Geographical Overview of the Great Rift Kenya
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geographical feature that stretches across East Africa, forming part of the larger East African Rift System. This massive geological formation is characterized by deep valleys, mountain ranges, and expansive lakes, showcasing the dynamic tectonic activity that continues to shape the region. Its diverse landscapes and rich natural resources make it a significant area for both scientific study and tourism, offering a glimpse into the Earth’s geological history and ongoing geological processes.
Location and Extent
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a significant geographical feature that stretches across the eastern part of the country, forming part of the larger East African Rift System. It is a major tectonic depression created by the movement of the Earth’s crust, resulting in a series of valleys, volcanoes, and lakes. The rift extends approximately 800 kilometers from the northern border of Kenya near Lake Turkana southward to the border with Tanzania. This expansive geological formation covers diverse landscapes, including highlands, lakes, and volcanic features, making it a prominent and defining feature of Kenya’s geography.
Topographical Features
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geological feature that stretches across the country from the north to the south, forming a vast and distinctive landscape. This rift valley is part of the larger East African Rift System and is characterized by its dramatic topographical variations, including deep valleys, escarpments, volcanic mountains, lakes, and plains. The region is renowned for its unique geological formations, which result from tectonic movements that have created a series of rift basins and highlands.
- Deep Rift Valleys: The valley itself is a series of deep, elongated depressions that have been carved out by tectonic activity over millions of years.
- Escarpments: Steep cliffs and escarpments line the edges of the rift, such as the Great Escarpment of the eastern side, offering breathtaking views and significant topographical variety.
- Volcanic Mountains: The region features numerous volcanic features, including Mount Kenya, Loyangalani Volcano, and other extinct and active volcanoes that contribute to the area’s rugged terrain.
- Lake Systems: The rift hosts several large lakes, such as Lake Turkana, Lake Naivasha, and Lake Nakuru, which sit within the rift valleys and are vital ecological and economic resources.
- Plateaus and Plains: Surrounding the rift are expansive plateaus and fertile plains that support agriculture and wildlife habitats, contrasting with the rugged valleys.
Major Sections of the Rift Valley
The Great Rift Kenya is a prominent geological feature that forms part of the East African Rift System, extending through Kenya and neighboring countries. It is recognized for its unique and dramatic landscape that results from tectonic plate movements, creating a series of valleys, lakes, and volcanic mountains. The Rift Valley in Kenya is a major geological and geographical landmark, contributing significantly to the country’s biodiversity and scenic beauty.
The major sections of the Rift Valley in Kenya include the Northern Rift, the Central Rift, and the Eyasi-Turkana Basin. The Northern Rift extends from the northern border to Lake Turkana, characterized by its deep valleys and volcanic landscapes. The Central Rift is the most prominent, hosting some of the world’s largest alkaline lakes such as Lake Nakuru, Lake Naivasha, and Lake Baringo, as well as numerous volcanoes like Mount Kenya and Mount Longonot. The Eyasi-Turkana Basin, located to the northwest, is distinguished by its arid environment, the expansive Lake Turkana, and various archaeological sites that reveal human evolutionary history.
Together, these sections of the Rift Valley in Kenya form a complex geological structure that is vital for understanding the nation’s natural heritage and ongoing geological processes. The area is also a major tourist destination due to its stunning landscapes, wildlife, and cultural significance.
Geological Formation and Evolution
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological feature that showcases the Earth’s dynamic processes. It represents a significant region of tectonic activity where the Earth’s crust is gradually pulling apart, leading to the formation of deep faults, valleys, and diverse landscapes. Understanding the geological formation and evolution of this rift provides insights into the Earth’s geological history and the forces shaping our planet over millions of years.
Plate Tectonics and Rift Formation
The Great Rift Kenya is a prominent geological feature resulting from complex processes of formation and evolution over millions of years. This expansive rift valley is part of the larger East African Rift System, which is an active divergent boundary where tectonic plates are gradually moving away from each other. The formation of the rift began millions of years ago as a result of plate tectonics, where the African Plate is splitting into smaller plates, creating a series of deep rift valleys and volcanic activity.
Plate tectonics play a crucial role in shaping the structure and evolution of the Great Rift Kenya. The movement of the African plate in a northeastern direction causes the crust to stretch and thin, leading to faulting, volcanic eruptions, and the formation of new landforms. As the plates continue to diverge, the rift valley widens, and new volcanic cones and lakes are formed by upwelling magma and subsidence of the land.
Rift formation in this region is characterized by a series of fault blocks that have tilted and subsided, creating the dramatic escarpments and valleys seen today. The process involves both tectonic stretching and volcanic activity, which contribute to the ongoing evolution of the landscape. The Great Rift Kenya is a significant geological see where crustal movements are visible and provide insights into the tectonic processes that have shaped the African continent over geological time scales.
Volcanic Activity and Lava Flows
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geological feature that illustrates the Earth’s dynamic natural processes over millions of years. This valley was formed through tectonic activity, where the Earth’s crust has been slowly pulled apart, creating a series of deep trenches and volcanic formations. The geological evolution of the Rift Valley involves complex interactions between tectonic plates, leading to continuous geological changes and landscape development.
Volcanic activity has played a significant role in shaping the landscape of the Great Rift Kenya. Numerous volcanoes, both active and dormant, are scattered across the region, including Mount Longonot, Mount Suswa, and Menengai Crater. These volcanic cones and craters are the result of eruptions that have occurred over the past few million years, depositing layers of lava and ash that have contributed to the region’s rich volcanic soil.
Lava flows are a common feature within the Great Rift Valley, resulting from volcanic eruptions that have erupted molten rock onto the surface. These flows have forged new landforms and altered existing ones, creating plateaus, escarpments, and volcanic cones. The cooling and solidification of lava flows have added to the diverse geological features of the area, making it a key location for studying volcanic processes and landscape evolution.
Fault Lines and Earthquake Activity
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a prominent geological feature resulting from the Earth’s crust splitting and creating a series of rift valleys. This region is part of the East African Rift System, where tectonic plates are gradually moving apart, leading to significant geological activity. Over millions of years, the continued divergence of tectonic plates has shaped the landscape, forming deep valleys, volcanic mountains, and numerous lakes.
Fault lines are fractures in the Earth’s crust along which movement has occurred. In the Great Rift Kenya, several major fault lines traverse the region, including the Gregory Rift and the Eastern Rift. These fault lines are active zones where stress accumulates and is periodically released, causing shifts in the Earth’s crust. Such movement is responsible for shaping the volcanic features and exposing the region’s geological complexity.

Earthquake activity in the Great Rift Kenya is largely driven by the movement along these fault lines. Seismic events are common in this area, especially along the rift zones where accumulated tectonic stress is released. While most earthquakes are minor, occasionally larger tremors occur, which can cause damage and influence the ongoing geological evolution of the region. Understanding these fault lines and earthquake patterns is essential for assessing seismic risks and ensuring the safety of local communities and infrastructure.
Ecological and Environmental Significance
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds immense ecological and environmental significance as one of the most remarkable natural features on the planet. This expansive geological formation not only shapes the landscape but also provides diverse habitats that support a wide variety of flora and fauna. Its unique ecosystem plays a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity, influencing climate patterns, and supporting local communities through sustainable resources and tourism. Understanding its importance is vital for conserving this extraordinary environment for future generations.
Biodiversity Hotspots
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is of immense ecological and environmental significance due to its unique geological features and rich biodiversity. It provides diverse habitats that support a wide range of flora and fauna, contributing to the overall health of the region’s ecosystems. The valley acts as a corridor for wildlife migration and sustains many endemic and endangered species, making it critical for conservation efforts.
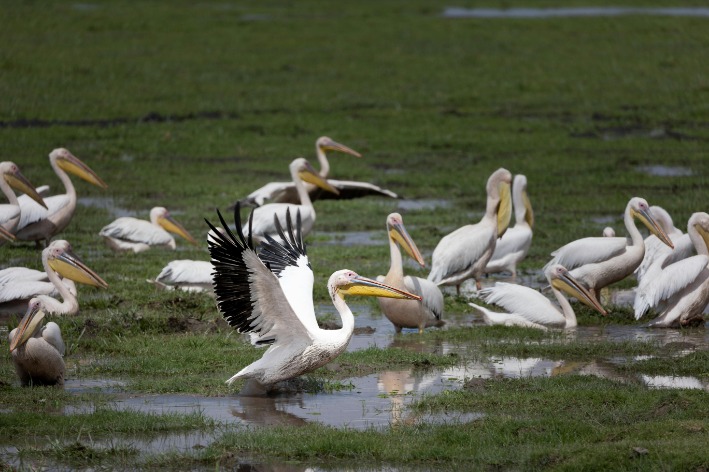
Recognized as a biodiversity hotspot, the Great Rift Valley hosts a variety of ecosystems, from lakes and wetlands to grasslands and forests. These ecosystems support thousands of species, including migratory birds, large mammals, and aquatic life, essential for maintaining ecological balance. Protecting these areas helps preserve genetic diversity and supports global biodiversity goals.
Unique Ecosystems and Habitats
The Great Rift in Kenya is of remarkable ecological and environmental significance, serving as a vital corridor for diverse ecosystems and a sanctuary for many unique habitats. This expansive geological feature hosts a variety of ecosystems, including lakes, wetlands, mountains, and savannahs, which support an extraordinary array of flora and fauna. Its varied terrains create microhabitats that are essential for the survival of numerous species, some of which are endemic and found nowhere else on Earth. The unique ecosystems within the Great Rift contribute to regional biodiversity, climate regulation, and serve as crucial sites for conservation efforts. These habitats not only sustain wildlife but also provide natural resources for local communities, underscoring their ecological importance and the need for sustainable management and protection. As a natural marvel, the Great Rift’s ecosystems play a key role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting Kenya’s rich environmental heritage.
Conservation Areas and National Parks
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya holds immense ecological and environmental significance due to its diverse landscapes, unique geological features, and rich biodiversity. It provides vital habitats for a wide array of flora and fauna, including rare and endangered species, and plays a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance in the region. Conservation areas and national parks within the Rift Valley, such as Maasai Mara, Hell’s Gate National Park, and Lake Naivasha, are essential for protecting this natural heritage, promoting sustainable tourism, and conserving biodiversity hotspots. These protected spaces enable research, environmental preservation, and serve as important sources of livelihood for local communities, ensuring the ongoing health and resilience of the ecosystem for future generations.
Hydrology and Lakes of the Rift Valley
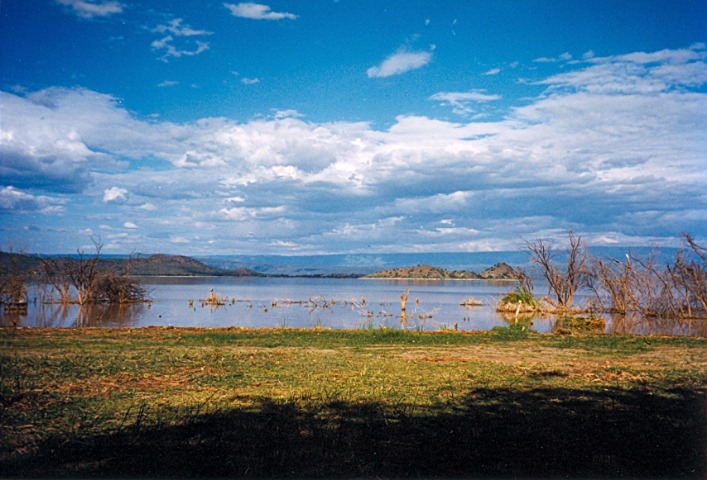
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a remarkable geological formation known for its stunning landscapes and diverse ecosystems. Central to this region are the hydrology and lakes that have shaped its unique environment. These lakes, often alkaline and intermittent, are vital for local biodiversity and provide important sources of water for nearby communities. Understanding the hydrology of the Rift Valley offers insight into the region’s geological history, ecological dynamics, and its significance as a natural wonder in Kenya.
Major Lakes and Their Characteristics
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is renowned for its unique hydrology and a series of major lakes that contribute significantly to the region’s ecological and economic landscape. This tectonic depression hosts some of Africa’s most prominent lakes, each displaying distinctive characteristics. Among these, Lake Turkana is the largest desert lake in the world, known for its high salinity and alkalinity, supporting specialized wildlife and fisheries. Lake Naivasha is a freshwater lake famous for its vibrant birdlife and domestic and commercial activities like fishing and tourism. Lake Baringo, also freshwater, is notable for its bird species and the presence of crocodiles and hippos. Lake Bogoria, in contrast, is a saline and alkaline lake with hot springs and geysers, supporting a diverse range of flamingos and other aquatic birds. The hydrology of these lakes is largely influenced by seasonal rainfall, the inflow from rivers, and subsurface sources. These lakes are interconnected with the Rift Valley’s tectonic activity, which shapes their depth, size, and water chemistry, making them vital for biodiversity, hydroelectric power, and local livelihoods in Kenya.
Water Resources and Hydroelectric Power
The Great Rift Valley of Kenya is distinguished by its extensive network of lakes, which play a crucial role in the region’s hydrology and water resources. These lakes, including Lake Turkana, Lake Naivasha, and Lake Nakuru, are vital for supporting biodiversity, local communities, and agriculture. The Rift Valley’s unique geological formations create a rich hydrological system that sustains these lakes and contributes to the overall water cycle in the area.
Water resources in the Great Rift Kenya are abundant due to the numerous lakes, rivers, and underground aquifers. These water bodies are essential for domestic use, agriculture, fisheries, and maintaining ecological balance in the region. Efficient management of these water resources is vital for sustainable development and environmental conservation in the Rift Valley.
Hydroelectric power generation is a significant aspect of Kenya’s energy strategy, with several hydroelectric stations situated along the rivers originating from the Rift Valley. The Nile Basin and other rivers provide opportunities for harnessing hydroelectricity, which helps meet the growing energy demands while minimizing reliance on fossil fuels. The development of hydroelectric projects in the Rift Valley is essential for economic growth and ensuring a reliable, renewable energy supply for Kenya and neighboring countries.
Significance for Local Communities
The Lakes of the Rift Valley in Kenya hold immense significance for local communities through their vital roles in providing water, supporting agriculture, and sustaining livelihoods. These lakes, such as Lake Naivasha, Lake Nakuru, and Lake Bogoria, are crucial sources of freshwater for nearby populations and serve as fishing grounds that contribute to local economies. Additionally, the lakes attract tourism, creating employment opportunities and fostering community development. The rich biodiversity found in these lakes, including flamingos and other wildlife, also supports eco-tourism initiatives. For many communities living along the Rift Valley, these lakes are not only natural resources but also cultural and social landmarks that shape their traditions and way of life. Their sustainable management is essential for maintaining the ecological balance and ensuring the continued prosperity of local populations in the Great Rift Kenya region.
Human Settlement and Socioeconomic Impact
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a significant geographical feature that has shaped human settlement patterns and influenced socioeconomic development in the region. Its unique landscape attracts both populations and economic activities, fostering diverse communities and opportunities. Understanding the relationship between human settlement and socioeconomic impact in this area is essential for addressing the challenges and harnessing the potential of this vital part of Kenya.
Historical Settlement Patterns
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya has significantly influenced human settlement and socioeconomic development over centuries. Its diverse landscapes, including fertile valleys and water sources, have attracted early human populations for agriculture and resource gathering. Historically, settlements along the Rift have evolved due to access to water, arable land, and trade routes, shaping the patterns of population distribution in the region. These patterns reflect a combination of environmental factors and socio-economic activities, such as farming, tourism, and mining, which continue to drive economic growth. The Rift’s rich cultural diversity and strategic location have also fostered vibrant communities and contributed to Kenya’s broader socioeconomic development.
Indigenous Communities and Cultures
The Great Rift in Kenya has significantly influenced human settlement patterns and socioeconomic development in the region. The rugged terrain and fertile volcanic soils have attracted communities for agriculture and settlement, leading to the growth of towns and villages along the Rift Valley. However, these areas often face challenges such as land disputes, limited access to infrastructure, and vulnerability to natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, which impact local livelihoods and development efforts.
Indigenous communities residing in the Great Rift Valley, including the Maasai, Kikuyu, and other ethnic groups, possess rich cultural traditions and social structures that are deeply connected to the land. Their ways of life—such as pastoralism, traditional ceremonies, and community-based livelihood practices—are intertwined with the Rift’s landscape. However, modernization, land commercialization, and tourism have posed threats to their cultural heritage and autonomous land rights, leading to tensions and displacement in some cases.
The socioeconomic impact of the Great Rift in Kenya extends beyond individual communities, affecting the national economy through tourism, agriculture, and mineral resources. Efforts to balance development with the preservation of indigenous cultures and ecological sustainability are crucial to ensuring that local communities benefit equitably from the region’s natural resources while maintaining their cultural identities.
Agriculture, Livelihoods, and Tourism
The Great Rift in Kenya has significantly influenced human settlement patterns and socioeconomic development in the region. As communities settled along the fertile valleys and volcanic soils, agriculture became the main livelihood, supporting crops such as maize, coffee, and tea. The availability of arable land and water resources has facilitated farming activities, which in turn have boosted local economies. Additionally, the Rift’s scenic landscapes and unique geological features attract numerous tourists, generating revenue and employment opportunities. Tourism centered around the Rift Valley’s natural beauty, wildlife, and archaeological sites has become a vital sector, contributing to community development. Overall, the Great Rift has shaped the livelihoods of Kenyans, fostering growth in agriculture and tourism, while also presenting challenges such as land degradation and environmental management concerns.

Challenges and Environmental Concerns
The Great Rift in Kenya presents unique challenges and environmental concerns that impact both the local communities and the ecosystem. As one of the most geologically active and ecologically diverse regions, it faces issues such as land degradation, habitat loss, and the effects of climate change. Understanding these challenges is essential for sustainable development and conservation efforts in this remarkable landscape.
Climate Change Impacts
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya faces numerous challenges and environmental concerns that threaten its unique ecosystem and local communities. Rapid population growth and urbanization have led to increased pressure on natural resources, resulting in habitat loss and deforestation. Climate change exacerbates these issues by causing unpredictable rainfall patterns, prolonged droughts, and increased occurrence of extreme weather events. These changes threaten wildlife populations, agricultural productivity, and water availability, impacting both biodiversity and the livelihoods of residents. Addressing these challenges requires sustainable management practices, conservation efforts, and policies aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change to preserve the region’s ecological and cultural heritage.
Pollution and Human Encroachment
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya faces numerous environmental challenges, with pollution and human encroachment being among the most pressing issues. Rapid population growth and urbanization have led to increased pressures on natural resources, resulting in deforestation, soil erosion, and habitat destruction. Pollution from industries, agriculture, and domestic waste further degrades the environment, impacting local ecosystems and biodiversity. Human encroachment into protected areas and conservation sites not only threatens wildlife but also disrupts ecological balance, making sustainable management and conservation efforts vital for preserving the Valley’s unique environment.
Geo-Environmental Hazards
The Great Rift in Kenya presents numerous challenges and environmental concerns that pose significant threats to the region’s sustainability. One of the primary issues is land degradation caused by erosion and human activities such as agriculture and settlement expansion, which destabilize the fragile geological formations. Additionally, the area is prone to geo-environmental hazards including earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, given its location along active tectonic boundaries. These hazards can lead to loss of lives, destruction of infrastructure, and displacement of communities. The presence of fault lines increases the risk of seismic activity, while the geothermal activities associated with volcanic zones also contribute to environmental concerns. Such hazards require careful monitoring, disaster preparedness, and sustainable land use planning to mitigate their impact. Protecting the biodiversity and natural ecosystems within the Rift Valley is also crucial, as environmental degradation could disrupt local habitats and the livelihoods of communities dependent on the land. Addressing these challenges is vital for ensuring the safety, stability, and sustainable development of the region.
Tourism and Cultural Heritage
Tourism and cultural heritage play a vital role in showcasing the rich history and traditions of regions around the world. In Great Rift Kenya, this connection is particularly profound, highlighting the area’s diverse cultural landscapes and natural wonders. Visitors are drawn to the unique blend of heritage sites, vibrant communities, and stunning geological features that make the Rift Valley a must-visit destination. Exploring this region offers a deeper understanding of Kenya’s cultural diversity and natural beauty.
Tourist Attractions and Activities
The Great Rift Kenya is a captivating destination that offers a rich blend of tourism and cultural heritage, making it an ideal location for travelers seeking adventure and cultural experiences. The region is renowned for its stunning landscapes, diverse wildlife, and historical significance, attracting tourists from around the world.
Among the major tourist attractions in the Great Rift Kenya are the Maasai Mara National Reserve, known for its exceptional wildlife viewing opportunities, particularly the annual migration of wildebeest and other grazing animals. Visitors can enjoy game drives, hot air balloon safaris, and bird watching in this iconic reserve. Lagoons and lakes such as Lake Naivasha and Lake Elementaita provide picturesque settings for boat rides, bird watching, and fishing activities.
Additional attractions include the ancient archaeological sites at Koobi Fora and Turkana, which showcase the region’s rich cultural heritage and early human history. Cultural tours offer insight into the traditions of the Maasai, Samburu, and Turkana communities, allowing tourists to experience traditional dances, crafts, and lifestyles firsthand. Visitors can also explore geothermal areas like Hell’s Gate National Park, renowned for its dramatic landscapes, hiking, rock climbing, and geothermal geysers.
The Great Rift Kenya combines natural beauty with cultural richness, providing a wide array of activities that cater to adventure seekers, nature lovers, and history enthusiasts alike. It remains a vital part of Kenya’s tourism industry, emphasizing the importance of preserving its unique heritage while offering unforgettable experiences to its visitors.
Historical and Cultural Sites
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya is a magnificent showcase of both natural beauty and rich cultural heritage. This iconic geological feature attracts countless tourists who are eager to explore its stunning landscapes, diverse ecosystems, and historical significance. Throughout the valley, visitors can discover ancient sites that offer insights into the early human history, making it a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The region is dotted with significant cultural sites, including archaeological excavations that reveal early hominid remains, as well as vibrant local communities that preserve traditional customs and lifestyles. Additionally, the Great Rift Valley boasts numerous lakes, volcanic formations, and wildlife reserves, offering unique opportunities to experience Kenya’s vibrant biodiversity and deep-rooted cultural traditions. A visit to this incredible site provides a captivating journey through Kenya’s natural marvels and historical milestones, highlighting its importance as a cultural and geological treasure.
Ecotourism Opportunities
The Great Rift Valley in Kenya offers a unique blend of tourism and cultural heritage, attracting visitors from around the world. This iconic geological feature provides stunning landscapes, abundant wildlife, and opportunities to explore diverse cultures and traditions of local communities. Ecotourism in the region promotes sustainable travel practices, allowing visitors to experience the natural beauty while supporting conservation efforts. From safaris in national parks to visiting archaeological sites and tribes, the Great Rift Valley is a vibrant hub for cultural and ecological exploration.




0 Comments