Overview of Namibia’s Economy
Namibia’s economy is characterized by a mix of mining, agriculture, and tourism sectors, which play a vital role in shaping its economic landscape. The country has a relatively small population, making GDP per capita an important indicator of individual prosperity and economic well-being. Understanding Namibia’s GDP per capita provides valuable insights into the standard of living and economic development within the nation.
Economic Structure and Key Sectors
Namibia’s economy is classified as an upper-middle-income economy with a diverse structure that includes mining, agriculture, manufacturing, and services. The country benefits from rich natural resources, particularly minerals and wildlife, which significantly contribute to its GDP. Despite having significant mineral reserves, Namibia faces economic challenges such as unemployment and income inequality, affecting its overall growth prospects.
The economic structure of Namibia relies heavily on the mining sector, which accounts for a substantial portion of GDP and exports, with assets like diamonds, uranium, gold, and copper playing vital roles. Agriculture, including livestock farming and crop cultivation, supports rural livelihoods but remains less dominant compared to mining. The manufacturing industry is developing gradually, focusing on processing raw materials and adding value locally. The services sector, including tourism, banking, and retail, is increasingly vital for economic growth, with tourism especially benefiting from Namibia’s famous wildlife and scenic landscapes.
Overall, Namibia’s economy is characterized by a reliance on resource exports and a growing emphasis on tourism and services to diversify income sources. Despite its resource wealth, the country seeks to improve economic stability, reduce poverty, and enhance the standard of living, which are crucial for increasing GDP per capita and fostering sustainable growth.
Historical Trends in GDP per Capita
Namibia’s economy is classified as an upper-middle-income economy, heavily dependent on the mining sector, particularly diamond, uranium, and zinc extraction. Agriculture and tourism also contribute significantly to the country’s GDP. Over the years, Namibia has experienced moderate economic growth, influenced by global commodity prices and regional economic dynamics.
Historical trends in Namibia’s GDP per capita reveal periods of growth and stagnation, often correlating with fluctuations in global mineral markets. After gaining independence in 1990, Namibia’s GDP per capita steadily increased, supported by robust mineral exports and a relatively stable macroeconomic environment. However, growth rates have varied due to external shocks such as commodity price declines and internal challenges like unemployment and inequality. In recent years, efforts to diversify the economy have aimed to improve economic resilience and sustain income growth per capita, but disparities and economic vulnerabilities remain significant challenges for long-term development.
Recent Economic Developments
Namibia’s economy is classified as an emerging market with a focus on mining, agriculture, and tourism sectors, which are significant contributors to its GDP. Over recent years, the country has experienced moderate economic growth, driven by diamond and uranium mining, as well as increased investments in infrastructure and development projects. However, Namibia faces economic challenges such as high unemployment rates, income inequality, and reliance on commodity exports that are susceptible to global market fluctuations.
Recent economic developments in Namibia include efforts to diversify the economy and reduce dependence on mineral exports. The government has implemented reforms aimed at attracting foreign direct investment and improving the business climate. Additionally, initiatives to develop renewable energy sources and boost the manufacturing sector are underway. Despite these efforts, Namibia’s GDP per capita remains relatively low, reflecting the need for ongoing economic reforms and sustainable growth strategies to improve living standards for its population.
Current GDP Per Capita of Namibia
Namibia’s current GDP per capita provides valuable insight into the country’s economic performance and living standards. As a middle-income country, Namibia has been working towards enhancing economic growth and improving the welfare of its citizens. Analyzing recent data on GDP per capita helps to understand the nation’s economic stability and development progress in the current global context.
Latest Statistics and Figures
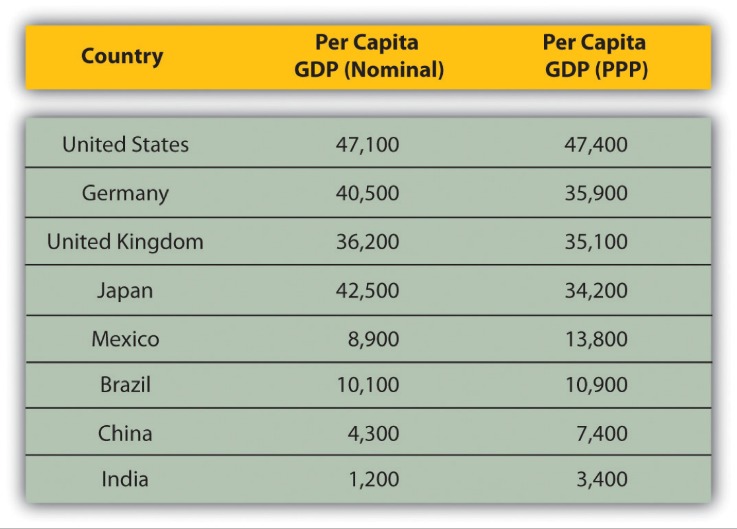
The current GDP per capita of Namibia provides an important indicator of the country’s economic performance and living standards. As of the latest available statistics, Namibia’s GDP per capita is approximately $4,340 USD. This figure reflects the economic output divided by the population, giving insight into the average economic well-being of its citizens. Namibia’s economy is primarily driven by mining, agriculture, and tourism sectors, which influence its overall GDP per capita. Despite steady growth over recent years, Namibia still faces challenges related to income inequality and unemployment, which impact the distribution of economic benefits among its population. Continued efforts to diversify the economy and improve infrastructure are essential for enhancing the GDP per capita and overall economic prosperity of Namibia.
Comparison with Regional and Global Averages
The current GDP per capita of Namibia provides insight into the economic situation of the country relative to its population size and overall economic output. This measure reflects the average economic productivity and living standards within Namibia. When comparing Namibia’s GDP per capita to regional and global averages, it helps to contextualize its economic development and identify areas for growth or improvement.
- Namibia’s GDP per capita is approximately $5,400 (based on recent estimates), which indicates moderate economic output per person relative to many neighboring countries.
- Compared to the Southern African Development Community (SADC) regional average, Namibia’s GDP per capita is slightly below or around the regional mean, highlighting economic disparities within the region.
- On a global scale, Namibia’s GDP per capita remains lower than the world average, reflecting its classification as an emerging economy with room for development.
Distribution of Wealth and Income Levels
Namibia’s current GDP per capita is approximately $5,500, reflecting its status as a lower-middle-income country with significant economic disparities. The nation’s economy heavily relies on mining, agriculture, and tourism sectors, which influence overall income levels. Wealth distribution in Namibia is notably unequal, with a small proportion of the population holding a large share of the country’s wealth. Income levels vary considerably between urban and rural areas, with urban residents generally experiencing higher income levels compared to those in rural regions. Efforts to enhance equitable growth and reduce income inequality remain central to Namibia’s economic development agenda.
Factors Influencing GDP Per Capita in Namibia
GDP per capita in Namibia is shaped by a variety of interconnected factors that influence the country’s economic performance. Key elements include natural resource availability, levels of investment, government policies, and infrastructure development. Additionally, demographic trends and global economic conditions also play crucial roles in determining the average income of individuals within Namibia. Understanding these factors provides valuable insights into the country’s economic growth and living standards.
Natural Resources and Mining Sector
Natural resources play a significant role in shaping Namibia’s GDP per capita, particularly through the mining sector, which is a major contributor to the country’s economy. Namibia is rich in mineral resources such as diamonds, uranium, copper, zinc, and gold, providing substantial revenue and foreign exchange earnings. The mining industry’s performance directly impacts overall economic growth and individual income levels, influencing the national GDP per capita. Additionally, the sustainability and regulation of resource extraction determine the long-term benefits to the economy, affecting income distribution and living standards. Fluctuations in global commodity prices can also lead to volatility in revenue, thereby impacting GDP per capita. Effective management of natural resources and investment in the mining sector are crucial for ensuring steady economic growth and improving the standard of living for Namibians.
Agriculture and Livestock
GDP per capita in Namibia is significantly influenced by various factors related to agriculture and livestock, which are vital sectors in the country’s economy. The productivity within these sectors depends on the availability of arable land, access to modern farming technology, and effective water management practices. Additionally, climatic conditions such as rainfall patterns directly impact crop yields and livestock health, thereby affecting overall economic output. Investment in infrastructure, including roads and market facilities, also plays a crucial role in enabling farmers and herders to efficiently distribute their products and access wider markets. Furthermore, government policies aimed at supporting sustainable agriculture and livestock development can enhance productivity and, consequently, improve GDP per capita. Overall, the sustainability and growth of Namibia’s agriculture and livestock sectors are essential determinants of its economic well-being and individual prosperity.
Tourism Industry Impact
Several factors influence the GDP per capita of Namibia, with the tourism industry playing a significant role. The tourism sector contributes substantially to the country’s income by attracting visitors who spend on accommodations, transportation, and local attractions, thereby boosting overall economic output. Additionally, tourism stimulates employment, increases foreign exchange earnings, and encourages investment in infrastructure, all of which positively impact GDP per capita. Other factors affecting Namibia’s GDP per capita include the availability of natural resources such as minerals and fish, the level of agricultural productivity, economic diversification efforts, and government policies aimed at fostering economic growth. External factors like global commodity prices and geopolitical stability also play a role in shaping Namibia’s economic performance, influencing household incomes and overall prosperity.
Foreign Investment and Economic Policies
Factors influencing GDP per capita in Namibia include a combination of foreign investment and economic policies that shape the country’s overall economic performance. Foreign investment plays a crucial role by providing capital, technology, and expertise, which contribute to the development of key sectors such as mining, manufacturing, and services. Increased foreign direct investment can boost productivity and create employment opportunities, thereby raising individual income levels and overall GDP per capita. Additionally, Namibia’s economic policies significantly impact GDP per capita by establishing a regulatory environment that encourages investment, promotes sustainable development, and stabilizes the economy. Sound fiscal and monetary policies, alongside efforts to diversify the economy and improve infrastructure, further support economic growth. The effectiveness of these policies can determine the extent to which Namibia benefits from both domestic and international economic activities, ultimately influencing the per capita income.
Challenges Facing Namibia’s Economy
Namibia’s economy faces several significant challenges that impact its GDP per capita and overall development. Despite being rich in natural resources, such as minerals and other commodities, the country struggles with issues like high unemployment, economic inequality, and dependence on resource exports. These factors hinder sustainable growth and pose difficulties in improving the standard of living for its citizens. Addressing these challenges is crucial for Namibia to achieve a more balanced and resilient economy.
Economic Inequality and Poverty
Namibia’s economy faces several ongoing challenges that impact its overall growth and development, particularly when examining its GDP per capita. Economic inequality remains a significant obstacle, with wealth concentrated among a small elite, leaving a large portion of the population in poverty. This disparity hampers social cohesion and limits access to essential services such as education, healthcare, and employment opportunities. Poverty is widespread, especially in rural areas where dependence on agriculture makes communities vulnerable to climatic fluctuations and resource scarcity. Additionally, Namibia’s economy is heavily reliant on mineral exports, making it susceptible to global price fluctuations, which directly affect income levels and GDP per capita. Efforts to diversify the economy and implement inclusive growth policies are essential to address these challenges and improve living standards across the country.
Unemployment Rates
The GDP per capita of Namibia offers insights into the overall economic health of the country, but several challenges hinder its growth and impact the standard of living. Namibia’s economy faces structural issues such as heavy dependence on diamond mining, which makes it vulnerable to global commodity price fluctuations. Additionally, the country struggles with high unemployment rates, particularly among youth, which hampers economic development and social stability. Limited diversification into other sectors like manufacturing and agriculture further restricts job creation and economic resilience. Socioeconomic inequalities and access to quality education also contribute to persistent unemployment and hinder efforts to boost GDP per capita. Addressing these challenges is essential for sustainable economic growth and improving the living standards of Namibians.
Infrastructure and Development Constraints
Namibia’s economy faces several significant challenges that impact its GDP per capita and overall development. These hurdles include limited infrastructure, high unemployment rates, and dependency on finite natural resources, which collectively hinder sustainable growth. Addressing these constraints is critical for improving the standard of living and enhancing economic resilience.
- Insufficient infrastructure development, including transportation, energy, and water supply systems, restricting economic activities and access to markets.
- Over-reliance on resource-driven sectors such as mining and agriculture, leading to vulnerability to commodity price fluctuations and environmental degradation.
- High unemployment rates, particularly among youth, limiting income growth and consumer spending, which are essential for economic expansion.
- Educational and skills development gaps that hinder workforce productivity and diversification into higher value-added industries.
- Limited access to finance and investment for small and medium enterprises, restricting entrepreneurship and economic diversification.
- Environmental challenges, including droughts and desertification, that negatively impact agricultural productivity and rural livelihoods.
Impact of Global Market Fluctuations
The GDP per capita of Namibia is influenced by various challenges that hinder the nation’s economic growth and stability. One significant obstacle is the reliance on primary commodities such as minerals and diamonds, which makes the economy vulnerable to fluctuations in global markets. When global demand and prices drop, Namibia’s revenue diminishes, adversely affecting income levels and living standards.
Global market fluctuations pose a considerable threat to Namibia’s economy by causing unpredictable commodity prices. These swings can lead to decreased export earnings, reduced government revenue, and increased economic uncertainty. As a result, income disparities may widen, impacting GDP per capita negatively.
Additionally, global financial shocks can lead to capital flight and reduced foreign investment, further hampering economic development. Namibia’s limited diversification and dependence on exports make it more susceptible to these external shocks, which can slow down growth and influence the overall GDP per capita of the country.
Strategies for Economic Growth and Improving GDP Per Capita
Enhancing economic growth and increasing GDP per capita are vital goals for Namibia’s development. Effective strategies involve fostering sustainable industries, investing in infrastructure, and improving education to boost productivity. By implementing targeted policies, Namibia can create a more inclusive economy that elevates the standard of living for its citizens and promotes long-term prosperity.
Diversification of Economy
To enhance Namibia’s GDP per capita and promote sustainable economic growth, it is essential to focus on diverse strategies that foster economic diversification. This includes investing in various sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and renewable energy to reduce dependence on a limited number of industries, particularly mining. Developing human capital through education and skills training can improve productivity and innovation across different sectors. Encouraging private sector growth by creating a conducive business environment, reducing bureaucratic barriers, and supporting entrepreneurship is vital for economic expansion. Additionally, infrastructure development, improved access to technology, and strengthening regional trade partnerships can facilitate broader market access and stimulate economic activity. Implementing these strategies can help Namibia achieve higher income levels, improved living standards, and a resilient economy capable of weathering global fluctuations.
Enhancing Education and Workforce Skills
Strategies for economic growth and improving GDP per capita in Namibia primarily focus on diversifying the economy, investing in education, and enhancing workforce skills. A key approach is to reduce dependence on traditional sectors like mining and agriculture by promoting sectors such as tourism, manufacturing, and renewable energy. These efforts can stimulate new job opportunities and increase national productivity. Additionally, investing in education systems to improve access and quality can equip the workforce with the necessary skills for a modern economy. Skills development initiatives, vocational training, and higher education reforms are vital to foster innovation and attract foreign investment. Encouraging entrepreneurship and supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) can further drive economic diversification and income growth. Infrastructure development, including transportation and digital connectivity, is also essential to facilitate business operations and expand markets. Ultimately, a comprehensive strategy combining economic diversification, human capital development, and infrastructure investment will be critical for Namibia’s sustained GDP per capita growth and overall economic resilience.
Promoting Small and Medium Enterprises
Enhancing Namibia’s GDP per capita requires a comprehensive approach focused on sustainable economic growth and development. Promoting small and medium enterprises (SMEs) plays a crucial role in this strategy, as they are significant contributors to employment, innovation, and diversification of the economy. Implementing policies that provide easier access to finance, reduce regulatory burdens, and support entrepreneurial skills can foster a vibrant SME sector. Additionally, investing in infrastructure, education, and technological advancements can improve productivity and competitiveness. Encouraging foreign direct investment and regional integration can also expand market opportunities for domestic businesses. These combined efforts can stimulate economic activity, improve income levels, and ultimately elevate Namibia’s GDP per capita, ensuring inclusive growth for all citizens.
Attracting Foreign Direct Investment
Enhancing Namibia’s GDP per capita involves implementing strategic policies that foster sustainable economic growth and attract foreign direct investment (FDI). Key strategies include diversifying the economy beyond reliance on natural resources such as minerals and fishing by developing sectors like tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing to create broader employment opportunities.
Improving infrastructure, including transportation, energy, and communication networks, can make Namibia more attractive to foreign investors by reducing operational costs and increasing efficiency. Additionally, streamlining bureaucratic processes and establishing transparent legal frameworks can enhance the ease of doing business, encouraging more FDI inflows.
Investment in education and skills development is crucial for creating a more competent workforce capable of supporting emerging industries. Offering incentives such as tax breaks, simplified licensing procedures, and investment promotion programs further incentivizes foreign companies to establish operations within Namibia.
Strengthening regional and international trade links through free trade agreements and participation in global supply chains can also boost Namibia’s economic growth and GDP per capita. Overall, a comprehensive approach that embraces economic diversification, infrastructure development, investment facilitation, and workforce capacity building can significantly improve Namibia’s economic standing and living standards.
Future Outlook for Namibia’s GDP Per Capita
The future outlook for Namibia’s GDP per capita presents a mix of opportunities and challenges as the nation strives for sustainable economic growth. With ongoing sectoral developments, investments in infrastructure, and diversification efforts, Namibia aims to improve the standard of living for its citizens. However, factors such as global economic fluctuations, resource dependency, and social development needs will play a critical role in shaping the trajectory of the country’s income levels in the coming years.
Projected Growth Trends
Namibia’s GDP per capita is expected to experience moderate growth in the coming years, supported by ongoing economic diversification and investment in key sectors such as mining, agriculture, and tourism. The country’s focus on stabilizing its economy and improving infrastructure will likely contribute to an upward trend in individual income levels. However, challenges related to reliance on commodity exports and external economic fluctuations may temper growth prospects.
Projected growth trends suggest that Namibia’s GDP per capita could benefit from increased foreign direct investment and government policies aimed at fostering sustainable development. If these initiatives are successful, Namibia may see a gradual rise in average income, thereby improving living standards. Nonetheless, maintaining consistent growth will require addressing issues such as unemployment, inequality, and economic vulnerability.
Overall, while uncertainties exist, Namibia’s future GDP per capita outlook remains cautiously optimistic, with potential for continued improvement driven by strategic economic reforms and sectoral development efforts.
Potential Economic Opportunities
The future outlook for Namibia’s GDP per capita presents a mix of challenges and opportunities driven by strategic economic reforms and global trends. As Namibia continues to diversify its economy beyond mining and resource extraction, there is potential for sustainable growth that can elevate living standards and income levels for its population.
One key driver of future economic prospects is investment in sectors such as tourism, agriculture, and manufacturing, which can create jobs and stimulate income growth. Additionally, harnessing renewable energy resources, particularly solar power, offers opportunities for Namibia to become an energy exporter and attract foreign direct investment.
Advancements in infrastructure and education are also crucial for improving productivity and enabling higher income levels. Namibia’s commitment to regional integration and trade agreements can further expand export markets, boosting GDP per capita over the coming years.
However, challenges such as economic inequality, unemployment, and dependence on commodity prices must be addressed to ensure inclusive growth. By implementing policies focused on diversification, innovation, and human capital development, Namibia can set a trajectory toward higher GDP per capita and improved economic resilience in the future.
Risks and Mitigation Strategies
The future outlook for Namibia’s GDP per capita appears cautiously optimistic, driven by ongoing efforts to diversify the economy beyond its traditional reliance on mining and agriculture. As Namibia invests in sectors such as tourism, renewable energy, and manufacturing, the potential for economic growth and improved income levels declines in both urban and rural areas. However, challenges such as economic inequality, unemployment, and dependence on commodity prices remain significant factors influencing future progress.
Risks to Namibia’s GDP per capita growth include global commodity price fluctuations, which can impact the mining sector’s output and revenues. Additionally, climate change poses a threat to agriculture and water resources, potentially hindering economic stability. Political instability or policy uncertainties could also deter investments, constraining growth opportunities.
To mitigate these risks, Namibia should focus on strengthening economic diversification to reduce reliance on a few sectors. Investing in infrastructure, education, and technological innovation can enhance productivity and resilience. Developing social safety nets and inclusive policies can help address inequality, ensuring that growth benefits a broader segment of the population. Furthermore, forming strategic partnerships and implementing sustainable practices can safeguard resources against environmental risks, securing long-term economic stability and improved GDP per capita.



0 Comments