species, including flamingos and pelicans.
- Culturally, it is home to ancient communities such as the Maasai, Kikuyu, and Luo, each with rich traditions, languages, and ways of life deeply intertwined with the land.
- The landscapes and resources of the Rift Valley have shaped the livelihoods and customs of these indigenous peoples for generations.
- Preserving the ecological integrity of the region is essential for maintaining the traditional practices and cultural heritage of the local communities.
- In addition, the valley’s cultural sites and archaeological remains offer insights into early human history, highlighting its importance as a site of human civilization and cultural identity.
Conservation Areas and Reserves
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds immense ecological and cultural significance, serving as a vital habitat for diverse flora and fauna, including many endemic and endangered species. Its unique landscape, shaped by tectonic activity, creates fertile soil that supports rich biodiversity and important agricultural regions. Culturally, the valley is home to numerous indigenous communities with deep historical roots, whose traditions and lifestyles are intertwined with the landscape. Conservation areas and reserves within the Great Rift Valley, such as Maasai Mara National Reserve, Amboseli National Park, and Lake Nakuru National Park, are crucial for protecting this unique environment. These protected areas help preserve wildlife, promote sustainable tourism, and maintain ecological balance, ensuring that both the natural heritage and cultural identities of the region are preserved for future generations.
Tourism and Accessibility
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a breathtaking region that attracts travelers from around the world, offering stunning landscapes and rich cultural experiences. Ensuring accessibility for all visitors is essential to make this natural wonder inclusive and enjoyable. Exploring the area through detailed maps helps tourists navigate easily and appreciate the unique features of the Rift Valley while promoting sustainable tourism practices that accommodate diverse needs.
Popular Tourist Destinations
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is one of the most popular tourist destinations, renowned for its stunning landscapes and rich cultural heritage. Accessibility has improved significantly over the years, making it easier for travelers to explore this remarkable region.
Visitors can enjoy a variety of attractions such as safaris in Maasai Mara, lakes like Nakuru and Bogoria, and volcanic formations. Many tourist spots are equipped with facilities to ensure accessibility for all travelers, including those with mobility challenges.
Other popular destinations around the Great Rift Valley include Hell’s Gate National Park, Lake Naivasha, and Mount Longonot. These sites offer breathtaking views and diverse wildlife, drawing nature lovers from around the world.
Overall, the Great Rift Valley map Kenya showcases a region that is not only culturally and environmentally significant but also committed to making tourism accessible to everyone, ensuring an unforgettable experience for all visitors.
Transport Routes and Accessibility
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prime destination for tourists, offering breathtaking landscapes and unique geological features. Ensuring accessibility for all visitors is essential to promote inclusive tourism and allow everyone to experience its natural beauty. Well-developed transport routes, including major highways, rural roads, and local pathways, connect key hotspots within the valley, making travel convenient and efficient. Public transportation options such as buses and shared taxis facilitate movement across different regions, while private vehicles offer more flexibility. Additionally, efforts are underway to improve infrastructure to suit visitors with mobility challenges, including accessible walking paths and transportation services. These advancements in transport routes and accessibility ensure that the wonders of the Great Rift Valley are accessible to a diverse range of tourists, enhancing their overall experience of this remarkable natural site in Kenya.
Guided Tours and Activities
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya offers a diverse range of tourism and accessibility options, making it a remarkable destination for travelers of all backgrounds. Guided tours provide insightful explorations of the valley’s stunning landscapes, abundant wildlife, and archaeological sites, ensuring visitors gain a comprehensive understanding of the region’s significance. Many tour operators prioritize accessibility, accommodating travelers with mobility challenges through specialized transport and tailored activities. Visitors can enjoy guided safaris, nature walks, and cultural experiences that showcase the rich heritage of the area. Overall, the combination of accessible tourism services and engaging activities makes the Great Rift Valley in Kenya an inclusive and memorable destination for everyone.




0 Comments