Geographical Overview of Blue Nile Ethiopia
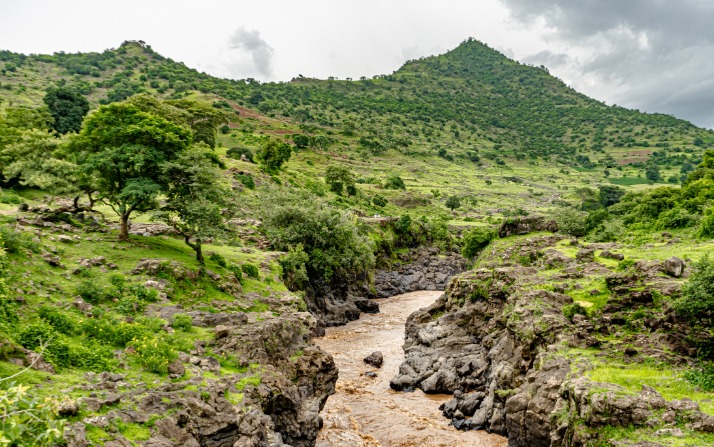
The Blue Nile, also known as the Abay River in Ethiopia, is a vital watercourse originating from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. It plays a crucial role in the region’s geography, serving as a major tributary of the Nile River and contributing significantly to Ethiopia’s natural landscape. The river’s course traverses diverse terrains, including mountainous areas and fertile plains, shaping the environment and supporting local communities along its path.
Location and Path of the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia is an essential part of the region’s geographical landscape, originating from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian Highlands. It flows through the northern part of Ethiopia, covering a significant distance before joining the White Nile in Sudan. The river is known for its dramatic course, meandering through rugged terrains and lush highlands. Its path begins at the Blue Nile Falls, located near Bahir Dar, and extends southeastward, playing a crucial role in Ethiopia’s agriculture and hydropower development. The Blue Nile’s journey through Ethiopia is marked by its scenic gorges and vibrant ecosystems, making it a vital water resource for both Ethiopia and neighboring countries downstream. The river’s strategic location and its source at Lake Tana emphasize Ethiopia’s importance as the origin of this major tributary of the Nile River system.
Source Points and Tributaries
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia is a significant water body that originates from the Ethiopian highlands, playing a crucial role in the region’s hydrology and water resource management. It is one of the major tributaries that feeds into the Nile River system, contributing a substantial portion of the water flow to Egypt and Sudan. The source points of the Blue Nile are primarily located from Lake Tana, which is considered the main source, situated in the northwestern part of Ethiopia. The Blue Nile begins its journey from the southern end of Lake Tana before flowing southward and then northwest, joining the White Nile at Khartoum in Sudan. Along its course, the Blue Nile receives water from numerous tributaries, including the Gumara, Abay, and Tis Issat Rivers, which help enlarge its volume and influence its flow patterns. These tributaries originate from the Ethiopian highlands, characterized by rugged terrain and high rainfall, which contribute to the river’s volume and seasonal variability. Overall, the Blue Nile’s geographical setting in Ethiopia underscores its importance as a vital water source for the region, as well as its role in the broader Nile River ecosystem.
Topographical Features Influencing the River
The Blue Nile, originating from the highlands of Ethiopia, is a vital component of the Nile River system. Its source is found in the Ethiopian Plateau, an area characterized by rugged terrain and elevated landforms that significantly influence the river’s flow and volume. The topographical features of this region include steep escarpments, deep gorges, and expansive plateaus that shape the course of the Blue Nile as it travels towards Sudan and Egypt. The Ethiopian highlands, with their high altitude and volcanic origins, create a natural watershed that captures a substantial amount of rainfall, contributing to the river’s seasonal flow variations.
Historical Significance of Blue Nile Ethiopia
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia holds immense historical significance as one of the world’s great rivers that has shaped ancient civilizations and modern development alike. Known locally as the Abay River, it is a vital waterway that has nurtured the region for millennia, supporting agriculture, trade, and cultural heritage. Its course through Ethiopia’s rugged terrains has also played a crucial role in the country’s ecological and geopolitical history, making it a symbol of national identity and regional influence.
Ancient Civilizations and Settlements
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia holds immense historical significance as it is a vital part of the history of ancient civilizations and settlements in the region. This river, originating from Lake Tana, has nurtured the development of early societies by providing essential water resources for agriculture, trade, and daily life. Throughout history, the areas surrounding the Blue Nile have been home to several ancient settlements and civilizations, including the Kingdom of D’mt and later the Aksumite Empire, which thrived due to their strategic location along the river. The Blue Nile has also played a crucial role in shaping trade routes and fostering cultural exchanges between different peoples in the Horn of Africa. Its waters not only supported the growth of these civilizations but also symbolized life, continuity, and resilience over centuries. Today, the Blue Nile remains a cornerstone of Ethiopia’s cultural heritage and historical identity, underscoring its enduring significance in human history.
Historical Trade Routes and Navigation
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia holds a remarkable historical significance as one of the world’s major sources of the Nile River, contributing approximately 70% of the water that flows through the Nile. Historically, it has been vital for agriculture, transportation, and trade in the region, shaping the development of ancient civilizations along its banks. The river’s journey from the Ethiopian highlands to Egypt has served as a crucial route for the movement of peoples, goods, and cultural exchanges for thousands of years. The Blue Nile’s waters have supported the growth of early societies, enabling trade in commodities such as gold, ivory, and spices that traveled along interconnected routes that linked sub-Saharan Africa with the Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations. These trade routes, along with the navigability of the Blue Nile, facilitated commerce and cultural interactions, making the region a crossroads of ancient and medieval trade networks. The importance of the Blue Nile has persisted through history, symbolizing both a vital water resource and a historical artery of commerce and cultural exchange in Northeast Africa. Today, it continues to be central to Ethiopia’s economy and regional geopolitics, highlighting its enduring legacy in history and trade.
Archaeological Findings and Cultural Heritage
The Blue Nile of Ethiopia holds immense historical significance as one of the world’s major tributaries of the Nile River, contributing approximately 85% of the water that nourishes the Nile Basin. Its waters have supported ancient civilizations for millennia, shaping the development of early societies in the region.
Archaeological findings in the Blue Nile region have uncovered numerous artifacts and ancient settlements that date back thousands of years, shedding light on the early human activity and technological advancements of the area. These discoveries include tools, pottery, and remnants of early agricultural practices, indicating the long-standing importance of the river to local communities.
Cultural heritage in the Blue Nile area is rich and diverse, reflecting the traditions, beliefs, and histories of various Ethiopian ethnic groups. The river is central to many cultural rituals and festivals, symbolizing life, fertility, and spiritual connection. Preservation efforts aim to protect this vibrant cultural landscape, ensuring that its historical and archaeological treasures continue to be celebrated and studied for future generations.
Hydrological and Environmental Aspects
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia plays a crucial role in the region’s hydrological and environmental systems. Its waters support agriculture, provide water for millions, and influence the local ecosystem’s health. Understanding the hydrological dynamics and environmental impacts of the Blue Nile is essential for sustainable management and development in Ethiopia and beyond.
Water Flow and Seasonal Variations
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia plays a crucial role in shaping the region’s hydrological and environmental landscape, significantly influencing water flow and seasonal variations. The river’s flow is highly dependent on seasonal rainfall patterns, with peak discharge occurring during the rainy season between June and September. This seasonal variation impacts downstream water availability, agriculture, and hydroelectric power generation. Additionally, the hydrological regime affects sediment transport and nutrient distribution, which are vital for maintaining ecological balance in the river basin. Climate change and upstream dam constructions further influence water flow patterns, potentially altering seasonal fluctuations and impacting both local communities and regional ecosystems. Proper management and understanding of these hydrological and environmental aspects are essential for sustainable development and resource conservation in the Blue Nile basin.
Ecological Diversity and Wildlife
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia plays a crucial role in shaping the region’s hydrological and environmental landscape. Its waters support diverse ecosystems, influence local climate patterns, and sustain agricultural activities. The river’s flow contributes significantly to downstream water availability, making it vital for both ecological balance and human livelihoods. Protecting the hydrological integrity of the Blue Nile is essential for maintaining environmental health and ensuring sustainable development in Ethiopia and beyond.
The ecological diversity surrounding the Blue Nile is remarkable, featuring lush riverine forests, wetlands, and highland grasslands. These habitats support a wide array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic and adapted to the region’s unique conditions. The area’s flora includes various medicinal plants, while fauna ranges from aquatic species to terrestrial mammals and bird life. Preserving this biodiversity is critical for the resilience of local ecosystems and for maintaining ecological services vital to local communities.
Wildlife in the Blue Nile Basin includes numerous species of fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. Notable among them are different fish species adapted to river currents and floodplains, as well as migratory bird species that rely on the wetlands for breeding and feeding. The region is also home to larger mammals such as baboons, monkeys, and antelopes. Conservation efforts are increasingly important to safeguard these species from threats like habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change, ensuring the sustainability of Ethiopia’s rich natural heritage.
Conservation Challenges and Initiatives
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia plays a crucial role in the region’s hydrology and environmental sustainability. The river supports diverse ecosystems, provides water for agriculture, and sustains local communities. However, rapid population growth, deforestation, and climate change threaten the health of the river’s environment, leading to reduced water quality and habitat degradation. Conservation challenges include sedimentation, water over-extraction, and pollution from agricultural and industrial activities. Numerous initiatives aim to address these issues, such as reforestation projects, sustainable water management programs, and community-based conservation efforts. International collaboration and government policies are essential to balancing development needs with environmental preservation, ensuring the Blue Nile remains a vital resource for Ethiopia and downstream countries.
Economic Impact of Blue Nile Ethiopia
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia plays a crucial role in the country’s economic development, serving as a vital water resource for agriculture, hydroelectric power, and transportation. Its significance extends beyond local communities, impacting regional stability and economic growth across Ethiopia and neighboring countries. Understanding the economic impact of the Blue Nile highlights the importance of sustainable management and infrastructure projects that can harness its potential for the nation’s progress.
Agriculture and Irrigation Projects
The Blue Nile Ethiopia project has a significant economic impact by enhancing agricultural productivity and water resource management in the region. The development of irrigation infrastructure and agricultural projects has led to increased crop yields, which contribute to food security and elevate local incomes. Additionally, these initiatives stimulate employment opportunities during construction and operational phases, fostering economic growth. The improved access to water resources supports sustainable farming practices, reducing vulnerability to droughts and climate change. Overall, the Blue Nile Ethiopia projects play a crucial role in strengthening the country’s agricultural sector, boosting rural development, and promoting long-term economic stability.
Hydropower and Energy Generation
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia has significant economic implications, primarily through its potential for hydropower development and energy generation. This region’s vast water resources enable the construction of large-scale hydroelectric projects, such as the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, which aims to transform Ethiopia into a regional energy hub. The generation of electricity from these hydroelectric facilities can boost economic growth by providing affordable and sustainable power, attracting investment, and supporting industrialization. Moreover, excess energy can be exported to neighboring countries, potentially increasing national revenue and improving regional economic stability. The development of hydropower on the Blue Nile also promotes job creation and infrastructure development, fostering long-term economic benefits for Ethiopia and its surrounding communities. However, the economic impact must be managed carefully to balance environmental sustainability and regional cooperation among Nile Basin countries.
Tourism and Cultural Attraction
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia has a significant economic impact through its role in tourism and cultural attraction, drawing visitors from around the world to explore its natural beauty and rich history.
- Tourism Revenue: The Blue Nile Cataract and surrounding areas generate substantial income through tourism, supporting local businesses, hotels, and tour operators.
- Cultural Heritage Preservation: The region’s ancient sites, including historical monasteries and archaeological sites, attract cultural tourists, promoting preservation efforts and generating employment.
- Infrastructure Development: Increased tourist footfall encourages investment in infrastructure such as roads, transportation, and facilities, boosting regional economic growth.
- Employment Opportunities: Tourism-related activities create jobs for local communities, including guides, craftsmen, and hospitality workers.
- Foreign Investment: The global interest in the Blue Nile encourages foreign investments in tourism infrastructure and hospitality services, contributing to Ethiopia’s overall economic development.
- Enhanced International Profile: Promoting the Blue Nile as a major tourism destination helps elevate Ethiopia’s standing in the global tourism market.
- Supporting Sustainable Development: Tourism centered around the Blue Nile can promote sustainable practices that protect the environment while maximizing economic benefits.
- Regional Development: The influx of visitors supports development in surrounding regions, reducing economic disparities and fostering regional stability.
Development and Infrastructure Projects
Development and infrastructure projects in the Blue Nile region of Ethiopia play a crucial role in enhancing the nation’s economic growth and connectivity. These initiatives aim to improve water management, transportation, energy, and social services, fostering sustainable development for local communities. As the region continues to evolve, strategic investments are vital to balance environmental conservation with infrastructural expansion.
Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD)
The Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) is a major infrastructure project on Ethiopia’s Blue Nile River, representing one of the largest hydroelectric projects in Africa. Its development aims to significantly enhance Ethiopia’s electricity generation capacity, promote economic growth, and improve access to sustainable energy for the region. The construction of GERD has been a symbol of national pride and a strategic step toward reducing dependence on fossil fuels and fostering energy stability.
Despite its benefits, the project has also sparked regional tensions, particularly with downstream countries like Sudan and Egypt, due to concerns over water rights and reservoir inflows. Ethiopia asserts that GERD is crucial for its development goals and renewable energy initiatives, while neighboring nations seek agreements to ensure fair water sharing and transparency during construction and operation phases. Efforts continue to balance Ethiopia’s development ambitions with regional cooperation and sustainable water resource management.
Transportation and Accessibility Improvements
Development and infrastructure projects along the Blue Nile in Ethiopia aim to enhance transportation and accessibility in the region. These initiatives focus on constructing and upgrading roads, bridges, and railways to ensure better connectivity between remote communities and urban centers. Improved transportation infrastructure facilitates the movement of goods and people, fostering economic growth and regional integration.
In addition to transportation improvements, efforts are being made to develop energy infrastructure, including hydroelectric projects like the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, which harness the Blue Nile’s water resources. These projects are designed to boost electricity generation, support regional development, and promote sustainable growth across Ethiopia and neighboring countries.
Enhancing accessibility involves deploying modern infrastructure to support agriculture, tourism, and local industries, creating opportunities for socioeconomic development. The overall goal is to create a resilient and efficient transportation network that benefits communities along the Blue Nile and supports Ethiopia’s long-term development objectives.
Water Management and Sustainability Efforts
The Blue Nile region in Ethiopia is at the forefront of significant development and infrastructure projects aimed at enhancing water management and promoting sustainability. These initiatives include the construction of large-scale hydropower dams, such as the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, which seeks to generate electricity for the country and neighboring nations. These projects are designed to improve water distribution, support agricultural activities, and foster economic growth while emphasizing environmental preservation. Ethiopia is also investing in modern irrigation systems and water conservation techniques to ensure sustainable use of its water resources. Efforts to protect the Blue Nile’s natural ecosystem and implement responsible water management practices are crucial in balancing development needs with ecological integrity. Overall, these initiatives demonstrate Ethiopia’s commitment to fostering sustainable development through advanced infrastructure and effective water resource management in the Blue Nile basin.

Political and Regional Implications
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia holds significant political and regional implications that influence both national stability and international relations. As a vital water source for agriculture, hydroelectric power, and economic development, its management and utilization are central to Ethiopia’s sovereignty and regional cooperation. The complex dynamics surrounding the Blue Nile involve negotiations with neighboring countries, concerns over resource sharing, and the pursuit of sustainable development, making it a key area of geopolitical interest in the Horn of Africa.
Blue Nile Dispute among Nile Basin Countries
The Blue Nile dispute among Nile Basin countries has significant political and regional implications, particularly involving Ethiopia, Sudan, and Egypt. Ethiopia’s construction of the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD) has been a source of tension, as upstream developments threaten downstream water security. This situation has intensified regional rivalries and led to diplomatic negotiations aimed at reaching a consensus on water sharing and dam operation. The dispute also impacts regional stability, economic development, and environmental management, making it crucial for all parties to engage in mutually beneficial agreements to ensure sustainable use of the Nile waters and maintain peace within the region.
International Agreements and Negotiations
The Blue Nile River holds significant political and regional implications for Ethiopia, Sudan, and Egypt, as it is a vital water source impacting their economies, agriculture, and overall stability. Ethiopia’s construction of dams and water management projects on the Blue Nile has led to tensions with downstream nations, particularly Egypt, which relies heavily on the Nile waters for its survival. These disagreements have necessitated international agreements and negotiations to ensure equitable resource sharing and prevent conflicts. Various treaties, such as the 1959 Nile Waters Agreement between Sudan and Egypt, have historically favored upstream nations, but Ethiopia’s recent initiatives challenge these frameworks, prompting calls for new, comprehensive negotiations. International actors and organizations, including the African Union and the United Nations, have sought to mediate negotiations, emphasizing the importance of cooperative management and sustainable development to address the region’s water security and political stability.
Impact on Ethiopia’s Relations with Sudan and Egypt
The Blue Nile, a crucial tributary of the Nile River originating from Ethiopia, holds significant political and regional implications for Ethiopia’s relations with Sudan and Egypt. The control and utilization of the Blue Nile’s waters are central to Ethiopia’s development plans, particularly the Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), which has stirred regional tensions. Egypt views the dam as a direct threat to its water security, given its reliance on the Nile for nearly all its freshwater needs, while Sudan’s stance has been more nuanced, balancing economic interests with regional stability.
Diplomatic relations among these countries are deeply intertwined with disputes over water rights and dam operations, often resulting in tensions and negotiating challenges. Ethiopia’s pursuit of dam construction to boost its electricity generation and economic growth has been met with resistance from Egypt, which advocates for binding agreements to ensure its downstream water rights. Conversely, Sudan seeks a collaborative approach to manage water flows, emphasizing regional cooperation rather than conflict. These dynamics significantly influence regional politics, as stability depends on effective cooperation and mutual understanding among the Nile Basin countries.
Challenges and Future Perspectives
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia presents unique challenges and promising future prospects that are crucial for the region’s development. Balancing environmental sustainability, economic growth, and local community needs requires innovative solutions and strategic planning. As Ethiopia continues to harness its natural resources, understanding the complexities surrounding the Blue Nile is essential for addressing the obstacles and shaping a sustainable future for the area.
Environmental Threats and Climate Change
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia faces several challenges and represents a critical focus for future efforts due to environmental threats and climate change. As one of the major tributaries contributing to the Nile River basin, the Blue Nile’s flow is highly sensitive to changes in regional climate patterns, which can lead to irregular water availability and impact downstream countries. Deforestation, improper land use, and increasing water extraction further exacerbate these issues, threatening the sustainability of local ecosystems and communities reliant on the river. Climate change is expected to intensify these problems by causing unpredictable rainfall, prolonged droughts, and rising temperatures, which can reduce water inflow and increase evaporation rates. Looking ahead, addressing these challenges requires integrated water management strategies, investment in sustainable infrastructure, and regional cooperation to ensure equitable resource sharing. Emphasizing environmental conservation, implementing climate-resilient agricultural practices, and encouraging innovative technological solutions are vital steps toward safeguarding the Blue Nile for future generations.
Technological Innovations and Management Strategies
Understanding the challenges and future perspectives of Blue Nile Ethiopia involves navigating complex geographical, environmental, and socio-economic factors. The region faces issues such as climate change, water resource management, and infrastructural development that impact the sustainability of harnessing the Nile’s immense potential. Technological innovations, including advanced hydropower, improved irrigation systems, and remote sensing technologies, are crucial for optimizing water utilization and ensuring environmental conservation. Management strategies must focus on fostering cooperative governance among Ethiopia, Sudan, and Egypt, balancing developmental ambitions with ecological preservation. Embracing innovative solutions and strategic planning can help overcome current obstacles, ensuring that Blue Nile Ethiopia contributes significantly to regional energy security and economic growth in a sustainable manner.
Prospects for Sustainable Development
The Blue Nile in Ethiopia faces numerous challenges that impact its sustainable development, including pollution, deforestation, climate change, and over-extraction of water resources. These issues threaten the ecological balance of the river and the socio-economic well-being of communities dependent on it. Addressing these challenges requires integrated management strategies that promote conservation, responsible usage, and pollution control. Furthermore, advancements in technology and infrastructure can enhance water efficiency and reduce environmental impacts, making development more sustainable.
Looking ahead, the prospects for sustainable development along the Blue Nile are promising if stakeholders engage in collaborative planning and governance. Investment in renewable energy projects like hydroelectric dams offers opportunities for economic growth while maintaining ecological integrity. Promoting community participation, strengthening policy frameworks, and embracing innovative solutions can ensure the river’s resources are preserved for future generations. Emphasizing sustainable practices will not only support Ethiopia’s development goals but also contribute to regional stability and environmental resilience.




0 Comments