Historical Background of Fez
Fez, one of Morocco’s oldest and most historically significant cities, boasts a rich cultural and academic heritage that dates back over a millennium. Founded in the late 8th century by Idris I, it quickly grew into a prominent center of learning, trade, and Islamic scholarship. Throughout its history, Fez has been a vital hub for the development of Moroccan identity, hosting the renowned University of Al Quaraouiyine, recognized as the world’s oldest continuous degree-granting university. The city’s historical background reflects a complex tapestry of Arab, Berber, and Andalusian influences that have shaped its unique architectural, cultural, and spiritual landscape.
Founding and Early History
Fez, one of Morocco’s most historic cities, has a rich and deeply rooted history that dates back to the 8th century. It was originally founded in 789 CE by Idris I, the founder of the Idrisid dynasty, making it one of the oldest imperial cities in Morocco. The city was established as a strategic military and religious center, positioned along important trade routes that contributed to its growth and significance. During its early years, Fez quickly became a hub for Islamic scholarship, culture, and commerce, attracting scholars, traders, and artisans from across the Islamic world. The city’s strategic location and involvement in trade helped it flourish, laying the foundations for its renowned architectural and educational institutions, such as the University of al-Qarawiyyin, which is considered one of the oldest universities in the world. Over the centuries, Fez developed a unique blend of religious, cultural, and economic importance, establishing itself as a vital center of Moroccan and Islamic civilization.
Medieval Significance and Development
Fez, located in northern Morocco, is one of the oldest and most historically significant cities in the Islamic world. It was founded in the late 8th century by Idris I, the first ruler of the Idrisid dynasty, making it a pivotal center for the spread of Islam and Islamic culture in North Africa. Over the centuries, Fez grew into a major trading hub, attracting scholars, artisans, and traders from across theMediterranean and beyond. Its strategic location contributed to its prominence in regional commerce and cultural exchanges.
During the medieval period, particularly between the 12th and 14th centuries, Fez reached the height of its medieval significance. The city became the capital of the Marinid dynasty in the 13th century and was renowned for its intellectual and religious scholarship, housing the legendary University of al-Qarawiyyin, founded in 859. This institution is considered one of the world’s oldest continually operating universities and played a crucial role in the development of Islamic sciences, theology, and philosophy. Fez also became a center for arts, crafts, and architecture, exemplified by its intricate tile work and the construction of extensive madrasas and mosques.
Throughout its development, Fez remained a thriving political, cultural, and religious center. Its medina, a UNESCO World Heritage site, showcases a dense maze of narrow streets, historic buildings, and vibrant markets that reflect its medieval heritage. The city’s strategic importance and its role as a hub for Islamic education and commerce fostered continuous growth and influence, shaping the cultural identity of Morocco and the wider Maghreb region.
Historical Landmarks and Heritage Sites
Fez, one of Morocco’s oldest cities, has a rich historical background that dates back to the 8th century. Founded by Idris I, it quickly became a center of learning, religion, and culture in North Africa. Over the centuries, Fez flourished under various dynasties, notably the Marinids and Alaouites, shaping its unique architectural and cultural identity. Its strategic location along important trade routes contributed to its prosperity and influence in the region, making it a vital hub for commerce, religion, and education.
Among the most notable historical landmarks in Fez is the medina of Fez el-Bali, a UNESCO World Heritage site. This ancient walled city is famed for its labyrinthine streets, bustling souks, and historic mosques. The University of al-Qarawiyyin, founded in 859 AD, holds the distinction of being one of the world’s oldest continuously operating universities and symbolizes Fez’s long-standing tradition of scholarship. The Bou Inania Madrasa, a beautifully preserved example of Marinid architecture, and the Dar Batha Museum, housed in a former royal palace, further highlight the city’s rich heritage. Additionally, the Karaouine Mosque, a spiritual and educational center, remains a vital part of Fez’s religious history, reflecting its significance as a religious hub.
Geography and Urban Layout
The city of Fez in Morocco exemplifies a rich tapestry of geography and urban layout that reflects centuries of history and cultural development. Nestled in the northern part of the country, Fez is characterized by its intricate labyrinthine streets, historic medina, and strategic location along important trade routes. Its unique topography and carefully-designed urban structure reveal a harmonious blend of natural landscape and human ingenuity, making it a fascinating subject for exploring how geography influences city planning and cultural identity.
Location and Topography
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its complex geography and distinctive urban layout, shaped by its historical development and natural features. Nestled in the northeastern part of the country, Fez is situated within the Atlas Mountains’ foothills, which influence its topography and climate. The city’s location along the Fez River, a tributary of the Sebou River, has historically made it an important hub for trade and commerce. The topography features a combination of flat plains in the urban core and hilly surroundings, contributing to its layered urban landscape. This varied terrain has led to the development of winding, narrow streets in the ancient medina, a UNESCO World Heritage site, reflecting its organic growth over centuries. Its strategic position and natural contours have played a crucial role in shaping Fez’s cultural, economic, and architectural identity as one of Morocco’s historic imperial cities.
City Districts and Quartiers
Fez, Morocco, is renowned for its complex urban layout and distinct city districts that reflect centuries of history and cultural development. The city is divided into several quartiers, each with unique characteristics, from the historic medina to modern neighborhoods. The medina of Fez, a UNESCO World Heritage site, is a labyrinth of narrow alleyways, bustling souks, and ancient mosques, forming the heart of the city’s traditional urban fabric.
The Old Medina, or Fes el-Bali, is characterized by its dense, maze-like streets and centuries-old buildings that showcase Islamic and Andalusian architecture. Surrounding this core are newer districts such as Fes Jdid, which was developed during the Marinid dynasty and features palaces, gardens, and administrative buildings. The city’s layout emphasizes accessibility to religious, cultural, and commercial centers, fostering a vibrant community life within each district.
Modern expansion has brought about new urban quarters with broader streets and contemporary infrastructure, contrasting with the historic quarters’ traditional designs. Fez’s urban planning reflects a blend of preservation and adaptation, maintaining its rich heritage while accommodating growth. The city’s districts are interconnected through a network of roads and pathways, illustrating the evolution of its urban landscape from ancient times to the present day.
Architectural Styles and Influences
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its rich geographical setting and distinctive urban layout, which together reflect centuries of historical development and cultural integration. Located in the northeastern part of Morocco, Fez is nestled within the fertile Saïs plain, bordered by the Middle Atlas Mountains to the south, providing a strategic position that historically contributed to its prominence as a center of commerce and learning. The city’s terrain is characterized by a mix of flat areas and hilly terrains, influencing the organic urban expansion seen in its old medina.
Fez’s architectural styles showcase a blend of Andalusian, Moorish, and Islamic influences, which have evolved over centuries to create a unique and cohesive aesthetic. The medina of Fez, a UNESCO World Heritage site, features narrow winding streets, bustling souks, and historic monuments such as madrasas, mosques, and palaces. Noteworthy architectural elements include intricate tilework (zellij), carved cedar wood, plasterwork (stucco), and traditional riads that serve as private residences with interior courtyards. The influence of Islamic architecture is evident in the grand minarets, courtyards, and decorative motifs, while elements of Andalusian design can be seen in the decorative patterns and layout principles. This architectural diversity reflects Fez’s longstanding role as a spiritual, educational, and cultural hub in Morocco and the wider Maghreb region.
Cultural Significance of Fez
The city of Fez in Morocco holds a profound cultural significance, serving as a symbol of historical heritage and Islamic tradition. Renowned for its centuries-old medinas, religious institutions, and artisan craftsmanship, Fez is often regarded as a spiritual and intellectual hub of Morocco. Its rich history and vibrant cultural landscape make it a vital part of Morocco’s identity and a treasured destination for those seeking to explore the depths of Moroccan culture.
Religious and Spiritual Heritage
Fez, Morocco, holds a profound cultural and spiritual significance rooted in its rich religious heritage. As one of the oldest imperial cities in Morocco, Fez has been a center of Islamic learning and spiritual development for centuries. The city is home to the Al-Qarawiyyin Mosque, founded in 859 AD, which is recognized as the world’s oldest existing, continually operating educational institution. This deep religious history contributes to Fez’s reputation as a beacon of Islamic scholarship and spiritual reflection.
The city’s architecture, mosques, and traditional medinas reflect its spiritual essence, serving as places of worship, community gathering, and cultural preservation. Fez’s religious institutions foster a sense of unity and identity among its residents and visitors, emphasizing the enduring importance of faith in shaping the city’s social fabric. Celebrations of Islamic festivals and religious rituals further highlight Fez’s role as a spiritual hub, connecting locals and pilgrims to their religious heritage across generations.
Overall, Fez’s cultural significance is intertwined with its religious and spiritual roots, making it a unique city where faith, history, and tradition continue to thrive and influence daily life. The city’s spiritual heritage not only attracts scholars and pilgrims but also preserves a way of life centered around faith and cultural continuity.
Traditional Crafts and Artisanal Industries
The city of Fez in Morocco holds a profound cultural significance rooted in its rich history, traditional crafts, and artisanal industries. Renowned as one of the world’s oldest medieval cities, Fez is a UNESCO World Heritage site that embodies the soul of Moroccan heritage. The city is famous for its intricate leatherwork, pottery, textile weaving, and metal crafts, which have been preserved and passed down through generations. These traditional industries not only represent the artistic mastery of local artisans but also serve as a vital part of Fez’s identity and economy. The bustling souks and medinas are vibrant centers where craftsmanship continues to thrive, attracting visitors eager to experience authentic Moroccan artistry. Overall, Fez’s cultural significance is deeply intertwined with its artisanal industries, reflecting a steadfast commitment to preserving the city’s historical and cultural legacy for future generations.
Festivals and Cultural Events
Fez, Morocco, is a city rich in cultural heritage and vibrant traditions that are showcased through its unique festivals and cultural events. The city serves as a vital center for Moroccan craftsmanship, music, dance, and religious practices, reflecting its deep historical roots and diverse influences. These events foster communal identity, preserve traditional arts, and attract visitors eager to experience authentic Moroccan culture.
One of the most significant festivals in Fez is the annual Festival of World Sacred Music, which brings together musicians, performers, and pilgrims from around the globe. This event highlights the city’s spiritual significance and promotes intercultural dialogue through spiritual and musical expressions. Additionally, the Fantasia (Tbourida) showcases traditional horse-riding displays and martial arts, emphasizing the importance of equestrian culture in Moroccan heritage.
Religious events such as Ramadan celebrations and the Moulay Idriss Festival, held in honor of the city’s patron saint, play a crucial role in community life. These festivals involve processions, communal prayers, and traditional cuisine, fostering social cohesion and spiritual reflection. Moreover, the enduring popularity of artisan markets and crafts fairs in Fez underscores the city’s reputation as a UNESCO World Heritage site and a global hub for traditional Moroccan arts and crafts.
Educational Institutions and Learning
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its rich educational heritage and vibrant learning environment. As one of the oldest and most culturally significant cities in the country, Fez is home to historic educational institutions that have shaped Islamic and Moroccan scholarship for centuries. Learning in Fez is deeply rooted in tradition, yet it continues to evolve with modern academic pursuits, making it a unique hub for knowledge and cultural exchange.
Al Quaraouiyine University
Al Quaraouiyine University, situated in the historic city of Fez, Morocco, is renowned as one of the oldest and most influential educational institutions in the world. Established in 859 AD, it has played a vital role in the academic and cultural development of the region, attracting scholars from across Africa, the Middle East, and beyond. The university specializes in Islamic studies, theology, law, and Arabic language, fostering a rich environment for learning and scholarly exchange. Its historic architecture and vibrant academic atmosphere make it a symbol of Fez’s illustrious intellectual heritage and its enduring legacy as a center of knowledge and education.
Madrasas and Religious Schools
In the historic city of Fez, Morocco, educational institutions and learning have played a central role in shaping the city’s rich cultural and intellectual heritage. Fez is renowned for its ancient universities and madrasa systems that have been centers of Islamic scholarship for centuries. The University of Al Quaraouiyine, founded in 859 AD, is considered one of the oldest continually operating degree-granting universities in the world, attracting students from across Africa and beyond. Alongside this, numerous madrasas and religious schools have contributed to the dissemination of knowledge in religious sciences, arts, and sciences, fostering a vibrant educational environment. These institutions not only serve as centers for religious learning but also promote critical thinking, cultural exchange, and the preservation of Moroccan heritage. Today, Fez continues to uphold its reputation as a city of learning, blending ancient educational traditions with modern scholarly pursuits to inspire future generations.
Modern Educational Initiatives
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its rich educational heritage and historic significance as a center of learning. Ancient universities such as the University of Al Quaraouiyine, founded in 859 AD, exemplify the enduring legacy of knowledge and scholarship in the city. Throughout centuries, Fez has been a hub for religious studies, sciences, and arts, attracting students from across Africa and the Middle East.
In recent years, Fez has embraced modern educational initiatives to complement its historical institutions. Efforts include integrating technology into classrooms, promoting vocational training, and establishing partnerships with international universities. These initiatives aim to equip students with contemporary skills while preserving the city’s cultural and historical educational traditions. As a result, Fez continues to be a vibrant center of learning, balancing its ancient academic roots with innovative approaches to education.
Economy and Local Industries
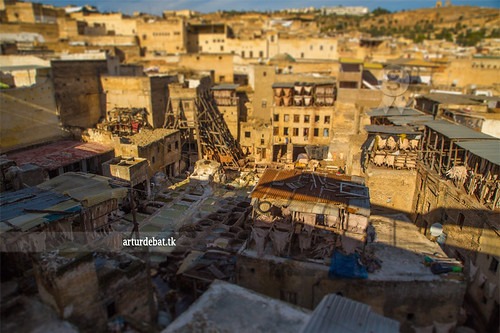
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned not only for its rich history and cultural heritage but also for its vibrant economy and thriving local industries. Traditionally, Fez has been a center for craftsmanship, including leather goods, textiles, and pottery, which continue to play a crucial role in the city’s economic landscape. These industries, combined with tourism and commerce, contribute significantly to local livelihoods and the overall development of Fez as a dynamic economic hub.
Traditional Handicrafts and Markets
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its vibrant economy driven by a blend of traditional industries and modern enterprises. Historically, Fez has been a center of commerce and craftsmanship, sustaining its economic vitality through the preservation of its rich cultural heritage. Local industries such as leather tanning, textiles, and pottery continue to thrive, drawing both domestic and international attention. Traditional handicrafts play a significant role in the city’s economy, with artisans crafting intricate leather goods, jewelry, and textiles that showcase centuries-old techniques. Markets, especially the famed Fez Medina, serve as bustling hubs where merchants and craftsmen sell their products, contributing to the city’s reputation as a hub of commerce and cultural exchange. These markets not only support local livelihoods but also attract tourists eager to experience authentic Moroccan craftsmanship, further bolstering Fez’s economic fabric.
Tourism and Hospitality Sector
The city of Fez, Morocco, boasts a diverse economy centered around its rich historical and cultural heritage. Traditionally, the local industries focus on craftsmanship, particularly in leatherworking, ceramics, and textile production, which have been passed down through generations. These artisanal industries not only preserve cultural traditions but also contribute significantly to local employment and entrepreneurship. Additionally, Fez plays a vital role in the Moroccan economy through its vibrant markets and manufacturing sectors.
The tourism and hospitality sector is a cornerstone of Fez’s economy, attracting visitors from around the world eager to explore its ancient medinas, UNESCO World Heritage sites, and architectural marvels. The city’s historical sites, including the University of al-Qarawiyyin and numerous mosques and palaces, draw scholars, history enthusiasts, and spiritual travelers alike. As a result, the city offers a range of accommodation options, from traditional riads to luxury hotels, supporting a thriving hospitality industry. Efforts to enhance tourism infrastructure aim to sustain economic growth and promote Fez as a premier cultural destination in Morocco.
Emerging Sectors and Economic Development
The city of Fez in Morocco is renowned for its rich history and vibrant economy, rooted deeply in traditional industries such as leather tanning, pottery, and textiles. These local industries continue to serve as significant employment sources and cultural symbols, attracting both tourists and investors interested in authentic Moroccan craftsmanship. In recent years, Fez has been focusing on expanding its economic landscape by fostering emerging sectors like artisanal food production, calligraphy, and digital services, which complement its historic industries and promote sustainable growth.
Economic development initiatives in Fez aim to modernize infrastructure, enhance connectivity, and promote tourism, ultimately boosting the local economy. The city is increasingly becoming a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, with a focus on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that leverage the city’s cultural heritage and strategic location. Efforts to diversify the economy include investing in vocational training, supporting startups, and encouraging foreign direct investment, all focused on creating jobs and improving living standards for residents.
Modern Developments and Urban Challenges
The city of Fez in Morocco is experiencing rapid modern developments that aim to enhance its infrastructure and economic growth. However, these advancements also bring about significant urban challenges, including maintaining the city’s rich cultural heritage while accommodating modern needs. Balancing tradition with progress is essential to ensuring Fez’s sustainable development and preserving its unique identity for future generations.
Urban Infrastructure and Public Services
The city of Fez in Morocco is experiencing rapid modernization while facing numerous urban challenges related to infrastructure and public services. As one of the oldest imperial cities, Fez is balancing its rich historical heritage with the demands of contemporary urban development.
Recent developments in Fez have focused on improving transportation, upgrading water and sewage systems, expanding healthcare facilities, and enhancing educational infrastructure. These efforts aim to support its growing population and boost tourism, which is vital to the local economy. However, integrating modern infrastructure within the ancient medina presents unique challenges, including preservation of heritage sites and maintaining the city’s traditional character.
- Urban Infrastructure Upgrades: Fez has seen investments in roads, public transportation, and utility networks to improve connectivity and service reliability.
- Public Services Expansion: Efforts are underway to enhance access to healthcare, education, and sanitation services for residents and visitors alike.
- Heritage Preservation Challenges: Modern developments must be carefully managed to safeguard historic sites and cultural identity while accommodating urban growth.
- Sustainable Development Initiatives: Projects are being implemented to promote environmentally friendly urban planning, such as renewable energy use and waste management improvements.
- Traffic Congestion and Pollution: Increased vehicular traffic has led to congestion and air quality concerns, prompting initiatives for traffic regulation and green spaces expansion.
Preservation vs. Modernization
The city of Fez, Morocco, exemplifies the complex balance between modern development and the preservation of its rich historical heritage. As one of the oldest imperial cities in Morocco, Fez boasts a wealth of medieval architecture, bustling souks, and cultural monuments that attract both tourists and scholars. However, rapid urbanization and modernization efforts pose significant challenges to maintaining its authenticity and historical integrity.
Modern developments in Fez include infrastructure upgrades, the expansion of residential and commercial zones, and efforts to improve transportation networks. While these initiatives are essential for economic growth and improving residents’ quality of life, they risk encroaching upon and diluting the city’s ancient character. The preservation of historic sites, such as the medina of Fez, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, requires careful planning to ensure that modernization does not compromise its cultural significance.
Balancing preservation and modernization involves adopting integrated urban planning approaches that respect the city’s historical context while accommodating contemporary needs. Initiatives such as restoring ancient buildings, promoting traditional crafts, and implementing sustainable tourism practices are crucial. Ultimately, Fez’s challenge lies in fostering development that enhances urban living without erasing the city’s unique medieval identity, ensuring that future generations can both experience and learn from its centuries-long history.
Environmental and Sustainability Issues
The city of Fez, Morocco, exemplifies the complexities of modern urban development while facing significant environmental and sustainability challenges. As one of the oldest cities in the Arab world, Fez has experienced rapid growth, necessitating innovative solutions to balance historical preservation with modern infrastructure needs.
Urban challenges in Fez include managing population density, traffic congestion, and preserving its UNESCO World Heritage site. The narrow, winding streets of the medina pose difficulties for transportation and urban planning, often leading to pollution and degradation of cultural sites. Efforts to modernize infrastructure must be carefully coordinated to maintain the city’s unique heritage.
Environmental issues in Fez are also prominent, with concerns about air and water pollution, waste management, and the impact of urban expansion on local ecosystems. Unregulated waste disposal and industrial activities contribute to pollution, threatening public health and the environment.
Sustainability initiatives in Fez aim to address these challenges by promoting eco-friendly urban planning, renewable energy projects, and sustainable tourism. Emphasizing the conservation of historic areas while encouraging green spaces and clean transportation options is vital for ensuring the city’s long-term resilience. Balancing tradition and innovation is essential to creating a sustainable future for the city of Fez.





0 Comments